Car electric motor: operation, breakdown, price | Vroomly, the operation of an electric car engine – Easy Electric Life – Renault Group
How an electric car engine works
On an electric car, the engine power depends on the power power in input and engine volume. Regarding output power, It corresponds to the difference between the power of the input current and themechanical energy that the engine needs. This is called the energy conversion yield.
Car electric motor: operation, breakdown, price
Find the best garage to repair your electric car engine:
The electric car engine has real differences with the heat car engine. Fueled exclusively by the energy of the battery, the electric car engine is easier to maintain than a heat engine since it contains fewer parts. On the other hand, the electric motor produces less power.
- ⚡ How does the car electric motor work ?
- �� What are the different types of car electric motors ?
- �� What is the lifespan of a car electric motor ?
- �� What is the power of a car electric motor ?
- �� What is the electric motor conversion kit ?
Find the best garage to repair your electric car engine:
⚡ How does the car electric motor work ?
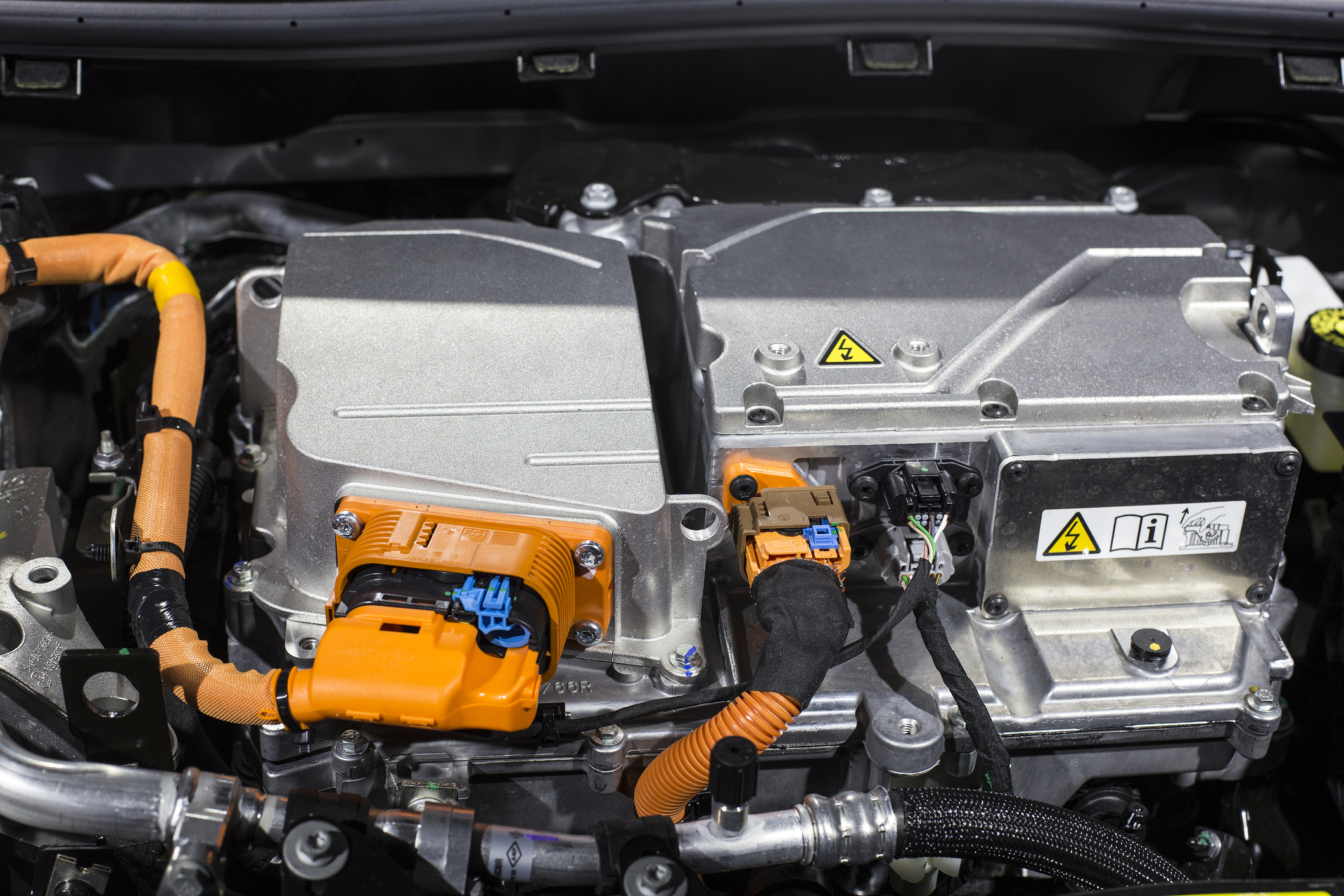

Unlike a heat engine, the car electric motor is only energy fueled by the electric car battery. To operate, the electric motor uses a process which consists in using a Electric power To create a magnetic field on a fixed part of the engine. This fixed part then moves to cause the rotation of a mobile part.
