My IP – What is my IP address?, Know your public IP address and private IP address
Know your public IP address and private IP address
Your broadband box has a private IP address and a public IP address. Find out what differentiates them and how to know them.
What is my IP address ?
An IP address (Internet Protocol) is a series of figures that uniquely identifies a device connected to a computer network using the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address is used to allow the delivery of data between devices on a network, whether on the Internet or on a local network (LAN).
IP addresses are essential to allow devices to locate themselves and communicate with each other on the network. When a device sends data, it addresses it to a specific IP address, and routers and other network equipment use this address to determine where to send the data.
There are two main versions of the Internet protocol in use: IPV4 (version 4) and IPv6 (version 6). IPV4 uses IP addresses made up of 32 bits (in the form of four decimal numbers separated by points, for example: 192.168.0.1), while IPV6 uses 128-bit addresses (in the form of eight hexadecimal figures separated by two-points, for example: 2001: 0db8: 85A3: 0000: 0000: 8A2E: 0370: 7334).
IP addresses play a crucial role in the operation of the Internet, because they allow traffic to lead to specific destinations and connect millions of devices around the world.
How to find my public IP address ?
To find your public IP address, you can use one of the following methods:
- Dedicated websites: There are websites specially designed to display your public IP address. You can access one of these sites using your web browser. For example, you can visit Mon-IP.Info to get your public IP address.
- Use of network orders: If you are comfortable with the commands, you can open a command prompt on Windows or a terminal on MacOS/Linux and type one of the following commands:
- On Windows: Use the NSLOOKUP MONIP command.org or curl ifconfig.me .
- On macOS/Linux: Use the IFCONFIG CURL command.me or curl ifconfig.io .
These methods will give you your public IP address, which is the address used by your router to communicate with the Internet. Keep in mind that this IP address can change periodically if your Internet service provider uses dynamic IP addresses. If you need the public IP address regularly or for specific uses, it may be useful to use online tools or services that automatically recover this information.
IPV4 and IPv6 address, what differences ?
IPV4 and IPv6 addresses are two different versions of the Internet Protocol (IP) used to uniquely identify devices connected to a network. Here are the main differences between the IPV4 and IPv6 addresses:
- Address format:
- IPV4: IPV4 addresses are made up of 32 bits, generally represented in decimal rating separated by points (for example, 192.168.0.1).
- IPV6: IPv6 addresses are made up of 128 bits, generally represented in hexadecimal rating separated by two-points (for example, 2001: 0db8: 85A3: 0000: 0000: 8a2e: 0370: 7334).
- Address pool size:
- IPV4: Due to its size limited to 32 bits, IPV4 offers a relatively limited address space, allowing around 4.3 billion unique addresses.
- IPv6: Thanks to its 128 bits, IPv6 offers a considerably larger address space, allowing about 3.4 x 10^38 unique addresses. This makes it possible to meet the needs of exponential internet connectivity and to ensure that each connected device can have a unique address.
- Migration and adoption:
- IPV4: being the historic internet protocol, IPV4 has been widely used since the beginnings of the Internet. However, due to the gradual exhaustion of available IPV4 addresses, the deployment of IPv6 has become necessary to meet the growing demand for Internet connections.
- IPv6: IPv6 has been developed to compensate for the limitation of IPV4 addresses and to meet future Internet needs. Although IIPv6 has been available for many years, its complete adoption is done gradually, as this implies a complex transition from the network and equipment.
- Notation:
- IPV4: IPV4 addresses are generally noted in the form of four decimal numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by points (for example: 192.168.0.1).
- IPV6: IPv6 addresses are noted in the form of eight groups of four hexadecimal characters, separated by two-points, with each group that can be abbreviated if necessary (for example: 2001: 0db8: 85A3 :: 8a2e: 0370: 7334).
Due to the exhaustion of IPV4 addresses, the transition to IPv6 has become inevitable to allow the continuous growth of the Internet and its connected devices. However, the coexistence of the two versions is common during the transition period, and the devices and networks must be configured to support both versions to ensure global connectivity.
