What is the autonomy of an electric car? Zeplug, electric car: no, a large battery is not always preferable, here is why
Electric car: no, a large battery is not always preferable, here is why
In addition, the density of battery exchange stations is for the moment very weak, when we are not in a country that does not yet offer them. If more than 1,000 stations are planned in the medium term by the giant Catl in Europe and elsewhere, there is to date only one handful in Norway, which strongly limits the interest for the inhabitants of the old continent. A new station has just opened in Germany.
What is the autonomy of an electric car ?
When buying an electric vehicle, autonomy is often at the center of concerns. Many fear insufficient autonomy. Besides, this fear is often a major obstacle to the purchase of an electric car. How to be sure that the autonomy of his vehicle will be sufficient for long journeys on the highway ? Zeplug enlightens you on the real autonomy of your electric vehicles and gives you some tips to optimize it.
By a.Cheve on 15.04.2020, modified on 24.05.2023 8 min

How is the autonomy of an electric car calculated ?
All electric cars, but also Rechargeable hybrids, have batteries, This is the energy reserve to activate the engine and set in motion the vehicle and its occupants.
There battery capacity is expressed in kilowatt hour (kWh) and will represent theElectric car autonomy. Like a thermal car that has a fuel tank, electric cars all have batteries.
You will therefore have understood: The more the capacity of your is important, the greater the autonomy of your electric car will be (with a 100% loaded battery on a charging station). But, its recharge time will also be more important (expressed in recharging hours).
The autonomy of an electric car is determined according to two elements:
- There Battery storage capacity, expressed in kWh (the equivalent of the tank size on a thermal car). Today, most models are equipped with minimum 40kWh batteries and the largest batteries can go up to 100 kWh.
- There consumption, expressed in kWh/100km. You should know that this data is quite variable depending on the temperature, the type of driving and the type of road. Unlike a thermal car, an electric car will consume less in town than on a highway. For a city car, it takes an average of a consumption of 14kwh/100km, for a sedan, we rather approach 24kWh/100km.
Calculation of electricity consumption is simple.
To calculate it you need:
– Electric consumption for 100 kilometers (in kWh)
– The annual distance traveled by your electric car (in kilometers)
The mathematical formula is then simple:
It is necessary to multiply the electricity consumption for 100 kilometers by the number of kilometers annual. It is then necessary to divide the result by 100:
(electricity consumption for 100 km x number of kilometers traveled) / 100.
The result will be expressed in kilowatt hours (kWh)
Autonomy is a recurring concern about electric cars. However, it all depends on Your daily mileage and the time you have to recharge your car. If you have the possibility of recharging yourself daily at your home or your workplace and you are traveling around thirty kilometers a day, all current electric cars models have more than sufficient to meet your need. Indeed, the average autonomy of electric cars marketed today varies between 150 to 600 km in WLTP cycle.
Discover recharging at home with Zeplug:
On the other hand, if you realize more than 200 kilometers per day, this criterion will have to be watched closely. Some manufacturers offer several battery size options and so -called “long range” options offering high maximum autonomy. More and more car manufacturers offer models of electric cars around 400 km of autonomy. For larger rollers, rechargeable hybrid cars can also be a good option.
You will find below a table presenting the autonomy of your car according to your use:
| Vehicle type (100% electric) | Average autonomy of your vehicle (in km) On the highway | Average autonomy of your vehicle (in km) Mixed | Average autonomy of your vehicle (in km) In the city |
| City car (40 kWh battery) | 173 | 286 | 363 |
| Compact sedan (60 kWh battery) | 260 | 400 | 500 |
| Sedan (100 kWh battery) | 330 | 428 | 550 |
The recharge frequency of your electric car
L’autonomy of your electric car go then determine there battery recharging frequency. This frequency depends on several criteria:
- There electric motor power
- THE vehicle type : city car, compact, sedan, road, SUV ..
