What 5G? Characteristics and uses, what is 5G?
What the 5G
Incredible progress has been made in the field of wireless technology in only forty years. In fact, we are about to go to the fifth generation of wireless communications: 5G. The Center for Research on Communications (CRC), the main research laboratory of the Government of Canada specializing in advanced telecommunications, makes every effort to deploy 5G in Canada, so that Canadians can benefit from systems, technologies and most modern applications in telecommunications.
What is 5G ?
Fifth generation (5G) networks arrive – in France, in particular.
Beyond the improvement of speed, 5G will facilitate the emergence of an immense ecosystem IoT (Internet of Things) in which networks will be able to meet the communication needs of billions of connected objects, thanks to a compromise between speed, latency (response time) and cost.
The following questions and answers clearly present 5G technology:
- How does it differ from today’s 4G lte?
- What are the new cases of use of the IoT?
- How will mobile network operators take advantage of it ?
What is 5G (and what is not) and what is the difference between 4G LTE and 5G ?
The fifth generation wireless network will discuss the evolution beyond the Mobile Ver L’IoT (Internet of Objects) Internet).
The main evolution compared to 4G and 4.5G (LTE Advanced) today is that beyond theSpeed improvement of data transmission, it is the new cases of use of IoT and critical communications that will profite improved performance of 5G.
For example, the low latency, A characteristic authorizing the interactivity in real time of services using the cloud, is essential for the success of driver -free cars, for example.
Likewise, the low power consumption will allow connected objects to operate for months or years without human assistance.
Unlike the current IoT services which opt for performance compromises in order to best benefit from current wireless technologies (3G, 4G, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, etc.), 5G networks will be designed to provide the level of performance necessary for a massive deployment of connected objects.
This technology will offer a perfectly connected world.
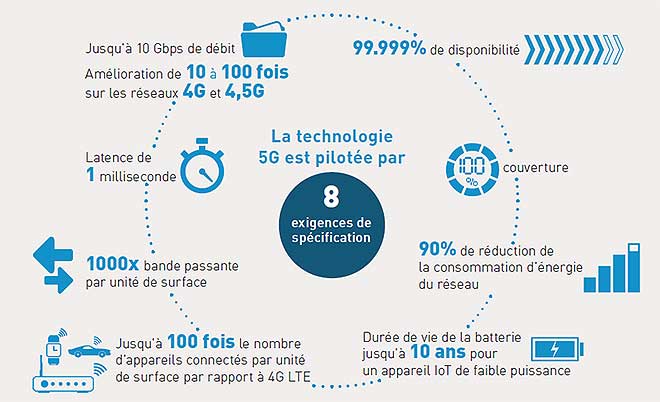
5G technology is based on 8 technical requirements
- Up to 10 gbit/s of data flow -> from 10 to 100 times more than 4G networks and 4.5g
- 1 millisecond of latency
- 1,000 times more bandwidth per unit surface
- Up to 100 times more devices connected per unit surface (compared to 4G LTE)
- 99.999 % availability
- 100 % coverage
- 90 % reduction in network energy consumption
- Up to 10 years of battery life for low -consumption IoT devices
5G technology also offers extremely low latency, that is to say the time between sending and receiving information. From 200 milliseconds for 4G, we descend to 1 millisecond (1ms) with 5G.
But what is 1 millisecondement exactly?
A millisecond is equivalent to 1/1000 second.
The average reaction time of humans to a visual stimulus is 250 ms or 1/4 of a second. Our reflexes are capped at around 190-200 ms in the best of cases.
Imagine now that your car can react 250 times faster than you.
Imagine that it can also respond to hundreds of incoming information and communicate its reactions to other vehicles and road signals in a few milliseconds.
At 100 km / h, the distance traveled by a vehicle before the driver presses the brakes is approximately 30 meters. With a reaction time of 1 ms, the car would only have rolled a little less than 3 centimeters.
Presentation of 5G – Questions and answers
What are the concrete use cases of 5G ?
Each new generation wireless network incorporates a whole series of new uses.
5G technology is no exception by focusing on IoT and critical communication applications.
- THE 5G networks (2020) developed broadband wireless services beyond mobile Internet to IoT and critical communication segments
- Networks 4.5G (LTE Advanced) have doubled data transmission speeds compared to 4G
- THE 4G networks (years 2010) introduced all IP services (voice and data), high speed internet experience, with unified network architectures and protocols
- Networks 3.5G have made the use of mobile Internet universal, and are behind the success of mobile application ecosystems
- THE 3G networks (2000s) improved the experience of mobile Internet, but with limited success to trigger the massive adoption of data services
- Networks 2.5G have made a slight improvement to data services with Edge
- THE 2G networks (1990s) were marked by the birth of digital cell phone services and basic data services (SMS, GPRS) – as well as homelessness services (Roaming)
- THE 1G networks (1980s) enabled analog telephone services to benefit from mobility
Certain essential applications such as the driver -free car require very reduced latency (quick response time) when it does not need quick data speeds.