In June 2023, Google statistics show that IPv6 is available for around 40 % of its users worldwide. The adoption of the IPv6 varies from country to country and depends on Internet access providers. Countries such as France, Germany and India now lead the majority of their traffic to Google via IPv6, while other countries like the United States, Brazil and Japan approach 50 %. However, Russia and China have an adoption of the IPv6 less than 10 %, and certain countries such as Spain, Sudan and Turkmenistan have an adoption of the IPV6 less than 1 %.
In June 2023, according to ARCEP, France reached an adoption rate of IPV6 of 62.9 %.
Public and private IP address, what differences ?
Public and private IP addresses are two types of IP addresses used as part of the Internet Protocol (IP) to identify devices connected to a network. Here are the main differences between public and private IP addresses:
- Use of use:
- Public IP address: a public IP address is a unique and route address on the internet. It is used to identify a device connected to the Internet and allow it to communicate with other devices on the global network.
- Private IP address: a private IP address is used to identify a device within a private local network (LAN). These addresses are not route on the internet, which means that they are not directly accessible from outside the local network.
- Availability :
- Public IP address: Public IP addresses are limited in number and must be allocated uniquely by Internet Access providers (ISP) or authorities responsible for the management of Public IP Addresses.
- Private IP address: Private IP addresses are reserved for use in private networks and can be reused inside various local networks without conflict, as they are not visible or route on the Internet.
- Configuration:
- Public IP address: the public IP address is assigned to your router by your Internet access provider (ISP). This is the address used to identify your network on the Internet.
- Private IP address: the private IP address is assigned to each device connected to your local network (LAN) by the network router. Private IP addresses are generally provided by a protocol called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which allows devices to automatically receive an IP address when they connect to the network.
- Examples of addresses:
- Public IP address: 203.0.113.45
- Private IP addresses (for the local network): 192.168.0.1, 10.0.0.1, 172.16.0.1, etc.
Public and private IP addresses play an essential role in the operation of the Internet and local networks. The use of limited public IP addresses has led to the implementation of network address translation technology (NAT) to allow multiple devices of a private network to access the Internet by sharing a single public IP address. This makes it possible to maximize the use of available public IP addresses while allowing local network devices to communicate with each other.
Static or dynamic IP address, what differences ?
Static and dynamic IP addresses are two types of IP addresses used to identify devices connected to a network. Here are the main differences between static and dynamic IP addresses:
Static IP address:
- Assignment: A static IP address is an address that is manually configured and remains unchanged over time, unless the network administrator decides to modify it.
- Stability: The static IP address remains constant, which means that the device to which it is attributed will always have the same IP address, even after a restart or disconnection/reconnection to the network.
- Use : Static IP addresses are often used for servers, network equipment and peripherals that need a constant and predictable IP address to allow permanent access from the Internet or other networks.
- Benefits : Static IP addresses are practical for distant access to servers or devices, for online service accommodation and for the configuration of precise firewall rules.
- Disadvantages: The main drawback of static IP addresses is that their management can become complex in networks with many devices, because each address must be configured manually.
Dynamic IP address:
- Assignment: A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned by a DHCP server (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) each time a device connects to the network.
- Variation: Unlike a static IP address, a dynamic IP address can change whenever the device reconnects to the network. The DHCP server allocates an address available in its address pool.
- Use : Dynamic IP addresses are commonly used in domestic networks, small offices and businesses where there are many devices connected to the network and where it is not necessary to have a constant IP address.
- Benefits : The use of dynamic IP addresses simplifies network management, because the allocation and release of addresses are managed automatically by the DHCP server. This also optimizes the use of available IP addresses, as they are reused when a device is disconnected from the network.
- Disadvantages: One of the drawbacks of dynamic IP addresses is that access to certain online services from outside the network can be more complex, because the IP address changes frequently and is not predictable.
In summary, static IP addresses are used when devices need a constant IP address for specific reasons, while dynamic IP addresses are commonly used in networks where the flexibility of addresses is preferred to simplify network management.
Why other Internet users can see my IP address ?