Thus, the electric car motor consists of two main parts:
- THE stator : This is the static part of the engine that uses battery current to create a magnetic field;
- THE rotor : it is the rotating part that receives the magnetic field.
These two elements are part of a larger set called the Electric Motoprop. This set includes all the equipment that allows the electric car to advance and recharge the car battery. We find in particular other important parts such as:
- THE Power electronic controller ;
- THE reducer which controls the transmitted speed of the engine to the wheels of the electric car.
To understand the operation of a car electric motor, keep in mind that two types of electric flow circulate within an electric car:
- THE alternating current (AC) : the electric charge circulates in different directions;
- THE DUR DURSE (DC) : the electrical load only circulates in one direction.
The operation of the electric car is based on the transformation of the continuous current of the electric car battery by alternating current which makes it possible to operate the engine of the electric car. This passage from a continuous current to an alternating current is made through a inverter.
�� What are the different types of car electric motors ?
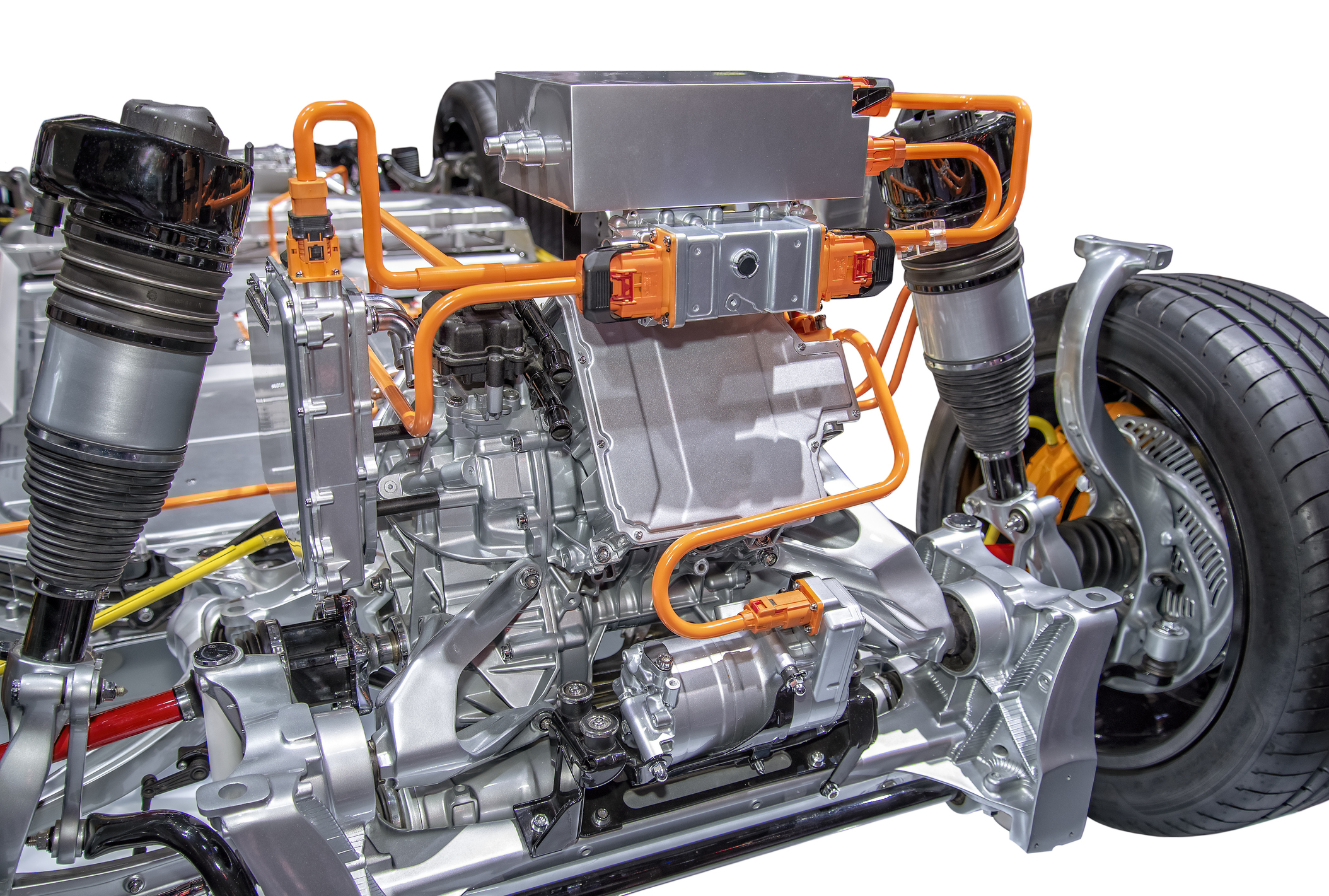
Depending on the electric car model we have, we can find two types of car electric motors:
- THE synchronous engine ;
- THE asynchronous motor.
THE synchronous engine relies on a magnetic field directly produced by the engine rotor thanks to its role as electro-deputy. We use the adjective “synchronous” To refer to the fact that the rotation speed of the rotor is proportional to the frequency of the continuing current sent by the electric car battery. Synchronous electric motors are present on city electric cars which must mark frequent stops.
THE asynchronous motor, also known as induction engine, is based on the use of a rotary magnetic field generated by the stator. This rotation of the magnetic field leads to the rotor which provides the power necessary for the engine to advance the vehicle. Asynchronous engines are found mainly on electric vehicles designed for long trips and high speeds.
