Wifi 6, Wifi 6th: what is and what it is for?, Wi-Fi 6th: What is it? What a difference with Wi-Fi 6? What smartphones and computers are compatible?
WiFi 6e: What is it? What difference with WiFi 6? What smartphone and computer are compatible
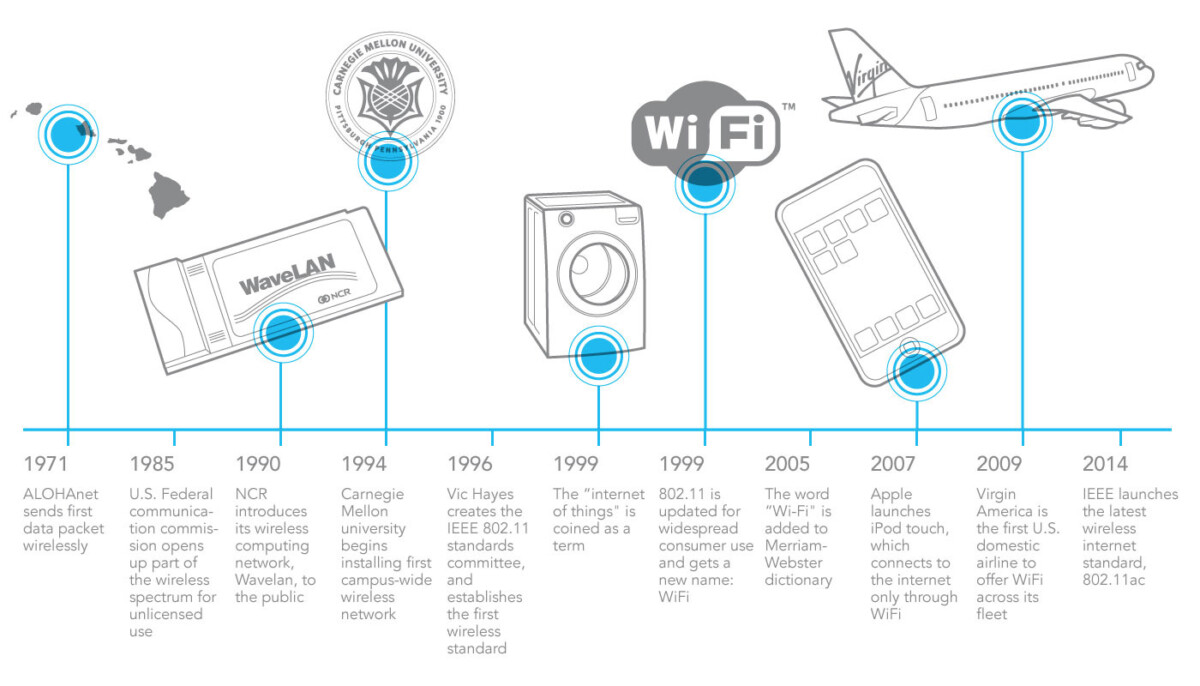
WiFi 6 is the latest wireless network standard certified by WiFi-Alliance, the consortium in charge of setting up the technical standards of WiFi technology. WiFi 6 and the 6th WiFi which we are talking about below are Declination of the same IEEE 802 standard.11ax.
Wifi 6, Wifi 6th: what is and what it is for ?
WiFi 6 is gradually starting to establish itself as the standard of wireless connections. But what is this designation exactly and what the 6th wifi that we are talking about ? We invite you to learn more in this file.

Routers, smartphones, computers … You may have noticed, more and more devices are compatible with the New WiFi 6 standard. But what does this mean concretely, and what consequences for the daily user ? Answer in this file.
WiFi 6, what is ?
WiFi 6 is the latest wireless network standard certified by WiFi-Alliance, the consortium in charge of setting up the technical standards of WiFi technology. WiFi 6 and the 6th WiFi which we are talking about below are Declination of the same IEEE 802 standard.11ax.

If you hear regularly talk about WiFi 6 when you have never seen any mention in Wifi 5 or lower, this is completely normal: some time ago, Wi-Fi Alliance has announced a change of strategy for The nomenclature of the different WiFi generations:
Flow, latency … The advantages of WiFi 6
One of the main advantages of WiFi 6 on its predecessors is speed . It is estimated to be approximately 40% gain allowed by this new technology in this regard. The maximum theoretical flow allowed by WiFi 6 is to 10 Gb/s . In practice, no one will benefit from such performance, but the average speed of connections will well be boosted with this standard.