Conversely, cloud -based business services with massive data analyzes favor speed compared to latency.
Virtual networks (5g Slicing) adapted to each use:
5G will support all the communication needs of local network (LAN) (such as domestic networks) with extensive networks (WAN), with the latency/speed parameters that suit.
The way to meet this need today is done by grouping a large number of communication networks (WiFi, Z-Wave, Lora, 3G, 4G, etc.)).
5G is designed to allow simple virtual networks to obtain better alignment of network costs compared to the needs of applications.
This new approach will allow operators of 5G mobile networks to take up a larger part of the IoT market while being able to offer economic solutions for applications with low bandwidth and low consumption.
When the 5G is operational ? Where is 5G technology in terms of standardization and how long will it take ?
- ITU-R launched “IMT for 2020 and beyond” in 2012, laying the foundations for 5G
- Japan and Korea began working on the requirements of 5G in 2013
- NTT Docomo started the first experimental trials of 5G in 2014
- Samsung, Huawei and Ericsson launched the development of a prototype in 2013
- South Korean Sk Telecom presented 5G in 2018 in 2018 at the Pyeongchang Winter Olympic Games
- Ericsson and Teliasonera offered the sales department at Stockholm and Tallinn from 2018
- In the United States, ATT announced national coverage in Mid 2020. Verizon was the first supplier.
- In Germany, Deutsche Telecom launched 5G in 2019 on Berlin, Darmstatdt, Munich, Bonn and Cologne.
- In the United Kingdom, deployment has been carried out since 2019.
- In India, 2021 is the year of starting.
- In France, 5G was launched in November 2020. More than 14.223 5G branches are installed at the end of April 2021. Bouygues Telecom, Free, Orange and SFR operators deploy a 5G network.
In how long will 5G be adopted ?
The adoption rate provided for 5G is completely different from previous generations of networks (3G, 4G).
While previous technologies were based on the use of the mobile Internet and the availability of star applications (“Killer app”), 5G should be based mainly on new uses of IoT.
Given the new perspectives of broadband connectivity, some equipment manufacturers like Ericsson provide more than 150 million devices connected in 5G in less than 12 months after its launch.
What are the consequences of 5G for mobile operators ?
- 5G remains high speed cellular technology and constitutes a “network of network”. The expertise and know-how of mobile network operators in the construction and operating of networks will be essential for the success of 5G.
- Apart from the provision of network services, mobile operators will be able to develop and operate new IoT services.
- The implementation of 5G networks while keeping operational 3G and 4G networks will certainly be a new challenge for operators regarding the frequency capacity on the spectrum (especially if the enormous volume planned on the IoT is materialized). Mobile operators (MNO) will have to make the request, then exploit a new spectrum on the frequency range 6 to 300 GHz, which involves huge investments in networks infrastructure.
- To achieve the goal of a latency of 1ms, 5G networks involve connectivity for the base station using optical fibers.
- On the savings side, 5G networks should be able to take care of virtual networks such as LPLT (Low Power Low Throughput) networks for ile of low power. Unlike today, where Lora networks meet this separately 4G need.
Will 5G technology be secure ?
Today’s 4G networks use the USIM application to execute strong mutual authentication between the user and its connected device and networks.
The entity hosting the USIM application can be a removable SIM card or an on -board chip on.
This strong mutual authentication is crucial to activate trust services.
Current safety solutions are already a combination of safety on the outskirts (the device) and safety at the heart (the network).
Several security executives will be able to coexist in the future and it is likely that 5G will reuse existing solutions used today for 4G networks and for the Cloud (SES, HSM, Certification, OTA and KMS supply))
The standard for strong mutual authentication of 5G networks is not yet finalized.
The need for security, protection of personal data and confidence will be as strong as for 4G or even more with the growing impact of IOT services.
Local operating systems of devices can not only secure access to the network, but also support secure services such as emergency call management and virtual networks for IoT.
What consequences will 5G have for consumers ?
For consumers, 5G does not only mean a faster mobile internet, but above all even more connected objects.
The car and the house are two examples of the great revolution IoT which is announced, taken care of by 5G networks.
How will 5G technology speed up the marketing of IoT devices based on cellular rather than Wi-Fi technology ?
Wi-Fi is a wireless local network technology, limited in its operating range and very limited in speed and latency.
Many IoT services require more presence, more mobility and more performance in terms of speed and response time.
5G will make possible a real IoT ecosystem.
How will the use of 5G networks change the world?
Thanks to 5G, the “perception” of speed, instant response time and performance for IoT will become a reality.