Other Internet users can see your IP address for various reasons related to the operation of the Internet and the communication protocols used. Here are some common reasons why your IP address can be visible for others:
- Internet communication: When you communicate with servers on the internet, your IP address is included in the database packets you send. This allows servers to send you the answers and the requested data. For example, when you visit a website, the web server receives your IP address to know where to send the web pages you ask.
- Online services : Some online services may need to know your IP address for security, geolocation or other features. For example, geolocation services use your IP address to provide you with relevant results based on your approximate geographic location.
- Pair-to-peer file sharing (P2P): In P2P networks, your IP address can be visible by other users with which you share files or data directly, because the P2P implies direct communication between users without going through a centralized server.
- Network security: In some cases, network administrators can monitor IP addresses accessing their network or services for security reasons, such as detection of suspicious activities or intrusion attempts.
- Online messaging: When you communicate with other users through instant messaging services, electronic messaging or any other online communication system, your IP address can be visible to facilitate the establishment of connection.
How to protect my IP address ?
Protecting your IP address can be important to preserve your privacy and your online safety. Here are some measures you can take to protect your IP address:
- Use a VPN (virtual private network): A VPN crypt your Internet connection and redirect all traffic via a remote server, masking your real IP address to websites and services you visit. This helps preserve your anonymity online and protect your data from prying eyes.
- Use a proxy: A proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and internet. It hides your real IP address and transmits requests to Internet servers. This can also help protect your IP address online.
- Configure a firewall: A software or hardware firewall can help you block unauthorized access to your network and protect your local IP address against possible external attacks.
- Avoid P2P downloads: If you use peer-to-peer file sharing networks (P2P), your IP address can be exposed to other network users. Avoid download or share P2P files if you want to protect your IP address.
- Pay attention to confidentiality parameters on social networks: On social networks and online forums, be sure to control your privacy settings to limit the visibility of your IP address by other users.
- Update your router: Make sure your router has the latest security updates to avoid potential vulnerabilities that could expose your IP address.
- Use browsers with privacy protection extensions: Some web browsers offer extensions or additional modules that can hide your IP address and strengthen your privacy online.
- Avoid clicks on suspect links: Avoid clicking on links or attachments from unknown or suspect sources, as they could be designed to collect information, including your IP address.
- Use encrypted connections (HTTPS): When you browse websites, favor those that support HTTPS connections, as they offer an additional level of security and protect your IP address from unwanted interceptions.
It is important to note that despite all these precautions, certain online activities can still expose your IP address. For example, when you send emails, your IP address will be included in the message header. However, by taking these measures, you can strengthen your online protection and reduce the risk of exposure of your IP address to unwanted third parties.
Which can locate an IP address ?
Several entities can locate an IP address, but the level of precision varies according to the nature of the entity and the laws and regulations in force in the country concerned. Here are some of the parties that can locate an IP address:
- Internet service provider (ISP): Your ISP is responsible for giving you a public IP address when you connect to the Internet. As an internet service provider, he has information on your approximate geographic location, because he knows where your Internet connection is located.
- Legal authorities: In some cases, legal authorities, such as police or other government agencies, may ask an ISP to provide information concerning the IP address of a user in the context of surveys on suspicious or illegal activities.
- Websites and online services: Website and online services you visit can record your IP address in their server newspapers. This allows them to follow and analyze traffic, detect malicious activities and personalize content according to your approximate geographic location.
- Geolocation companies: Some companies specializing in geolocation may provide services to estimate the geographic location of an IP address according to the available public information, such as IP address database and public information databases.
- Virtual private network services (VPN): VPN suppliers can locate the IP address of users connected to their services, as they must know where the connections come to properly transport them. However, a good VPN service will focus on protecting the privacy of its users and will not store activity newspapers or identifiable personal information.
It is essential to understand that the location of an IP address is generally based on an estimate of the geographic position and may not be extremely precise. In addition, many VPN services and websites respect the privacy of their users and do not collect identifiable personal information, which makes it difficult to locate an IP address according to the information available publicly. However, in certain specific cases, the legal authorities may obtain more detailed information from ISPs under local laws and regulations.
How to know who belongs to an IP address ?