- Model electric car
- Ability drums
- …
The higher the battery capacity, the more you can make kilometers between two recharges. But with a powerful electric motor, your electricity consumption will increase, reducing your autonomy and increasing the requirement number required per week or per month.
The autonomy of electric cars
As a rule, the more expensive an electric car, the more its autonomy is important. The purchase price of an electric car strongly depends on the capacity of its battery. The higher the battery, the more expensive the car will be.
An electric car with a range from 100 to 300 km
THE entry -level electric cars have autonomy ranging from 100 to 300 kilometers. These cars are ideal for daily journeys to go to work, go shopping, get your children at school ..
On average, French people and French are about 30 kilometers per day. A electric car with a range of 100 to 300 kilometers is adapted to the vast majority of uses.
An electric car with a range from 300 to 500 km
There majority of electric cars currently sold battery allowing them to achieve between 300 and 500 kilometers per recharge.
Thanks to this autonomy, you will be able to reduce the number of slow recharge at home, thanks to your charging station. You can also calmly consider your vacation or weekends with your electric car.
Currently, this is the average autonomy of electric cars put on the automotive market. They are often cheaper than cars with better autonomy, while remaining practical on a daily basis.
An electric car with a range from 600 to 800 km
Electric cars with the best autonomies, that is to say more than 600 kilometers, are the most expensive cars. These are often premium models, the best known being Tesla electric cars:
- Tesla Model S
- Tesla Model 3
- Kia Ev6
- …
You regularly make long journeys ?
Consult our article dedicated to electric vehicles with the greatest autonomy.
How to optimize the autonomy of your electric vehicle ?
Adopt eco-driving
The autonomy of your electric car depends strongly on your driving style. You may have sporty driving or rather a fairly flexible driving, depending on your driving style you lose or gain autonomy during your trip. Indeed, even if your car already consumes less energy during your trips in town than during your long journeys on the highway, good driving habits can save you up to ten percent of autonomy. This non-negligible gain requires increased vigilance when starting and braking.
To take a step towards eco-driving, start and curb brutally are to be avoided. On the other hand, promoting soft driving without repeated acceleration peaks and anticipating your braking will allow you to drive much longer without having to recharge your car.
Did you know ?
The stake of eco-driving is such that many manufacturers now offer a “eco” driving mode directly integrated into the car in order to best accompany you in your daily trips and optimize the autonomy of your electric car.
Excess air conditioning or heating decrease the autonomy of your battery
You will understand, when it comes to autonomy, parameters such as the use of air conditioning or heating come into play. On this subject, several tips exist.

- For Improve the autonomy of your electric vehicle in summer, Protect it from hot weather. In order to limit the use of air conditioning, you can park your electric car in a closed parking. Thus, your vehicle will be protected from external temperatures. By taking this habit, your electric car will remain in the fridge and you will avoid the often excessive use of air conditioning at the start of the trip.
- In winter, optimize the autonomy of your battery by protecting your car from the cold. Park your car in a closed space remains very relevant especially during cold waves. You may also remember to cover yourself as much as you drive to minimize the use of heating throughout your trip.
These simple tips have a significant impact on the autonomy of your car since they allow you to gain between 10% and 30% of autonomy per journey !
Did you know ?
Today, many technologies respond to this problem and make it possible to limit the impact of external temperatures on the autonomy of your vehicle. In some models of electric cars you can benefit from the “remote control” option. You can start the air conditioning or heating your electric car remotely, before your departure. Air conditioning or heating will be started while your car is connected to your plug or charging station. Thanks to this technology, you anticipate and enter a car already heated or refreshed depending on the season. Thus, you limit the use of air conditioning or heating by rolling and decrease your loss of autonomy !
The autonomy of your electric car is not the only factor to take into account
Maximum charging power: a criterion as important as vehicle autonomy
Upon purchase, in addition to autonomy, it is also necessary to take into account the maximum charging power which is an important parameter for your choice of electric car.