Find the best garage to repair your electric car engine:
�� What is the lifespan of a car electric motor ?

It is difficult to determine the precise lifespan of a car electric motor since it depends on many parameters. Indeed, it is necessary to take into account the frequency of use of the engine, but also of the climatic conditions and the level of maintenance.
Thus, it is estimated that an average lifespan of a car electric motor is between 15 and 20 years old. The advantage of this type of engine is that it contains fewer parts than a heat engine and therefore requires less maintenance.
�� What is the power of a car electric motor ?

On an electric car, the engine power depends on the power power in input and engine volume. Regarding output power, It corresponds to the difference between the power of the input current and themechanical energy that the engine needs. This is called the energy conversion yield.
However, because of heat and friction, part of the energy is lost during the process. Thus, the electric motor of the car is unable to use all the energy produced by the electric car battery.
Good to know : The power generated by a car electric motor is expressed in kilowatt (kW).
�� What is the electric motor conversion kit ?

THE conversion kit electric motor is equipment that transforms a thermal motor car in electric motor. Called Electric Retrofit, This process can only be used by a approved company and in compliance with European legislation.
The conversion of a heat engine into an electric motor is done in several steps. You must first remove all the elements that will be useless on the electric motor, namely:
- THE engine ;
- THE exhaust pipe ;
- THE Fuel tank ;
- There gearbox ;
- THE Cooling system, etc.
Then, the equipment specific to the electric car motor is added to conclude the conversion. Once the operation is completed, the company gives the owner of the vehicle a Certificate of conformity. This document is essential to modify the gray card of the vehicle.
Converting a heat engine into an electric motor helps reduce the environmental impact of your thermal car. In addition, even if the cost of high conversion (almost € 20,000), this is a good way to fight against the increase in fuel prices.