As an individual, it is generally difficult to know directly to whom a public IP address belongs, because this information is generally managed by Internet access providers (ISP) and protected by confidentiality rules. However, here are some methods that you can try to obtain general information on a public IP address:
- Use an IP geolocation service: Some websites offer IP geolocation services which can give you an approximate estimate of the geographic location of the IP address, based on public databases of IP addresses.
- Search the online IP address: You can use a search engine to search for the IP address and see if it is associated with a server, a website or other online information.
- Whois: There are online services called “Whois” which allow you to search for public information associated with an IP address. You can try to search for the IP address on a Whois website to see if certain information on the owner or domain recording is available.
- Contact the FAI: If you have a valid reason, you can contact the IP of the IP address and ask him for information about its owner. However, ISPs generally have strict privacy protection policies of users and may not disclose this information without an official request from the competent authorities.
It is important to note that most public IP addresses are dynamic, which means that they can change regularly when you reconnect to the Internet. Therefore, even if you find information on an IP address at a given time, they may no longer be valid in the future. Finally, it is essential to respect the privacy of other users and not to try to obtain confidential information or to break down the online confidentiality rules.
How to change my IP address ?
To change your public IP address, you have several options depending on your situation:
- Restart your router: One of the simplest methods to obtain a new public IP address is to restart your router. After restarting, your Internet service provider (FAI) will likely assign you a new IP address.
- Use a VPN: A VPN (virtual private network) can help you hide your public IP address by redirecting your Internet traffic via a remote server. By choosing a VPN server in another region or another country, you can get a different IP address from that awarded by your FAI.
- Contact your ISP: In some cases, you can contact your Internet service provider and ask him to assign you a new IP address. This can be useful if you have a specific reason to change your IP address.
- Modify your router settings: Some routers allow you to modify the parameters of the Public IP address. You can check the configuration options of your router to see if you can renew the IP address or modify it manually.
It is important to note that certain IP addresses can be attributed static by your ISP, which means that they do not change frequently. In such cases, it can be difficult to change your public IP address. In addition, if you use a VPN, your public IP address may change depending on the VPN server to which you log.
Finally, it is essential to respect the conditions of use of your ISP and not to try to bypass policies or established rules in terms of the allocation of IP addresses. If you need a new IP address for specific reasons, it is best to contact your ISP directly to discuss your options.
How to hide my IP address ?
To hide your IP address and preserve your anonymity online, you can use different methods, such as:
- Use a VPN (virtual private network): A VPN is one of the most effective ways to hide your IP address. He encrypts your internet traffic and redirects it via a remote server, masking your real IP address to the websites you visit. You can choose a VPN server in another region or another country to obtain a different IP address.
- Use a proxy: Proxies act as intermediaries between your device and Internet. They receive requests from your device and send them to websites using their own IP address. This masks your real IP address to the websites you visit.
- Navigate in private mode: Many browsers offer a private navigation mode (for example, “incognito mode” in Google Chrome) which does not store navigation history, cookies and session information. This can hide your online activity, but it does not hide your IP address with websites you visit.
- Use the TOR network: The Tor network is a network of anonymity that transports your internet traffic via several nodes (TOR nodes) to hide your real IP address. This makes your connection more difficult to draw, but it should be noted that the speed can be considerably slowed down.
- Disable geolocation services: On your mobile device or in some browsers, you can deactivate geolocation services to prevent websites from knowing your approximate geographic location from your IP address.
- Use browser extensions: Some browser extensions, such as advertising blockers or privacy protection modules, can help hide your IP address by blocking trackers and online tracking scripts.
It is important to note that even if these methods can mask your IP address to the websites you visit, they do not guarantee complete anonymity online. Other monitoring techniques and tools can always be used to follow your online activity. In addition, be sure to respect local laws and regulations when using these methods, as certain actions may be illegal in certain jurisdictions.
mon-ip.Info: know your public IP address with a click !
Know your public IP address and private IP address

What is the difference between the private IP address and the public IP address on your broadband box ? How to know them ?