In addition, WiFi 6 gives the frequency band 2.4 GHz up to date with better flows. As a reminder, it offers a much better scope and better crosses the obstacles than the 5 GHz band. WiFi 6 will make a huge difference in public places with high density (airports, stations, open space, shopping center, etc.), where dozens or even hundreds of users use connection at the same time.
The promise : a speed up to four times higher Now in these kinds of situations. At the home of individuals, the beneficial effects also exist: this will make it possible to boost performance if you are equipped with many connected objects or if you are a large number to share the same connection.

To achieve such feat, WiFi 6 is based on two protocols. L’ Ofdma (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) is used to carry out a canal division during simultaneous communication with several devices, thus avoiding the size of the bands. In parallel, the Mu-milo (Multiple-input multiple-output multi-user) has also been improved, allowing all devices connected to the WiFi network to communicate with the router simultaneously.
In theory, WiFi 5 already ensured this functionality. But if the routers could send information to several devices at a time, they could not however receive all the answers at the same time. It is on this point that WiFi 6 comes into play. The interest of WiFi 6 does not stop there since it also allows you to benefit from a better autonomy on his devices.
Thanks to the TWT (Target Wake Time), the battery of our smartphones, tablets or laptops should run out less quickly. The WiFi 6 router is actually capable of transmitting to devices when they have to put themselves in standby and when they have to wake up. Our devices spend less time in “wifi alert”, which is an energy -consuming function.
What is WiFi 6e ?

In parallel with WiFi 6, you have probably heard of WiFi 6th. This is actually exactly the same standard. The E simply means Extended to reflect a spectrum extended to the 6 GHz band (between 5,945 and 6,425 MHz). Thanks to this increased frequency range, WiFi 6e can deliver clearly higher flows up to 11 GB/s, as well as a lower latency.
The 6 GHz beach nevertheless required being released, which took time. In France and in the rest of Europe an agreement was reached to harmonize technology on the continent. The use of the beach has been slightly limited to avoid interference with the CBTC rail signal system, as well as digital television.
According to the ANFR, this evolution of the standard will be available in March. But it will undoubtedly take more time for this technology to become more democratized – unlike the simple WiFi 6 for which some devices are already available, there is not yet much compatible with WiFi 6e.
The WiFi 6e standard is of course back -up – all WiFi 6e devices are compatible with previous standards.
Devices already compatible WiFi 6 or WiFi 6e

Some devices are already compatible with WiFi 6/6th, in particular:
WiFi routers
- SFR Box 8 (WiFi 6)
- Bouygues Bbox Fiber (WiFi 6)
- TP-Link Deco X76 Plus / X96 (mesh, WiFi 6e)
- TP-Link Archer AX6000 (WiFi 6)
- TP-Link Archer AX1500 (WiFi 6)
- LINKSYS AXE8400 (WiFi 6th)
- Netgear Nighthawk Raxe500 (WiFi 6th)
- Asus GT-AXE11000 (WIFI 6th)
- Asus Zenwifi AX (mesh, wifi 6)
- Netgear orbi ax6000 (mesh, wifi 6)
Orange, which presented its Livebox 5 in October 2019, still does not take this standard into consideration.
Smartphones
- Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra (Wifi 6th)
- Samsung Galaxy S21, S21+ (WiFi 6)
- Samsung Galaxy S10 and S10E (WiFi 6)
- Samsung Galaxy Note 10 (Wifi 6)
- Samsung Galaxy S20 (Wifi 6)
- Samsung Galaxy Fold 1/2 (Wifi 6)
- Xiaomi Mi 11 (Wifi 6th)
- Huawei P40 Pro (Wifi 6)
- iPhone 12 Mini, iPhone 12, Pro and Pro Max (WiFi 6)
- iPhone 11, 11 Pro et11 Pro Max (Wifi 6)
- iPhone SE 2020 (WiFi 6)
- LG V60 Thinq (WiFi 6)
- Motorola Edge Plus (WiFi 6)
- OnePlus 8 and 8 Pro (Wifi 6)
- OnePlus 8T (WiFi 6)
Computers
- Apple MacBook Air M1, MacBook Pro M1 and Mac Mini M1 (Wifi 6)
- Acer Aspire 5 Slim Laptop (Wifi 6)
- Asus ZenBook Pro Duo UX581 (Wifi 6)
- Dell XPS 12/13 2020 (WiFi 6)
- HP spectrum x360 (WiFi 6)
- Lenovo Yoga X940 (WiFi 6)
- LG Gram 17 (Wifi 6)
- MSI Prestige range (WiFi 6)
- Razer Blade Pro 17 (Wifi 6)
- Microsoft Surface Pro 7 (Wifi 6)
- Microsoft Surface Laptop Go (WiFi 6)
We expect a very rapid evolution of the number of compatible laptops, thanks to the generalization of more recent chipsets. A few years ago, we were praised the WiFi 802.11 AD (60 GHz frequency band), also called Wigig For Wireless Gigabit, and its exceptional flows.
