Comparison / 48 CPU processors tested September 2023 – Numériques, comparison between Intel® processors
Comparison between Intel® processors
You can see how Intel® produced Celeron® and Pentium®. But it was made with the intention of replacing the Pentium®. They are intended to occupy the side market by side according to the preference and the price that is given to them. Although Celeron® is less powerful than Pentium®, they both offer excellent services, performance and a reasonable budget.
Comparison / 48 CPU processors tested September 2023
The processor is the brain of a computer. The faster it is, the faster the data. So, AMD or Intel ? Mono, dual, sorting, quad or octo-core ? What to choose according to its use (games, office automation, video, etc.) ?
AMD and Intel offer a fairly wide range of processors. If the racing at the frequency – to the one who will have the most GHz on his CPU – and the number of hearts was very popular a few years ago, it is now less topical. To gain in performance, the two protagonists improve and optimize above all the internal functioning of the processors, that is to say their architecture. In addition to performance, AMD as Intel are working to reduce the electrical consumption of CPUs which, between two generations, are less energy -consuming while being faster.
Choosing a processor is not always easy. At the time of purchase, we will choose according to criteria such as the price, performance or even the nature of the computer (gaming, office automation, professional). Our processor comparison is there to guide you in your choice. We test all types of Laboratory CPUs, whatever their range, so as to bring out models at the best value for money on the market.
The key points
Socket
Be careful, from one generation to another, the processors do not use the same socket – the fitting format in a way. It is therefore essential to make sure to acquire a motherboard at the adequate socket.
Hyper-threading
This is the trade name of a technique used by Intel to accelerate the processing on software that is optimized for parallel calculations-which is almost generalized. Physical hearts (core) of the processor are doubled in order to obtain a number of threads higher and thus better performance.
Turbo
AMD as Intel suggests increasing the frequency (in GHz) of hearts when certain conditions are met. Often called Turbo, this function is similar to a kind ofoverclocking automatic. This increases performance when all hearts are not requested by applications.
Comparison between Intel® processors
We invite you to compare, in this article, the different Intel Atom®, Core ™ I, Celeron®, Xeon® and Pentium® processors. Indeed, most industrial PCs that we offer integrate with Intel processors, including sometimes references (figures, letters. ) can confuse. To do this, and in order to help you make the best choice, we will take an overview of the different types of Intel processors that exist and bring you the major characteristics of these. But above all, below some definitions/details to know above all else. Please note, the processor is not the sole responsible for the good performance of your PC. In addition to a good processor, you must also have an SSD or faster hard drive, a larger RAM (8GB at least) and a good graphics card with a powerful power supply block. These elements strengthen the speed of the PC and make it faster.
Some details before comparing.
Letters
Some Intel processors have letters in their name after the digital part, for example, Intel® Core ™ i7 6920HQ. If we follow the denomination scheme, we can understand that this is a sixth generation processor, but what about HQ ? The rule is not that you will always find two letters after the digital part, but here is what these letters mean.
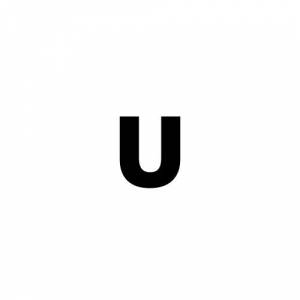
Ultra low power (ultra low consumption) – The U classification only concerns laptop processors. These consume less energy and are better for the battery.

Low Power (low consumption). Is usually found on old -generation laptops and mobile processors.
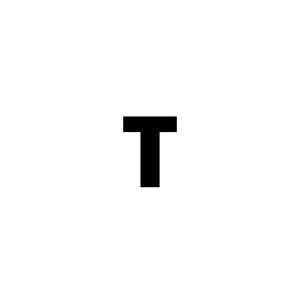
Power Optimized – For desktop processors.

Quad-core. The q index is reserved for processors with four physical hearts.

High-Performance Graphics. Chipset is equipped with one of Intel’s best graphic units.