It will also interest you
[In video] How to protect your IP address ? What is an IP address, what is it for and above all, how to protect it to avoid.
Your broadband box has a private IP address and a public IP address. Find out what differentiates them and how to know them.
Public IP address
A box has an ip address “outside” and materializing its address on the Internet Internet network: this is the Public IP address. This is the address that “sees” for example a server server on which you are going to make transactions. This is its connection to the net. These addresses are used for computers of the network to communicate with each other. Thus, each computer of a network has a single IP address.
Private IP address
A box also has an IP address “inward”, that is to say to connect one or more computers. This is the private IP address.
How to know your public IP
- The public IP address is issued by your ISP (Internet access provider) at the time of your installation and the synchronization of the box.
- Some widget widgets also allow you to know it.
Here’s how to know your public IP:
- Connect to your box:
- Go to my services → Internet access → Internet connection condition
- http: // www.Whatismyip.com
- http: // addressip.com
- http: // www.Aboutmyip.com
- http: // www.ipchicken.com
- http: // www.showmyisp.com
How to know your private IP with Windows
- If you are under Windows 2000, Windows XP Windows XP or Windows Vista Windows Vista, Go on Start /Run then type “CMD /K IPCONFIG /ALL”.
- If you are under Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 7 Windows 7, Windows 8 Windows 10 Windows 10, go to Start / Run, then type “Winipcfg”.
Here is the detailed procedure under Windows to recover its private IP address:
- Go to start → run → cmd
- Type the “IPCONFIG /ALL” command
Then appears the list of all the Ethernet cards of your PC PC, with their IP addresses and the following information:
- Connection name in Windows properties;
- Mac address of the network card;
- Address “IPV4 IPV4” deprived of your computer.
Windows 10 tip
- In the taskbar, click on the icon icon of your connection, then select the “connected” marked active connection;
- In the window window that opens, click the active connection again. You will then see the information relating to your connection with in particular your private IPV4 address.
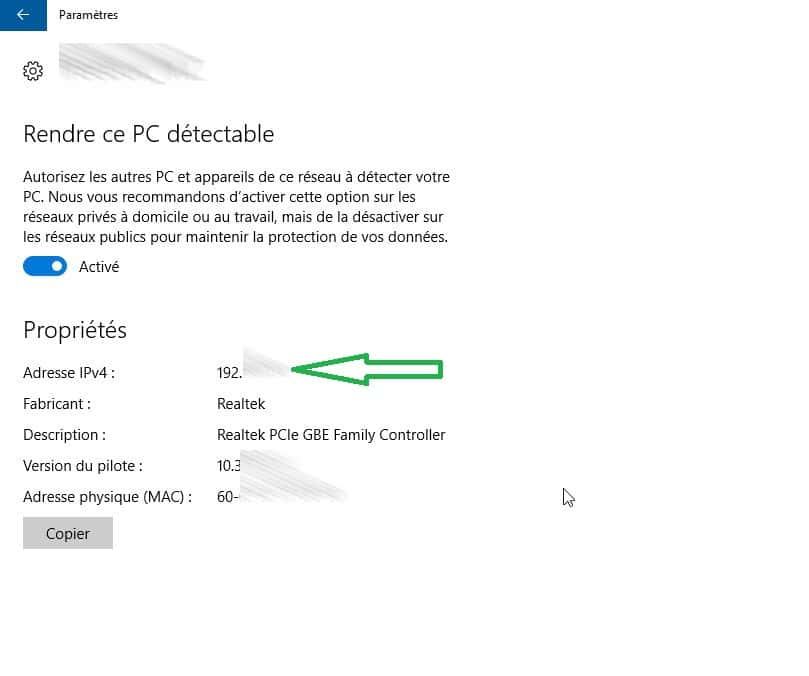
Windows 10 provides access to its private IP address in three clicks. © Futura
How to know your private IP with MacOS
- Go to the “System Preferences” menu (apple icon at the top left of the screen), then open the “network” menu.
- Then click on your active connection, the private IP address is then displayed in the upper right of the window.
See this content in German: Wie Lautet Meine Öffentliche und Private ip-Adresse ?