This standard has never been able to impose itself, because it suffered from an important drawback: a very low range. WiFi 6, gives access to such a dazzling speed as with Wigig, but with better management of the multiplicity of devices, a much greater emission distance and with a functionality helping to preserve the battery life. In short, at all good for users.
- Share Share ->
- Tweeter
- Share
- Send to a friend
WiFi 6e: What is it ? What difference with WiFi 6 ? What smartphone and computer are compatible ?
While the market is still struggling to adopt the Wi-Fi 6 standard, the manufacturers are already making war to offer devices compatible with Wi-Fi 6th, an even more recent standard. We take stock of all these standards and their specificities, their advantages and the differences to know.

Wi-Fi 6 pointed out its standard at the beginning of 2021. Since then, it has become an argument of sale for Internet operators or even wireless access points manufacturers. The promise is enticing with, for example, theoretical flows exceeding the usual Gigabit Ethernet port.
However, this standard is already beginning to be supplanted by its first evolution: Wi-Fi 6th. The main advantage of this new iteration is to use a frequency band hitherto unused. However, it does not bring a big revolution concerning flow rate, which are very close to those of Wi-Fi 6.
That provides Wi-Fi 6 to our digital uses ? Should we invest in a computer compatible with these standards ? We explain everything to you in this folder which will in fact complete our tests of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6th devices. Do not hesitate to discover the best routers and PC cards to enjoy this standard.
Wi-Fi 6th: a little story
We are not going to redo all the history of Wi-Fi and its different iterations here. We already have a file summarizing everything you need to know about Wi-Fi and its flows. Here, we will rather focus on Wi-Fi 6 and its evolution. However, it is advisable to make a quick point on Wi-Fi 5, to fully understand the advantages of the new standards we are going to talk about here.
To put things in context, Wi-Fi 5 had a gang of 60 MHz in Europe around 2.4 GHz and two bands of around 455 MHz in total around 5 GHz. This strip width, although obscure for ordinary people, represents, in a way, the place available for your Wi-Fi network.
These different bands as well as the technologies used allow Wi-Fi 5 to offer real speeds of approximately 800 Mb/s in good conditions, on a given machine. At the level of a network, with the latest standards and efficient devices, we can theoretically reach almost 10 cumulative GB/s.
The problem is that these frequency bands have changed little since the beginnings of Wi-Fi. In fact, with the development of the Internet and new technologies, we had to find ways to be able to obtain better performance in Wi-Fi. This is where Wi-Fi 6 comes in.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11AX), a necessary evolution
With the exponential development of connected objects, our old Internet boxes and Wi-Fi 5 which teams them struggle to provide a quality network. This is all the more true in dense environments such as buildings in which all networks must cohabit and share the different frequency bands which are already very busy.