As soon as you have the right cable, an electric car can recharge everywhere (domestic outlet or charging station). However, each model has its own maximum charging power, expressed in KW. The charging power corresponds to the speed at which a car can recharge per hour. A 3.7KW charging station allows you to recharge 3.7kWh per hour, which corresponds to around 25km of autonomy recharged in one hour on a small city car.
If some cars, such as the Audi e-tron, can recharge up to 150kw, others are limited to 7.4kw for example.
Good to know : If an electric car limited to 7.4kW were to connect to a 22kW terminal, it can still recharge, with a recharging limited to 7.4kw, as soon as it uses an adapted cord.
Some manufacturers offer several possible maximum charging powers for the same model. This is particularly the case for the Renault Zoé whose Q90 version allows recharging at 22kW. If you want to use your electric car as a main car and make long journeys, such as vacation departures, this criterion can be decisive. On the other hand, for a secondary car, normal charging power will largely suffice. Indeed, you can recover your daily consumption in less than 2 hours of charging.
To summarize, if the criteria for choosing an electric car remain for the moment, more focused on use than on performance, it is mainly the measurement units which differ from the concepts associated with thermal cars. To ensure that your electric vehicle is able to ensure long journeys, it is therefore as important to pay attention to the maximum recharge power as its autonomy.
Electric car: no, a large battery is not always preferable, here is why
And if the most interesting electric vehicles were not those with the greatest possible autonomy ? We are going to look at certain received ideas with regard to the autonomy and size of the batteries of electric cars in this file.

Updated article on October 12, 2022 : A few days before the World Cup, Ademe gives its opinion on electric cars, and in particular the size of the batteries. His analysis confirms the information you will find below in this file. In summary: prefer an electric car with a small battery, for your wallet, but also for the planet. And without forgetting the use of the train for long distances.
Original article of October 8, 2022 : Traveling as an electric vehicle is not always easy, but some trendy cars are doing very well in this exercise. What formula is the most suitable for covering hundreds of kilometers as quickly as possible ? Is a large battery necessary, or, on the contrary, having a car with ultra-fast charging is preferable ?
We will try to provide some answers by returning to the conceptual differences between an XXL battery and a faster recharge than the lightning. We will see that some electric cars with a smaller battery allow you to reach your destination faster, even if the long journeys are more expensive.
Finally, we will talk about innovative solutions such as the exchange of batteries to minimize journeys when they exceed the real autonomy of the vehicle. Without further ado, let’s examine the advantages and disadvantages of a large battery on board an electric car.
Large battery does not necessarily rhyme with high autonomy
Quite naive, we can think that To increase the autonomy of an electric vehicle, it is necessary and it is enough to increase the size of its battery (expressed in kWh). Indeed, the energy necessary to roll an electric car is stored in the battery, and the more there are, the more the car can go far. However, a major enemy comes with a more substantial battery: the weight.
The current energy density makes it possible to equip medium -sized cars with a battery of around 70 to 80 kWh, as is the case on a Tesla Model 3, Hyundai Ioniq 5 or MG ZS EV, while displaying a weight total between 1,700 and 2,200 kilograms. These battery packs weigh around 450 kilograms, And significantly increasing their capacity would amount to offering increasingly heavy vehicles, then involving higher consumption.