Includes discreet graphics cards. Generally found on laptops, this means that there is a dedicated GPU with the processor.
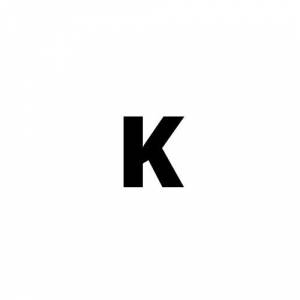
Unblocked. This means that you can overclock the processor beyond its nominal value.
Turbo Boost
Turbo Boost is an overclocking function that Intenl has integrated into its processors. The Turbo Boost function allows the processor to operate faster than its basic clock speed when only one or two processor cores are necessary. This increase in speed is not frozen and is in fact dynamic, depending on the situation. The Turbo Boost depends on the number of active cores, the estimated current consumption, the estimated power consumption and the processor temperature. It works by 133MHz increments and can be increased if necessary. The speed of the clock continues to increase until it reaches the limit of the turbo boost or that the processor temperature reaches its maximum thermal power. In substance, the nominal thermal power of TDP is the temperature to which a processor can operate safely. Intel® Core ™ i5 and Intel® Core ™ i7 processors both use Turbo Boost, Core ™ i7 processors reaching higher clock speeds.
Hyper-threading
Hyper-threading is a technology that allows a single physical nucleus to act as two nuclei, thus improving multitasking without having to activate another nucleus. This makes it possible to obtain more performance by physical kernel while saving energy. Thanks to the hyper-threading, your Double Coeur Intel® will be more efficient than any other normal double heart processor, especially with regard to multitasking. If you are gifted in mathematics, you may have understood that hyper-threading is in fact to create four cores from the two cores available. And it’s true here, but these are four virtual hearts and not real physical hearts. All Intel® Core ™ i7 processors use Hyper-Threading, so a processor with eight cores can manage 16 flows, one with four cores can manage eight flows and one with two cores can manage four flows. The Core ™ i5 uses Hyper-Threading to ensure that a two-core processor acts as a four-core processor, but if you have a Core ™ i5 processor with four real cores, it will not have hyper-threading.
Integrated graphics
Integrated graphics save energy since there is no additional graphic chip on the motherboard of your laptop or office that consumes energy.
Comparison between Intel® processors
The best -selling and best known Intel® processors are Intel® Core ™ i3/i5/i9/i9 processors. Today, most PCs are equipped with these processors because they are affordable and powerful enough to perform daily tasks. These processors are the best in terms of everything. They offer the best performances and meet our needs, whether it be edition, design, etc. These Intel® Core ™ I processors do their job very effectively. These processors are generally available in all categories such as dual-core, quad-core, hexa-core, octa-core, etc. with hyper-threading technology and turbo boost as a main characteristic.
Intel® Core ™ i3 processor
The Intel® Core ™ i3 processor is the slowest and cheapest and can be seen on laptops from low -end to low -end. This processor is the cheapest in the range of the “I” series of Intel. Today, there are in double version and quadruple hearts, with the hyper-threading activated in certain variants. Example of Industrial PC: PC Fanless Nise 4200 with Intel® Core ™ i3-6102e processor, Dual-Core, 1.9 GHz and 4M cache memory.
Intel® Core ™ i5 processor
The Intel® Core ™ i5 processor is a middle and economical class processor. This processor is suitable for most users because it is balanced for each task. If you want a decent computer or laptop for your daily activities, you can opt for an Intel® Core ™ i5 processor. Example of Industrial PC: IPPC 1680p PC panel with Intel® Core ™ i5-6300U processor, 2.40 GHz.
Intel® Core ™ i7 processor
The Intel® Core ™ i7 processor is the fastest and most expensive compared to Intel® Core ™ i3 and Intel® Core ™ i5 processors. This processor is reserved for those who want extreme performance in each task. This processor is very powerful and in many tasks, it is very close to its counterpart The Intel® Core ™ i9 processor. Intel® Core ™ i7 processors have greater cache (on -board memory) memory to help the processor treat repetitive tasks faster. If you edit and calculate spreadsheets, your CPU should not have to recharge the frame where the figures are. Example of Industrial PC: PC Fanless Specific Railway Nrok 7251 with Intel ®Core ™ i7-9700te processor, 4.3 GHz, octa-core.
Intel® Core ™ i9 processor
The Intel® Core ™ i9 processor is a new CPU Intel class (a renamed name of high -end XEON CPU to compete with AMD) which begins with 8 cores and 16 threads. The latest Intel® Core ™ i9 10th generation processor is currently the most powerful processor with its 10 cores and 20 threads. This processor is only intended for those who want ultimate performance in each of their tasks.
In short, if we had to qualify these different processors
- i9: the flagship
- i7: the high -end
- i5: the general public
- i3: entry -level
The main differences between an Intel Core i3, i5 and i7 processor reside in the number of hearts, hyper-threading and turbo-boost (or their absence), clock size and clock speed. The cache memory is the proper memory of a processor and it can considerably affect performance. As with normal RAM, the greater the size of the cache, the simpler the rule. Finally, there are other differences, such as energy consumption and the integrated graphic chip. The integrated graphics are acceptable, but if you really want to use applications with a high graphic component, it is always better to have a dedicated GPU.

Intel® Xeon® processor
Intel ® Xeon® processors are very high -end and are used for animation or for research purposes. These processors have a very low emergency battery due to their higher TDP (thermal envelope). But in terms of performance, they are the best and can perform very heavy tasks easily. These processors are very expensive and very energy delicious. Usually, Intel ® Xeon® processors are used in businesses, servers, where great data processing power is required. These processors work perfectly in servers and data processing when associated with Intel ® Optane memory which is a non -volatile cache solution.