It is for this reason that Wi-Fi 6 was created. Its objective is above all to improve performance at a network. For this, different technical choices have been made, in order to obtain better performance, while continuing to use the same frequency bands as those used on Wi-Fi 5. Among these technical improvements, we will note, for example, the use of:
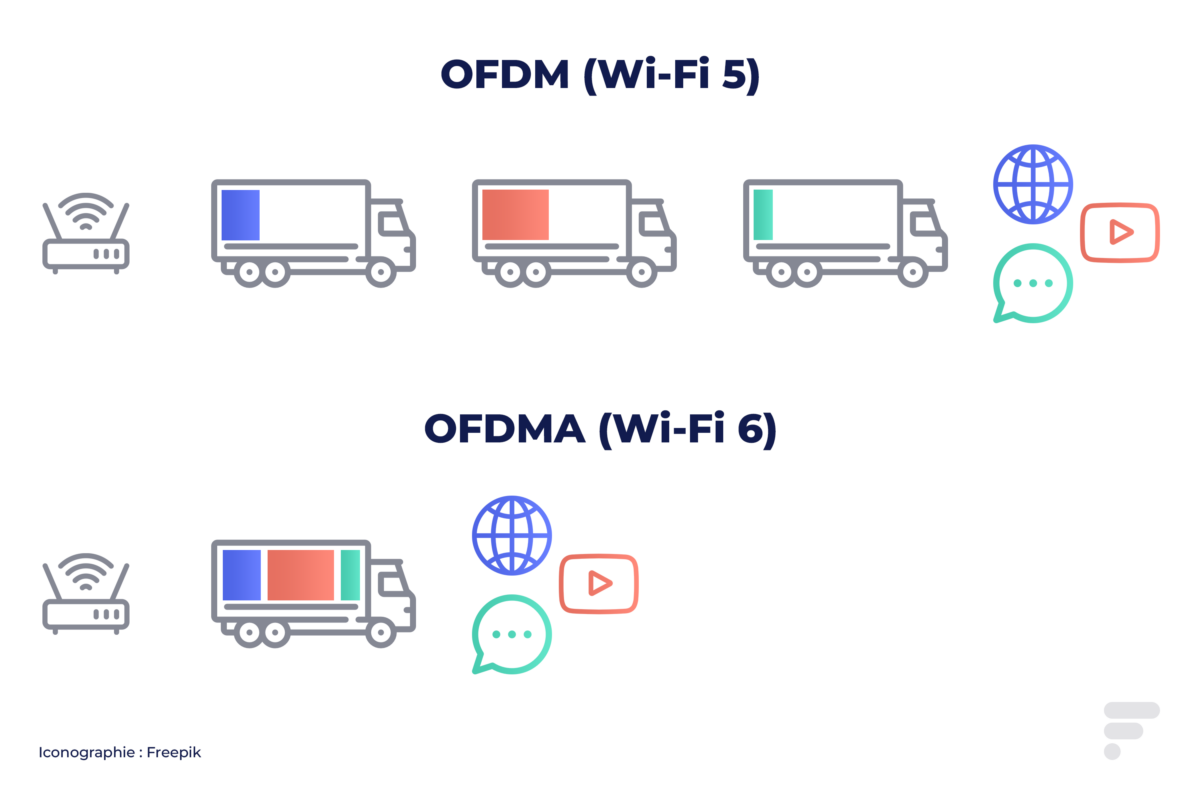
- Ofdma : a modulation technique that allows channels to be pooled in order to transmit data simultaneously to the various devices. To schematize, it is as if you could simultaneously deliver several customers with a single truck where you needed a truck per customer on Wi-Fi 5. OFDMA is particularly interesting in dense environments and for moderate uses such as web browsing.
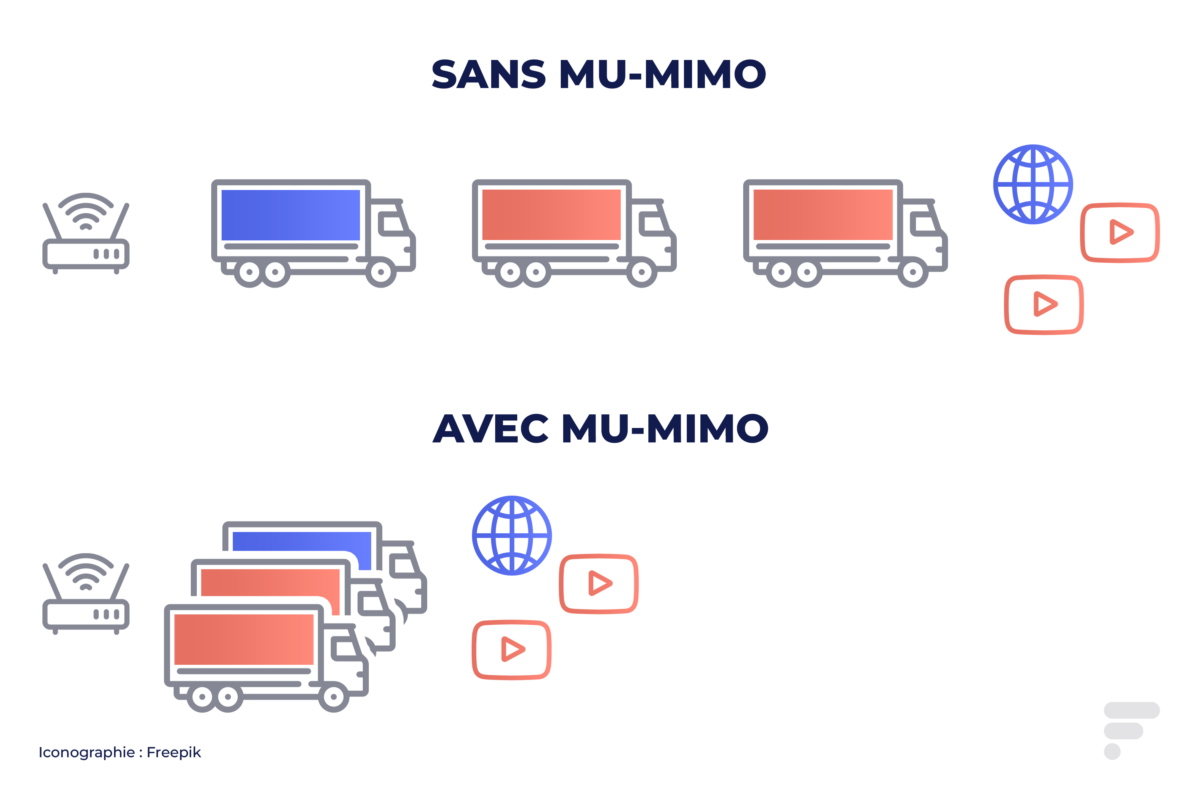
- Mu-milo : already present in Wi-Fi 5 (but now operating in both directions), the MU-MIMO allows the router to communicate with several devices simultaneously. By taking up our example of trucks, we can therefore use several trucks, which would circulate in parallel to deliver more goods. This technique works perfectly with a single customer, thus making it possible to substantially increase the flow to a machine with big bandwidth needs for video playback or streaming for example.
- 160 MHz channels : the generalization of the channels with a width of 160 MHz on compatible devices makes it possible to increase the flow for the latter as well as the latency. It’s as if you had a wider pipe, then more data transit and faster.
