L writing Braille | Valentin Haüy association, Braille translator – Decoding the alphabet – Online translation
Braille alphabet
Braille is a practical means of communication for the blind. There are Braille books covering almost all subjects, from mathematics to music, including architecture without forgetting literature.
Writing Braille
Became blind by accident at the age of three, Louis BRAILLE studied at the Royal Institution of the Blind Young people in Paris. In 1821, he became aware of a writing method in relief points Invented specifically for the blind by Charles Barbier de la Serre. This method proposed a phonetic writing made up of 12 points maximum as well asAlphabetical writing Composed of 10 points maximum. It was that held by the students.
After several years of research based on Barbier’s alphabetical method, Louis Braille published in 1837 the final version of his own six -point system. It is the Braille spell writing as we know it today. This system uses the principle of the Braille cell formed from 6 points in relief and, thanks to the 63 combinations of this cell, we obtain a writing can also be used for mathematics and music.
It was not until 1833 that Barbier and Braille met for the first time. Braille was then a teacher at the institution.
Here is an enlarged braille cell:

Different combinations of these 6 points form the letters of the alphabet.
Thus the letter “A” is represented by point 1 of the cell, the letter “B” by points 1 and 2, as we can see below.

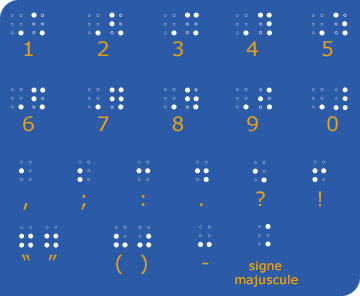
Note that a separate sign announces the figures.
Likewise, the capital letters are reported by two points – points 4 and 6- placed before the letter or group of letters.
Now try to read the quote from the Book of Saint-Exupéry, “the little prince”:

This text is written in full braille, that is to say letter by letter.
Like the lights that have developed stenography, the blind also use an abbreviated version of Braille. This allows them to read and write faster.
Here, for example, the abbreviated version of the first line of the above-mentioning message:

Braille is a practical means of communication for the blind. There are Braille books covering almost all subjects, from mathematics to music, including architecture without forgetting literature.
Since its foundation, the Valentin Haüy association has attached itself, with the help of many volunteers at teach Braille and to constitute A Braille library which is today among the largest in the world and whose works are loaned for free to the blind.
The use of Braille has spread universally, and many objects of common use such as watches, board games, measuring devices have been adapted to the use of blind people using this writing.
Learning Braille is like learning a second language ; It takes time and patience. It is estimated that two years are necessary to be able to read and write the abridged version correctly. It’s not just the blind who learn Braille. The transcription of texts is generally made by visible volunteers. After eight months of learning, a person can transcribe a novel. It is however essential to improve if you want to transcribe texts for students or specialize in musical transcription.
Braille is produced in different ways. You can use a metal or plastic tablet and a punch, a special typewriter whose six keys correspond to the six points of the Braille cell or even a computer that translates, transcribes and reproduces Braille. Computers has indeed opened new paths for entry, repetitive reproduction and remote transmission of texts in Braille.
Braille alphabet
The alphabet is a touch reading system designed for blind people or having a visual impairment.
How to encode in Braille ? (Encryption principle)
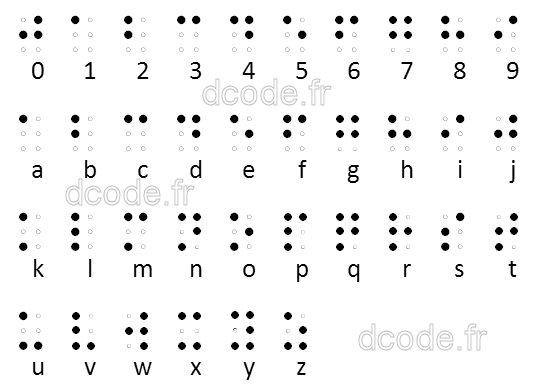
Code translation uses a specific alphabet for visually impaired/blind, composed of relief points adapted to the touch of 1 or more fingers. Each character therefore corresponds to a combination of 6 points (in relief or not) arranged in two columns of three points each.
There are different alphabets, all based on the French alphabet (created first by Louis). Today, the international alphabet is the most used.
| HAS | .png) | B | .png) | VS | .png) | D | .png) | E | .png) | F | .png) | G | .png) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | .png) | I | .png) | J | .png) | K | .png) | L | .png) | M | .png) | NOT | .png) |
| O | .png) | P | .png) | Q | .png) | R | .png) | S | .png) | T | .png) | U | .png) |
| V | .png) | W | .png) | X | .png) | Y | .png) | Z | .png) | ||||
| dcode.Fr | |||||||||||||
Example : is written ‘⠃ ⠗ ⠁ ⠊ ⠇ ⠑’ (Unicode characters) or .png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png) (images)
(images)
The points read in column and its numbered 1-2-3 for the first column and 4-5-6 for the second.
Example : can therefore also be written 12,1235,1,24,123,123.15
For figures, there are 2 modes, the international mode uses the symbol ⠼ (3-4-5-6 L upside down) and the letters from A to J worth 1.2,3,4.5 respectively, 6,7,8,9 and 0. The second French mode, says Antoine, uses the symbol ⠠ (6) instead of ⠼ but keeps the letters from A to J for the value of the figures.
Example : 1 is therefore written ⠼⠁ (International mode) or ⠠⠁ (Antoine mode)
An ambiguity can occur on the interpretation of many number numbers ‘⠼⠁ ⠼⠁’ can mean 11 or 1a, to avoid this the digital symbol ⠼ can be repeated with each figure.
How to decode the Braille ? (Principle of deciphering)
Decoding requires a substitution of a symbol (6 points) with the alphabet .
Example : .png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png) Or 145 14 135 145 15 decipher DCODE
Or 145 14 135 145 15 decipher DCODE
For figures, according to the alphabet used, take into account the prefix ⠼ (3456) or ⠠ (6)
How to recognize the Braille ?
The message is made up of relief points stored by 2 columns of 3. Be careful however, it can be presented in forms unsuitable for tactile reading (see variants).
What are the variants of Braille ?
Depending on languages, certain rare characters such as those with accents can become other characters.
It can be presented in unicode characters, in digital code (composed of figures from 1 to 6 in groups), or even in binary (each figure of 1 to 6 can be listed by a bit 0 or 1).
Example : D is coded 145 or 100110 (bits 1.4.5 are 1, starting from the left)
The 6 bits can be used in octal format (backward reading per group of 3,001 per 1, 011 for 3).
How to print braille ?
The printing of the can be made from a embitreuser. More recently the 3D impression, although much longer, allows you to make your own impressions .
According to Authority, a point must have a diameter of 1.44 mm and a height of 0.48 mm. The center distance between 2 points of the same character (horizontally or vertically) must be 2.34 mm. While the center distance between 2 identical points of 2 consecutive characters must be 6.20 mm. here (link)
When Braille was invented ?
Louis presented his alphabet in 1829.
Ask a new question
Source code
DCODE reserves the property of the source code for “alphabet braille”. Except Code License Open Explicit Source (indicated Creative Commons / Free), the algorithm for “Braille alphabet”, the applet or snippet (converter, solver, encryption / deciphering, encoding / decoding, encryption / decryption, translator) or functions Linked to “alphabet braille” (calculate, convert, solve, decrypt / encrypt, decipher / encrypt, decode / encode, translate) Coded in computer language (python, java, c#, php, javascript, matlab, etc.) or data, for download, script, or API access to “alphabet braille” are not public, ditto for offline use, PC, mobile, tablet, iPhone or Android app !
Reminder: DCODE is free.
Quote
Copy and paste of the “Alphabet Braille” page or its results is authorized (even for commercial use) as long as you cite DCODE !
Exporting results in the form of file .CSV or .txt is free by clicking on the icon export
Quote as a bibliographic source:
Braille alphabet on dcode.fr [online website], accessed 09/25/2023,