For example, the expected success of the driverless car will only be possible when 5G networks are available.
5G SIM
Discover the Definition & Benefits of A 5G Sim for 5g Virtualized Networks.
Reaching 5G’s “Plateau of Productivity”
Big Data Analytics, Machine Learning & Ai Are Critical for Service Providers to Master 5G Operational Complexity.

A New Trust Model for the 5g Era
5G USE CASES Will Bring New Requirements On The Storage, Compute and Network Domains and Will Introduce New Risks to the Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of Enterprise & User Data. This White Paper Provids Gemalto’s Recommendations to Address these New Challenges and Build A New Trust Model for the 5g Era.
What is 5g?

Incredible progress has been made in the field of wireless technology in only forty years. In fact, we are about to go to the fifth generation of wireless communications: 5G. The Center for Research on Communications (CRC), the main research laboratory of the Government of Canada specializing in advanced telecommunications, makes every effort to deploy 5G in Canada, so that Canadians can benefit from systems, technologies and most modern applications in telecommunications.
In the early 1980s, the first generation of wireless technology, 1G, gave us access to wireless phones (mobile communications). These devices were only used to speak, and their data transmission capacity was almost zero. They were alongside other wireless technologies, but there was no connection between these various technologies, which did not manage to “communicate” between them.
With the 2G, the second generation launched in the early 1990s, the quality of the sound as well as the safety and the capacity of our mobile phones have significantly increased. This kicked up mobile email services and text messages. Consumers have started replacing their telewans with mobile phones, because they could now send text messages directly to people.
3G networks allowed us to benefit from high -speed transmissions, multimedia access and global homelessness. In other words, wireless phones allowed us to remain connected to the network in more places and communicate over greater distances.
Thanks to faster connectivity and at lower internet cost, 4G has favored the launch of new applications and new services. It made it possible to send data, to browse the internet, watch, broadcast and send videos, listen to continuous music in addition to having access to social media and many other applications On our smartphones.
The 5G will profoundly transform wireless telecommunications, by opening the way to the network of future generations which will include more devices and will allow faster and greater communications.
“Imagine it’s Canada’s Day,” said Doris Camire, research director at CRC. “A considerable crowd gathered for the festivities on the hill of the Parliament, and all want to use their cell phone to send photos or videos and communicate with the help of FaceTime with their parents and their friends. This represents a huge amount of data. Everyone tries to connect at the same time, but it is impossible to get a signal because the capacity of the network is insufficient. »»
The 5G will solve the problem with breakthroughs in three key areas: connectivity, latency and band width.
There connectivity relating to the number of devices that can communicate with each other, and there are already more than five billion. In short, we are more connected than ever, but by 2020, their number should reach 50 to 100 billion worldwide. Nowadays, people use these devices, for example smartphones, mainly to communicate with other people. With the arrival of the 5G, the devices and the machines will be able to communicate more and more directly between them. This is called the Internet of Things, namely the connection of objects to the Internet and between them. This already exists: let’s take for example the thermostat connected to WiFi, which allows you to adjust the heating or air conditioning of your home or your chalet, even when you are elsewhere.
There latency, Or the response time, designates the time that takes a device, between sending and receiving data, that is to say the time required to transmit a set of data to a network to a network to a other person. With 4G, latency is around 50 milliseconds. To find out how fast it is, a wink takes 0.1 to 0.4 seconds, or from 100 to 400 milliseconds. For the wireless transmission of data with the 5G, it will take even less time, about a millisecond, a thousandth of a second.
To properly grasp the importance, let us think of driver -free cars. A response time as short as it will be necessary to make decisions in less than a fraction of a second. For example, imagine that you run on the highway in your driver -free car and that an accident occurs just in front of you. The 5G sensors along the road would instantly transmit this information to your car, which would communicate it to the car behind you and so on, alerting each car of the danger and potentially avoiding another accident or a pile up.
A bigger bandwidth For 5G will allow very high download speeds for new applications, such as 360 -degree and 3D continuous video playback. The experience in class will be transformed: it will be more realistic, immersive and interactive because the listening helmets will be mobile and not connected to a computer. Learning a new language can be done by engaging the conversation with other students in virtual environments. We can study history by virtually walking in the streets of old civilizations.
The 5G will be a completely new and versatile network, ensuring the interface with all current generations and evolution of wireless technologies to come. Faster and more flexible, it will allow the connection of billions of new devices to each other. The CRC research projects focused on major challenges, aimed at knowing the principles of use of the spectrum, finding more judicious and innovative means to take advantage of current spectrum resources and increase our wireless communication capacity, will help Canada to be a world leader in 5G.
Contact us to learn more about our research activities on 5G, as well as on our other research projects focused on major CRC challenges and collaboration possibilities.