- 1024-QAM : instead of 256-qam, a modulation scheme that makes sense for very demanding bandwidth uses and thus offering the possibility of transit more data in the same width of band.
We will also note the arrival of the TWT for Target Wake Time which allows access points to indicate to customers when they have to stand in standby and wake up. This first makes it possible to relieve the battery of the devices (especially connected objects) and also to release the different frequency bands when there is no need to use them.
Wi-Fi 6 also marks the arrival of BSS Coloring. The idea is to “color” the data transmitted using a unique identifier to help each access point to find their young in very busy environments such as buildings. We also find the beamforming whose role is to optimize the route of waves to in particular improve the scope and efficiency of transmission.
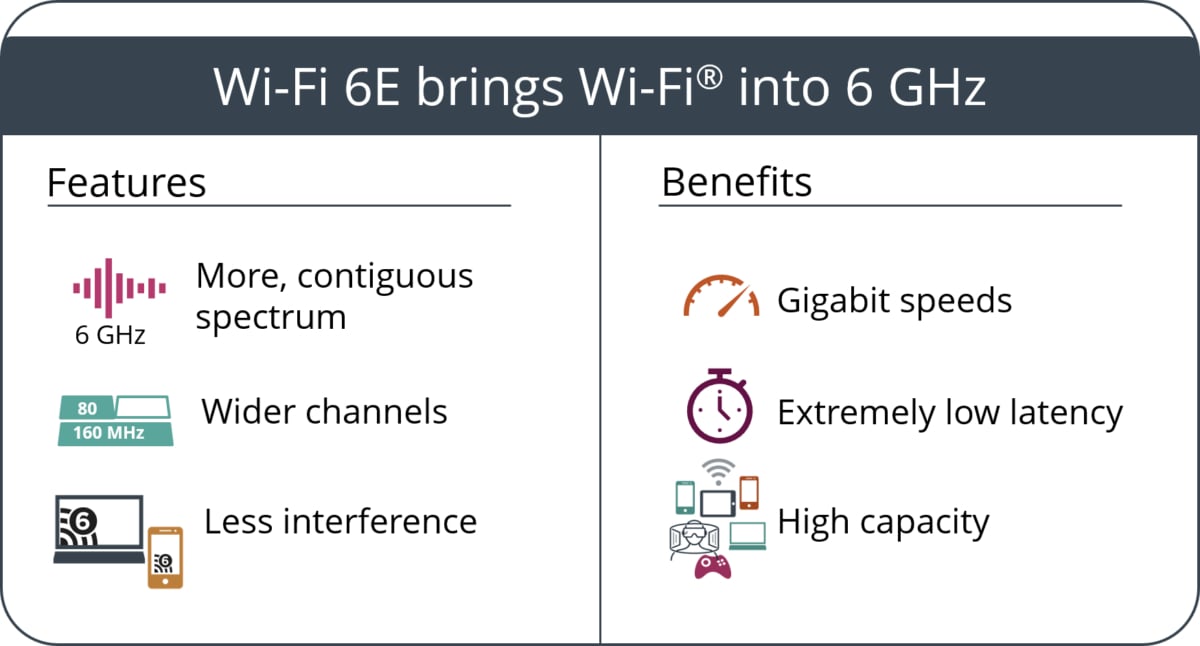
The main objective of all these technical improvements is to optimize and make the historic frequency bands of Wi-Fi more reliable and more reliable frequency bands. The results are clear: on a network scale, the flow is improving by around 300 % and the latency drops by 75 %. On the other hand, at the scale of a single machine, the gains are less substantial with an improved speed of approximately 40 %.
Concretely, with a good access point and a correct client machine, we can hope to reach a real speed of 1 to 1.5 GB/s. We cheerfully exceed the performance of the Ethernet Gigabit ports that equip most of the devices.