Good to know : financial aid such as bonuses and Conversion bonuses are available to convert your heat engine or to simply buy an electric car.
The car electric motor has a very different operation from the heat engine. It only works through an electric battery which transmits a direct current transformed into alternating current. The electric motor rarely falls into it because it does not contain as many elements as the heat engine. However, if this happens, do not hesitate to compare the garages near you to repair your car electric motor.
Find the best garage to repair your electric car engine:
How an electric car engine works ?
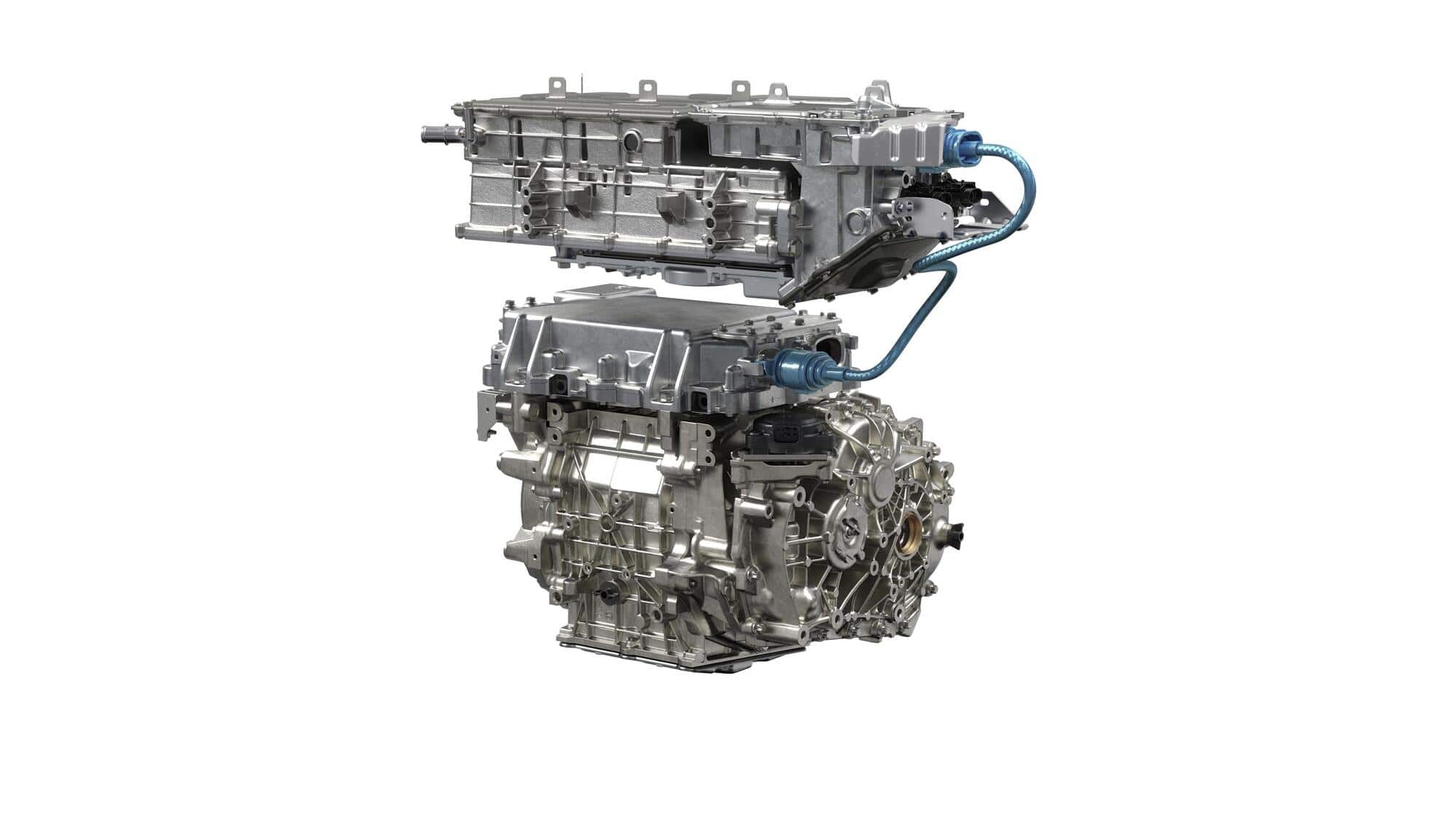

No more cylinders, pistons and exhaust gases: the engine of an electric car is built on the basis of a set of parts designed to convert electricity into mechanical energy thanks to the creation of a magnetic field.
