Wifi 5 vs Wifi 6: What is the difference? | TP-Link France, WiFi standards: which choose between Wifi 5, WiFi 6 or WiFi 7?
WiFi standards: which choose between wifi 5, wifi 6 or wifi 7
Scheduled for this year, it suggests a maximum speed of at least 30 GB/s but, to have the maximum capacity of the standard, it will be necessary not only compatible equipment but also a dedicated router. “” Technological evolution is continuous and before trying to systematically renew the infrastructure to the rhythm of WiFi standards, it is also judicious to fully exploit the potential of equipment already deployed “, Recommends Guillaume Suzenne.
Wifi 5 vs Wifi 6: What is the difference ?
![]()
Home and business owners looking for networking equipment are facing a range of choices. WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 products are the two options between whom most people hesitate.
A glance at product promotions or technological news can immediately tell you that WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 identify different generations of wifi, WiFi 6 being more recent with better performance.
However, a more recent standard does not always mean that is the one you need. If you plan to get the latest generation, you may want to take a little time to examine your options in advance.
To make a rational choice, we must first understand the main differences between WiFi 5 and WiFi 6.

What is WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 ?
WiFi 5 (WiFi 802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11AX) are part of the WiFi networks family. The WiFi Alliance has simplified the name with a labeling based on the generation of wifi instead of their standards.
Wifi 5, the 5th generation of WiFi, deployed with Wave 1 certification in mid-2013.
WiFi 6, the 6th generation of WiFi, was introduced in 2018 and arrived on the market in 2019, with OFDMA, 1024-QAM, MU-MIMO (both in rising and descending connection), Target Wake Time and the BSS coloring. WiFi 6 is designed to improve speeds, increase efficiency and reduce congestion in intensive bandwidth scenarios based on WiFi 5.
What are their differences ?
The new generation of Wi-Fi standards is retrocompatible with previous standards. This represents a significant jump in the technology used and the available features. WiFi 6 supports all the features of WiFi 5 while providing more advantages.
Each generation of wifi increases WiFi speeds. The same goes for WiFi 6, although this is not its main objective. Nominal data speeds are brought to 9.6 Gbps, around 40% more than that of WiFi 5.
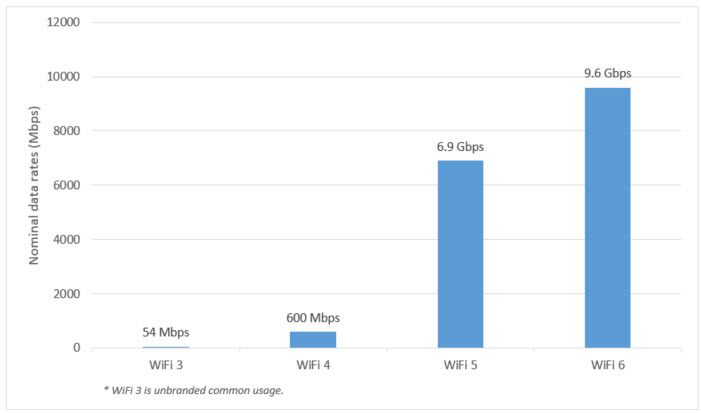
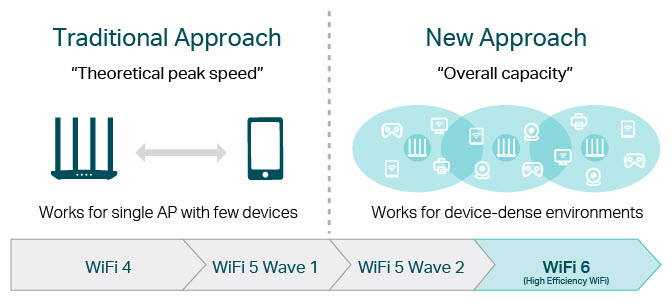
Performance in congested networks are ultimately the signing characteristic of WiFi 6. Also known as “high efficiency WiFi”, WiFi 6 shines the most in the high density environments of devices such as corporate offices, shopping centers and dense residential apartments. While the improvement in nominal data flow compared to WiFi 5 is around 40 %, the overall improvement of the flow rate on the whole of a network is 300 % (hence high efficiency). This also results in a reduced latency of 75%. WiFi 6 also maintains stable advanced speeds when connected to many devices simultaneously, even where the previous WiFi versions would trip.