Beyond improving performance, Wi-Fi 6 brings interesting new features in terms of security with the arrival of WPA3. For the rest, he still uses 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands and band widths identical to what we found on Wi-Fi 5. And this is where Wi-Fi 6th enters the scene !
What differences between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6th ?
Wi-Fi 6th is no different from Wi-Fi 6. Indeed, this is exactly the same standard and both use the same technologies. The only difference lies in the frequency strip used since the 6th Wi-Fi allows you to use the 6 GHz band where we were limited before to 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz strips.
This new band has a very particular advantage: it was previously unused by Wi-Fi networks. There is therefore no congestion problem like those present on the usual bands 2.4 and 5 GHz. It is as if a new road was created in parallel with others and accessible only to the most recent vehicles.
Better yet, this band is more than twice as large as historic bands. This therefore leaves this theoretically more room for our networks and data to circulate correctly. By taking up the example of our route, it is as if in addition to enjoying a dedicated road, it had more traffic lanes.
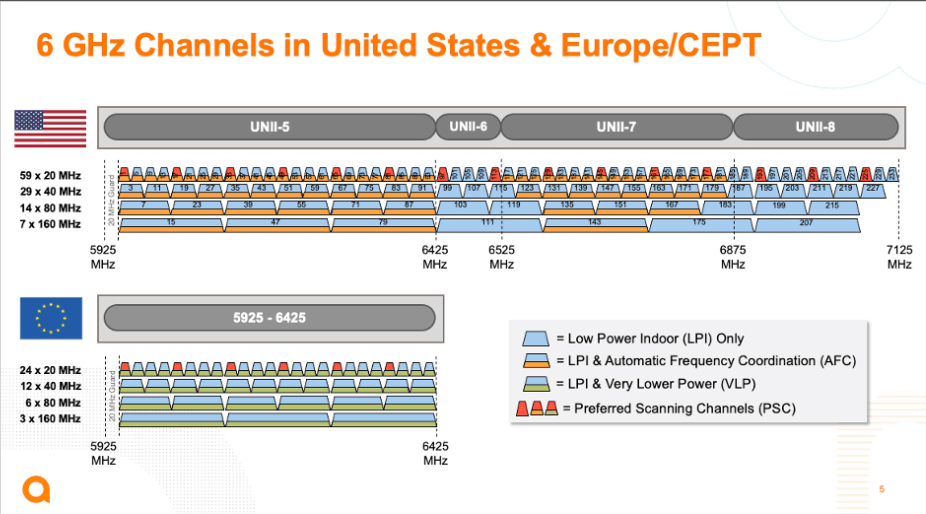
However, European regulations do not allow the use of the entire spectrum hoped for in Wi-Fi 6th. If 1200 MHz of band width are available for channels in the United States, we must be satisfied with barely 500 MHz, which does not really revolutionize the raw flows of our machines.