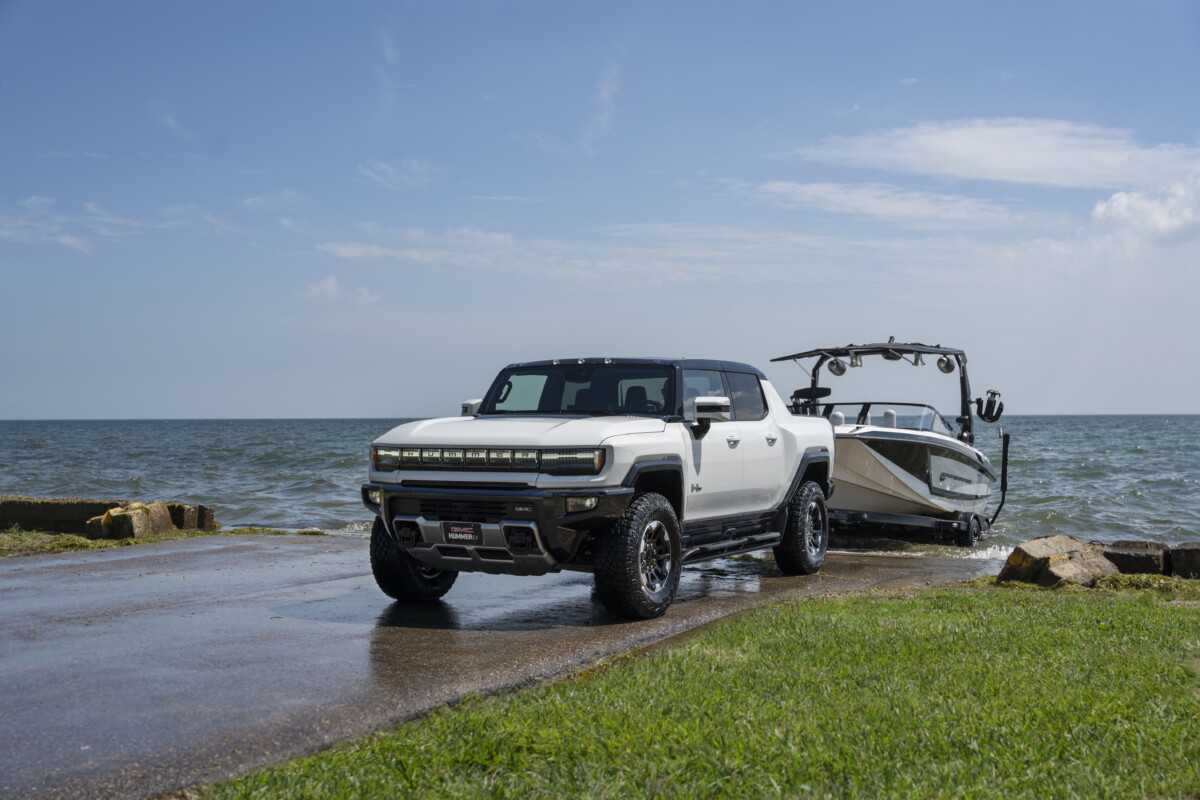

A vehicle of more than 3 tonnes which would have a 210 kWh battery for example would not allow to travel 800 kilometers without stopping, as shown by the examples of the electric pick-ups embarking a huge battery to, in the end, do not not have significantly greater autonomy than smaller vehicles.
This is the case with Hummer EV with its 530 km autonomy on American EPA cycle (around 600 km in European WLTP) and its 212.7 kWh battery. For comparison, the Tesla Model 3 large autonomy and its smallest battery of 80 kWh offers similar autonomy, thanks to its more moderate consumption.
However, a larger battery in some vehicles that optimize their consumption has real interest, and this is the reason why we find variants of Renault Mégane e-tech, Kia Ev6 or Tesla Model Y with different battery sizes. Note, however, that The increase in autonomy is not done in the same proportion as the increase in the size of the battery.
For example, a tesla model y great autonomy has a 33 % larger battery that that of the Tesla Model Y Propulsion (80 kWh against 60 kWh), but a Autonomy only 17 % larger (533 km against 455 km). Consumption thus goes from 14.9 to 16 kWh to cover 100 km, because of the increased weight (+ 247 kg) but also from the second engine (for the four -wheel drive), which adds a little consumption.
We will also see that embarking on a battery pack more of greater capacity is not always the key to reaching safely as quickly as possible during long journeys.
Bigger battery does not rhyme with faster journey
During our examples of large journeys in different electric cars, we highlighted the fact that some trips were finally longer with a vehicle that displayed WLTP autonomy and a more imposing battery than another.