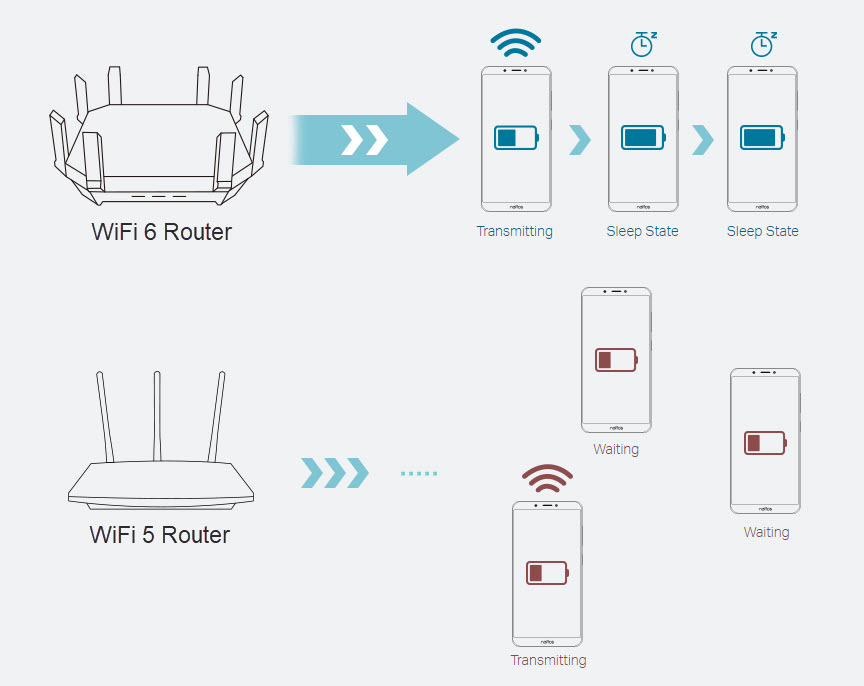
- Improved battery life
Target Wake Time (TWT) allows devices to negotiate when and how often they wake up to send or receive data. This feature increases the monitoring time of the device and considerably improves the life of the battery of mobile devices and IoT.
Global adoption of WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 devices
WiFi 6 is widely adopted in WLAN markets around the world.
According to the Worldwide Quarterly Wireless Lan Tracker of IDC in the third quarter of 2021:
On the business wlan market, WiFi 6 access points (access points) represented 62.2 % of income from the dependent access points segment. They represented 50.7 % of unit shipments in the segment in the third quarter 2021. WiFi 5 products constituted the vast balance of the remaining sales of dependent access points.
On the general public Wlan market, WiFi 6 products continued to grow, reaching 27.9 % of the total turnover of the consumer segment, against 24.5 % in the second quarter of 2021. WiFi 5 access points still represent most income (61.4 %) and unit shipments (63.6 %).
Many products, including smartphones, tablets, PCs, networking products and some high -end home entertainment devices are now equipped with WiFi 6. The number of products continues to grow. It’s now time to search for a WiFi 6 router to get the most out of your new WiFi 6 customers !
TP-Link Editorial Group
WiFi standards: which choose between wifi 5, wifi 6 or wifi 7 ?

WiFi: Wireless Fidelity, synonymous with agility and connectivity. The choice of WiFi standards has a real complexity often underestimated. Guillaume Suzenne, Product Manager for Bouygues Telecom Entreprises shares his vision and advice.
WiFi network, what about today ?
While standards 802.11a and 802.11b were created in 1999, with the theoretical maximum flows of 11 Mb/s, the new standard WiFi 6e opens the track to a bandwidth greater than 11 GB/S.
For over 20 years, the WiFi standards succeed one another, bringing their prizes of profits in terms of flows, latency as of security. “” But the speed race is not the only aspect to be taken into account “, Underlines Guillaume Suzenne.
Indeed, while companies and their employees are always more connected, that the peripherals are always more numerous, the density of the devices considerably affects the performance of a WiFi network and, ultimately, the experience of users.
“” The generalization of access by optical fiber or by very high speed mobile have accustomed employees to low latency and maximum connectivity. They do not understand why the experience can be lower in the premises of the company than within their home »».
For Guillaume Suzenne, the observation is clear: ” The number of antennas integrated, the question of Mimo connectivity and the choice of frequency bands must be central elements of DSI reflection »»
WiFi standards: which choose between wifi 5, wifi 6 or wifi 7 ?