Currently, compatible Wi-Fi 6th devices therefore do not concretely revolutionize uses and performance. On the tests carried out by our colleagues and ourselves, the raw flow increases slightly compared to Wi-Fi 6, but that does not change much in practice. In the idea, and in perfect conditions, some devices nevertheless manage to easily reach 1.8 GB/s of flow, enough to tickle the performance of an Ethernet 2.5 GB/s Ethernet port.

The gang of 6 GHz, however, has only advantages since with the increase in frequency arrive the usual litter problems. Indeed, the higher the frequency of waves, the more the latter struggle to cross the walls and other structures of this type. The performance is therefore quickly affected.
Finally, like Wi-Fi 6, this new “E” version does not seem to have the vocation of offering exceptional raw performance. Here again, we are on an evolution aimed at relieving existing bands and improving performance and reliability on the network scale. All this in order to guarantee a flawless operation of networks despite the explosion of the number of connected devices.
What are the 6th Wi-Fi compatible devices ?
At the end of 2022, the overwhelming majority of mobile devices, computers and tablets are at least compatible with Wi-Fi 6. Be careful, that does not mean that they are compatible with the latest 6th Wi-Fi standard and they will probably never be unless they replace their Wi-Fi chip.

Among smartphones manufacturers, Samsung is in advance since the ultra S21 released in 2021 was already compatible with Wi-Fi 6th. Since then, other models have followed. Without being able to be exhaustive, we can cite the Galaxy S22 Ultra, the Galaxy S22 Plus and the Galaxy Z Fold 4 as well as the Xiaomi Mi 11, Xiaomi 12 Pro or the Asus Rog Phone 6 Pro and Zenfone 9. On the side of laptops, most recent models, from middle to high -end, are compatible with the standard. This is particularly the case for the SWIFT 5 of Acer for example.
If you use Wi-Fi on a desktop computer, know that it will be even easier to enjoy the 6th standard. Indeed, Wi-Fi cards, equipped with the Intel AX210 chip, are found for about fifty euros at Amazon for example. This is the easiest way to enjoy the 6 GHz band.

Currently, all operators with the exception of SFR offer a box capable of broadcasting a 6th Wi-Fi network. If you do not want to be dependent on your operator for this, you still have the opportunity to equip yourself with a Wi-Fi router or a Wi-Fi Mesh kit.
Wi-fi 6th: Understanding everything to the Wireless Network Champion of Debit
Wireless internet connections are preparing to become even more efficient thanks to a new standard, WiFi 6e. What exactly is, and when we can enjoy it ?

Yann Daoulas – modified on 07/21/2023 at 2:42 p.m
A new step towards a really efficient, fast and stable Wi-Fi. This is what the arrival of the standard promised Wi-Fi 6th On our equipment connected to the Internet. Its novelty of this last evolution of Wi-Fi: the use of a third WiFi frequency band, in 6 GHz. What still gain in flow And less suffer from traffic jams on the network. The fact remains that it will be necessary to wait a little more to be able to really enjoy the advantages of Wi-Fi 6th in your living room. Explanation.
Wi-Fi standards: if you have missed the previous episodes
A little reminder to start. Until recently, Wi-Fi standards were not very readable by the ordinary, with notations like 802.11 b, g, n, then ac, ax. To improve their understanding by the general public, the Wi-Fi Alliance certification body has decided to simplify their name. We are now talking about Wi-Fi 2, Wi-Fi 3 (prehistoric), then:
- Wifi 4 : appeared on our Internet boxes towards the end of the 2010s
- WiFi 5 : Available on the boxes of French operators since 2013
- Wifi 6 : Available since 2019 and now offered on most Internet boxes
- WiFi 6th : commissioned in December 2021 and accessible only with the Orange, Free and Bouygues Telecom Internet offers from Orange, Free Internet offers
To summarize, compared to Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5 brought an additional frequency band (5 GHz in addition to 2.4 GHz). The key: improved Wi-Fi flow (up to 7 GB/s), less disturbances, and better management of simultaneous connections. Crucial contributions that allow us today to benefit from much better performance on current boxes, sometimes at the price of some settings.
As for Wi-Fi 6, it is distinguished from Wi-Fi 5 in several ways: even higher theoretical flow (up to 10.5 Gb/s), better scope, increased efficiency in dense environment, and also less energy-consuming. And Wi-Fi 6th, then what is its contribution ?