Intel® Celeron® processor
Intel® Celeron® processors are real entry -level processors for low -budget laptops as we know them. They have lower TDP than Pentium® and Core ™ processors and are also the cheapest. A lower TDP leads to a lower heat emission and a longer battery life lifetime. These processors are perfect for trivial tasks such as word processing, research, etc. As they consume less energy, they are also quite effective on battery life. To better understand the Celeron® processors, you must also understand the prefixes. Intel® Celeron® processors have either prefix n, j, or g. In general, the difference lies in their TDP and their clock speed. The lower the nominal thermal power (TDP), the slower the speed of the clock, because the speed of the clock requires energy.
The very first Celeron® processor was based on the design of Pentium® II. The majority of its processors are based on Pentium® II/Pentium® III hearts. However, the latest chips are in Pentium® 4. Celeron® is the second least dominant processor in the Intel® family. In comparison with Pentium® processors, Celeron® is a less powerful version. It is mainly designed for low -budget personal computers. The majority of Celeron® processors operate at a speed of 1.4 GHz or less. Celeron® consists of low-end IA-32 and X86-64 chips designed specially for low-cost PCs. Compared to Pentium®, Celeron® chips have slightly lower performance and low cache memory.
When it was based on the design of Pentium® II, it had a low bus and a smaller cache memory but over time, the Celeron® processors have evolved towards the design of Pentium® III and Pentium® 4. These chips are cheaper than Pentium® processors. The Celeron® processors use a 400 MHz bus and have a 128Ko cache memory. It is designed for a motherboard that uses a 66 MHz system bus. The quickest Celeron® processor has a 2.8 GHz clock speed and does not support multi-thread and hyper-threading.

Intel® Pentium® processor
Pentium® or Intel® Pentium® is part of a family of X86 microprocessors. It originally replaced the 80486 processor and in 1993, the first processor of the P5 family (586), called Pentium®, was introduced. Compared to the 80486DX, Intel® processors had speeds between 60 MHz and 300 MHz, a 64bits data bus. The word pentium® comes from the Greek word which means “five”. This name is used because it is the fifth processor of the 80 × 86 range.
Followed by the first processor in 1993, Intel® introduced Pentium® Pro in 1995. He became the first to contain a high -speed level 2 -speed cache memory with his own bus. Subsequently, Intel® evolved and released several P6 chips. In the late 2000s, she had introduced 4 powerful Pentium® chips. Intel® Pentium® processors are classic and inexpensive fleas for entry -level PCs. The latest processor with 32-bit Intel architecture (IA-32) is Pentium® 4. It is the oldest family produced by Intel®, even above the Celeron® family.
The term “bus” refers to the communication channel between other devices and the processor. The bus speed indicates the speed at which the data can enter and leave the processor case. The fastest bus speed for Pentium® is 1066 MHz. This means that the Pentium® processor communicates much faster with other computer devices, such as keyboard, hard drive, etc.
The Pentium® III processors are equipped with a 512 ko L2 cache memory and rely on a 133 MHz system bus. It supports multi-treatment and hyper-threading. In addition, the fastest processor in the Pentium® range has a clock speed of 3.8GHz.
Main differences between Pentium® and Celeron®
- Pentium® is an extended family of X86 microprocessors, while Celeron® is the Intel family of low-end fleas IA-32 and x86-64.
- The fastest processor in the Pentium® range has a 3.8GHz clock speed and the fastest Celeron® processor has a 2.8GHz clock speed.
- PENTIUM® processors support multitramenting and hyper-threading
- The fastest bus speed for a Pentium® is 1066MHz with 512KO L2 cache memory and the fastest bus speed for a Celeron® processor is 400 MHz with only 128 KB of cache cache
- Celeron® fleas are cheaper than Pentium® fleas.
You can see how Intel® produced Celeron® and Pentium®. But it was made with the intention of replacing the Pentium®. They are intended to occupy the side market by side according to the preference and the price that is given to them. Although Celeron® is less powerful than Pentium®, they both offer excellent services, performance and a reasonable budget.
Intel® ATOM® processor
If we had to make a classification of the different processors (Intel® Core ™ I, Xeon®, Celeron®, Pentium®, Atom®. ) then Intel® Atom® would be at the bottom of the scale. Intel® ATOM® processors have been developed with the intention of providing solutions to very low voltage For integrated systems such as smartphones and other devices of this type. The latest Intel® ATOM® processors have followed a denomination standard similar to that of the Intel® Core ™ “I” series. They used the “x” prefix instead. Here they are: Intel® ATOM® X3, Intel® ATOM® X5 and Intel® ATOM® X7.
Request for additional information
You have questions or need additional information concerning this article on Intel® Core ™ I, Xeon®, Pentium®, Atom® or Celeron® processors ? To do this, we invite you to fill out the contact form below specifying your request. Our entire team of expert is at your disposal to answer you as soon as possible.