The recharge speed of of course comes into account as soon as we travel several hundred kilometers and there is a need to recharge the vehicle, but efficiency is also a preponderant factor. This is why we find in particular the Tesla Model 3 Propulsion in the examples of the vehicles considered as champions of the fast load, while it only arises a 60 kWh battery.
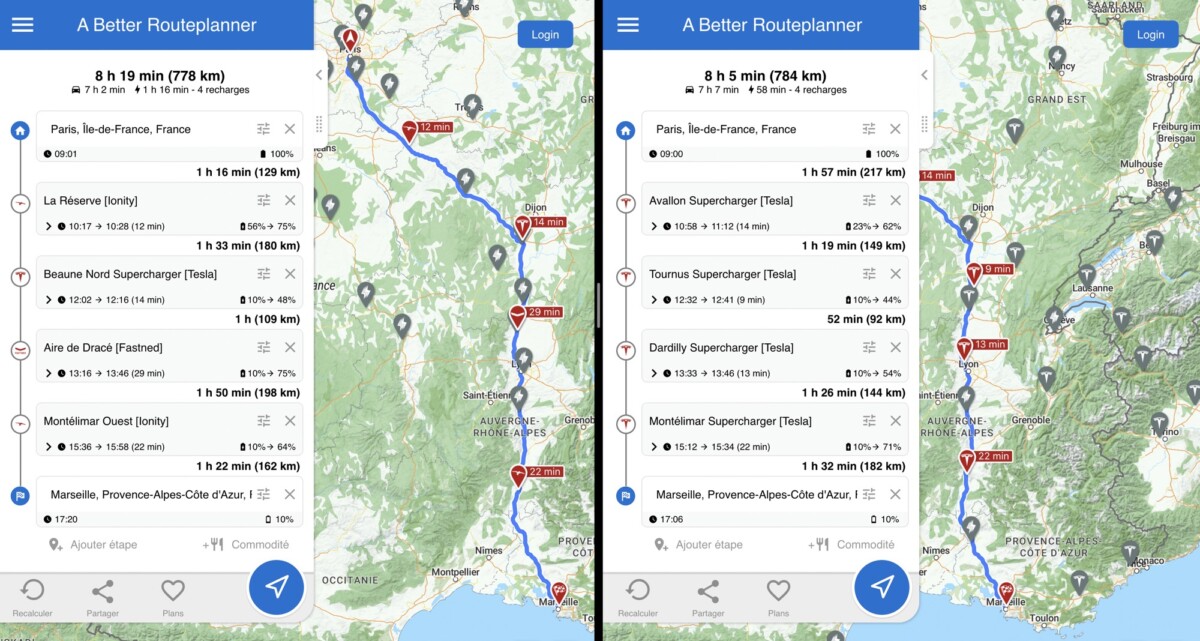
If we compare it, for example, to a Volkswagen ID.4 With its 77 kWh battery, the simulation of a Paris-Marseille route gives the Tesla Model 3 Propulsion as arriving in Marseille in mind, almost fifteen minutes ahead. Consumption is 33 % greater on this journey for the Volkswagen SUV, not allowing it to fully benefit from its advantage in terms of battery capacity.
The best of the two worlds in terms of efficiency and battery capacity is for the moment to seek on the side of the Mercedes Eqs, which has no 100 % electric rival so far. Backing 1,000 kilometers by electric car is never faster than with the German sedan, but it will be necessary to accept its XXL rate.
And if we also take into account the load speed, then it is the Kia Ev6 which is most likely to make long journeys as quickly as possible. Indeed, she managed to recover 70 % of her battery in 18 minutes, against 30 minutes for Mercedes EQS. Provided you find such rapid charging stations on its route. The future Hyundai Ioniq 6 should reduce the cards well with a potential first place for its speed on long journeys.
We will see that it is however possible to save money in large trips when you enjoy a bigger battery.