And 6th wifi, what is ?
Wi-Fi 6 is a very recent standard, and the devices compatible there are still relatively few. And on the side of our operators, only Bouygues Telecom, Orange and SFR offer, for the moment, internet boxes and/or Wi-Fi repeaters supporting this wireless standard.
However, this already evolves with Wi-Fi 6th. What is this new version consists of ? Very simply, at the allowance of More frequencies for the use of the wireless network. 500 MHz more, in the 6 GHz band, between 5,925 MHz and 6,425 MHz. And thanks to this foray into the 6 GHz band, Wi-Fi connectivity will cross a new level.
While waiting for the arrival of the 6th Wi-Fi standard and take advantage of these multiple advantages, you can do our flow test to know the real speed of your Internet connection.
Wi-Fi 6th: multiple advantages
In these higher frequencies, the available band widths are higher, which allows you to sell more traffic but also to have higher speeds. While the maximum theoretical flow is 7 GB/s with Wi-Fi 5, it is 10.5 Gb/s with Wi-Fi 6 and 11 GB/S with Wi-Fi 6th. Result: while current Wi-Fi does not always allow Take full advantage of flows up to 1 GB/s or more Bring to your box by optical fiber, the 6th Wi-Fi will therefore prove more efficient on this point.
A higher flow thanks to Wi-Fi 6th, therefore. But also a higher flow for the whole worlde. Let us not forget that radio waves are shared by all. When all households will be equipped with fiber optics, cohabitation on wireless networks of increasingly gourmet bandwidth could give rise to a traffic jam.
Wi-Fi 6th is indeed very appreciated for its greater ease of managing multiple and simultaneous connections on a box. In particular in dense areas, such as buildings, where Wi-Fi networks overlap. This little video of the WiFi Alliance (in French) sums up these advantages:
The 6 GHz will therefore support this growth in uses. It also promises a shorter (latency) response time, which will be interesting for cloud or virtual reality applications in particular. As well as increased security thanks to the use of WPA3 safety protocol.
. and disadvantages
By going to tease a new frequency band, the 6th Wi-Fi therefore has undeniable assets. But it does not go without inconvenience. For domestic use, first, the reverse of its best performance in terms of flow is its shorter range. Covering whole accommodation in 6th Wi-Fi will be complicated, unless it is a small apartment. Do not panic, however: the other bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) which spread further, remain active alongside 6 GHz.
Other disadvantages of Wi-Fi 6th, more technical those: it comes to walk on the flowerbeds of other devices using the 6 GHz band: hertzian beams, fixed service by satellite and radioastronomy. And also close to a little too close with road transport and rail signaling systems. Discussions are underway to allow all these uses to cohabit under satisfactory technical conditions.
Internet boxes compatible with Wi-Fi 6th
Even if it was put into service in December 2021, the 6th Wi-Fi is still not very present on our daily equipment. Nevertheless, there are still more and more Wi-Fi 6th compatible devices, and in particular computers or smartphones put on the market since 2022.
As for the modems that equip Internet boxes ? They are gradually starting to become wi-fi 6th compatible. Orange was the first to draw in April 2022 with its new Livebox 6, included in the Livebox Max offer. Bouygues Telecom quickly followed him. Only a few days later, it changed its Bbox Ultym offer, with an update of the Bbox Ultym modem to make it compatible Wi-Fi 6th. Finally, in June, it was free from boosting the Freebox Delta, by passing it from Wi-Fi 6 to Wi-Fi 6th.
To date therefore, on the Internet box market, Wi-Fi 6th remains reserved for premium offers and an operator, SFR, has not yet taken the plunge. So when is the Wi-Fi 6th at SFR ? Business.
Share this info by clicking here
These files may also interest you:
- Wi-Fi 7: All about the next generation of the Wireless Network
- Wi-Fi repeater: an effective solution to improve its internet connection
- 8 tips for improving your Wi-Fi connection
- Wi-Fi 6: what is it and which operators offer it ?
- How to change the wi-fi password of your internet box ?
- Good or bad Wi-Fi: how to measure the power of your Wi-Fi signal ?
- How to cut or deactivate Wi-Fi on its internet box ?
- How to create a guest Wi-Fi network ?
- How to choose the best wifi channel ?