If WiFi 4 is now unanimously considered obsolete, WiFi 5 is today a standard technology established and commonly widespread in companies. “” Today it constitutes an essential base of WiFi connectivity »Says Guillaume Suzenne, but already notable developments appear.

What a difference between WiFi 5 and 6 ?
The difference between wifi 5 (802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11AX) is of crucial importance for companies that seek to improve their network infrastructure and provide high quality wireless connectivity to their customers and employees. Here are the main distinctions between the two:
– Supervisor : WiFi 6 offers a theoretical flow much higher than WiFi 5, which allows faster data transfer and better user experience.
– More simultaneous connections : Unlike WiFi 5, WiFi 6 is designed to effectively manage a large number of devices connected simultaneously, which is particularly beneficial for companies with many users and devices connected to their network.
– Improved security : WiFi 6 offers advanced security features to protect sensitive data from companies against potential threats.
– Retrocompatibility : Although WiFi 6 is more recent technology, it is retro compatible with devices operating with WiFi 5, companies will not need to replace all their existing devices to benefit from the advantages of WiFi 6.
WiFi 6 or WiFi 6e: what differences between these new WiFi standards ?
Presented at the beginning of 2021, WiFi 6 is the penultimate WiFi standard certified by the WiFi Alliance. If the main performance promise remains linked to the bandwidth, theoretically 40% higher than the previous standard, WiFi 6 returns to the 2.4 GHz frequency band that offers better range And better cross the obstacles than the 5 GHz band. “But in itself, this already poses a problem because in urban areas, in high density areas, the 2.4 GHz band is already saturated,” comments Guillaume Suzenne who pleads more for the 6th WiFi standard:
“” It opens a third way by integrating the 6 GHz frequency band which can deliver flows far exceeding 11 GB/s while offering a lower latency »».
WiFi 6e also provides security plans with the generalization of WPA 3 which “constitutes a real advance but does not relegate WPA 2 to the rank of colander”.
Going from WiFi 5 to WiFi 6 or 6th, however, has advantages because with wider coverage, the 6th wifi allows you to loosen the mesh of the terminals scattered in professional premises. “” Fewer WiFi terminals, this makes it possible to save real savings but it also means renewing the peripheral park “, Specifies Guillaume Suzenne.
WiFi 2023 standard: We are talking about WiFi 7
So you have to renew your WiFi park now ?
Not so sure ! If successive WiFi standards are still retro-compatible and do not systematically oblige to renew all of the parks, the peripherals compatible with the new WiFi 6th standard are still not very numerous and already, the WiFi 7 standard begins to speak D ‘She.
Scheduled for this year, it suggests a maximum speed of at least 30 GB/s but, to have the maximum capacity of the standard, it will be necessary not only compatible equipment but also a dedicated router. “” Technological evolution is continuous and before trying to systematically renew the infrastructure to the rhythm of WiFi standards, it is also judicious to fully exploit the potential of equipment already deployed “, Recommends Guillaume Suzenne.
WiFi connection: how to optimize the existing ?
Renewal of the WiFi park or optimization of equipment already deployed: in all cases, it is essential to achieve a complete inventory of the situation. “” It always starts with a WiFi audit »». An audit that takes stock of the configurations and dimensioning of WiFi infrastructure as well as on the uses of employees. It can be achieved in two ways:
– the first, both the simplest and fastest, consists of an analysis of WiFi in terms of.
– the second, by involving a technician who performs precise radio measures. “” More complete and more reliable, this second audit often makes it possible to identify avenues for improvement and nourish reflection on migration to a new WiFi standard in order to be sure to make the most enlightened choices “Concludes Guillaume Suzenne.
What to remember:
– WiFi 6 has essential differences compared to WiFi 5, including higher speed, effective management of simultaneous connections and advanced safety features.
– The 6th WiFi offers theoretical flows greater than 11 GB/s and allows better management of the density of devices connected simultaneously.
– Going from WiFi 5 to WiFi 6e allows wider coverage with fewer WiFi terminals, but this also requires the renewal of the peripheral park.
– although WiFi 7 is in development with a maximum flow rate of at least 30 GB/s, it is advisable to fully operate the potential of the equipment already deployed before renewing the infrastructures. WiFi audit is recommended to assess possible needs and improvements.