A higher price for purchase, but savings in use
There are indeed vehicles with an XXL battery with a strong interest, whether to use daily without having to recharge frequently, or to limit stops during long journeys. Indeed, with a fast charge price which only increases, being able to travel hundreds of kilometers in a slat can be very economical.
Thus, recharging at home is equivalent at a price between two and three euros per 100 kilometers. On the highway, fast chargers transform the addition into 10 to 20 euros per 100 kilometers.
These savings in use which may be around 70 euros for a 500 -kilometer journey should be taken into account when buying a vehicle, to give you an idea of the cost to use. We also have a series of files simulating journeys crossing France in different electric vehicles by summarizing the associated costs.

Daily consumption will however be higher with a vehicle taking on a larger battery, due to the higher weight. That said, this greater consumption will be inexpensive if you are in charge of you at night, where KWH is inexpensive compared to roaming operators in roaming.
Be careful not to make an illusion, The few 17,000 euros that separate, for example, a Tesla Model Y Grande Autonomy de a propulsion will not be filled before hundreds of thousands of kilometers of large motorway motorways. Financially and in the medium term, less expensive versions remain more interesting, even if it means putting the hand a little more in the pocket during the few annual journeys exceeding the autonomy of the vehicle.
The future of the fast charge nevertheless seems to be left to be even more expensive than today, and the vehicles allowing to arrive safely with a stop recharge are more and more attractive. Another way of traveling begins to point the tip of your nose, not requiring recharge: the exchange of batteries. So let’s see if this service has the future in our regions.
Batteries exchange, a service for the future ?
Arrived straight from China where he met with some success, the exchange of batteries is a simple concept, which allows to start 100 % in a few moments. This requires having a vehicle provided for this operation, as are the NIO ET7 or ET5, or the future electric vehicles of the MG group.
In practice, the battery exchange requires only about five minutes to see its battery freshly attached to a load level of 90 %, where rapid recharging will require about 18 to 30 minutes to be only 80 % of charge. The main advantage therefore lies in the speed of the maneuver, which can be similar to the duration of a full of gasoline.

However, if the fast load is more and more expensive, the battery exchange is not necessarily less expensive. Indeed, manufacturers offering the battery exchange currently do so on the condition of renting the battery of its vehicle, at a cost of around 1,600 euros per year (price for the nio es8).
In addition, the density of battery exchange stations is for the moment very weak, when we are not in a country that does not yet offer them. If more than 1,000 stations are planned in the medium term by the giant Catl in Europe and elsewhere, there is to date only one handful in Norway, which strongly limits the interest for the inhabitants of the old continent. A new station has just opened in Germany.
The future will tell us if this battery exchange service will be popularized outside China or not, but to date, it absolutely does not exempt from having a big battery as the stations are rare.
Indeed, if we take up the example of the Nio ES8, the electric car managed to travel 1,000 km on a highway in 9 hours thanks to the battery exchange. But 11:25 a.m. on the same route with fast recharges (without battery exchange) ! To be compared to the 9:15 am necessary for the Tesla Model 3 Performance to complete the same exercise with the fast recharges.
Conclusion
As we have seen, a larger battery in an electric vehicle does not only have advantages. The theoretical autonomy displayed is greater, but concretely, if consumption is higher due to the more substantial on -board weight, you will not happen more quickly.
The smaller batteries have the advantage of making it possible to offer a vehicle at a more reasonable price, and the additional cost generated during large trips remains not very significant. A big battery is actually synonymous with comfort and peace of mind on a daily basis as in a big way rather than a need to travel.
The density of rapid charging stations has increased significantly for many months, with new players who arrive on the market, causing the concern of the charge in roaming in roaming. Finally, In the interest of limiting the carbon footprint of the electric car, choosing the one that has a smaller battery makes sense : from manufacturing to use, it is more ecological than a more imposing battery.
Want to join a community of enthusiasts ? Our discord welcomes you, it is a place of mutual aid and passion around tech.