What is an electric motor ?
An electric car engine operates thanks to a physical process developed at the end of the 19th century. This process consists in using a current to create a magnetic field on the fixed part of the machine, the “stator”, which, by moving, will set in motion a rotating room, the “rotor”. We will dwell on these two pieces a little further in this article.
The principle of an electric motor
What is the difference between a heat engine and an electric motor ? Both terms are often used indiscriminately. It is therefore important to differentiate them from the start. Although they are currently used almost as synonyms, in the automotive industry, an “electric motor” designates a machine that converts energy into mechanical energy and therefore in motion, while a heat engine accomplishes the same task, But by specifically using thermal energy. When we evoke the transformation of thermal energy into mechanical energy, we therefore speak of combustion, and not electricity.
It is therefore the type of converted energy that determines the type of engine, thermal or electric. With regard to electric vehicles, since mechanical energy is generated by electricity, the term “electric motor” is used to describe the system that advances the electric vehicle . This is called traction.
How an electric motor works in an electric vehicle ?
Now that it is established that we are talking about electric motors here, and not thermal motors, let’s take a look at the operation of the engine in an electric vehicle.
Today there are electric motors in many everyday objects. Those who are equipped with DC MOTORS (DC) have fairly basic features. The engine is directly connected to an energy source and its speed of rotation therefore depends directly on the intensity of the current. Although easy to produce, these electric motors do not meet the requirements of power, reliability or size of an electric vehicle. They can nevertheless be used to activate wipers, windows and other small mechanisms inside the car.
The stator and the rotor
To understand the operation of an electric vehicle, you have to familiarize yourself with the physical components of its electric motor. It starts with a good understanding of the principles of its two main parts: the stator and the rotor. A simple way to remember the difference between the two: the stator is “static”, while the rotor is in “rotation”. In an electric motor, the stator uses energy to create a magnetic field which then turns the rotor.
How then an electric motor works to supply an electric vehicle ? This requires using alternating current engines (AC), which require the use of a conversion circuit to transform the DC current (DC) supplied by the battery. Let us look at both types of current.
Power an electric vehicle: alternating current (AC) VS DC (DC)
First of all, to understand the operation of an electric car engine, it is necessary to know the difference between the alternating current and the direct current (electric currents).
There are two ways for electricity to circulate in a driver. The alternating current (AC) designates an electric current in which the electrons periodically change direction. DUR COURT (DC), as its name suggests, circulates in one direction.
Electric car batteries work with direct current. Regarding the main engine of the electric vehicle (which ensures the traction of the vehicle), this direct current must however be transformed into alternating current via an inverter.
What happens once this energy reaches the electric motor ? It all depends on the type of engine used: synchronous or asynchronous.
Types of electric motors
There are two types of alternating electric current engines in the automotive industry: synchronous engines and asynchronous engines. In the case of an electric vehicle, synchronous and asynchronous engines each have their strengths; One is not necessarily “superior” to the other.
Synchronous and asynchronous engines
The asynchronous engine, also called induction engine, is based on the stator powered by electricity to generate a rotating magnetic field. This then causes a perpetual rotation of the rotor, as if he tried to catch up with the magnetic field without ever getting there. The asynchronous engine is often installed in electric vehicles intended for long and high -speed trips.
In the synchronous engine, the rotor itself fulfills the function of electro-loving and thus participates actively in the creation of the magnetic field. Its speed of rotation is therefore directly proportional to the frequency of the current which feeds the engine. The synchronous engine is therefore ideal for urban driving, which generally involves regular stops and low -speed restarts.
Synchronous and asynchronous engines work reversibly, which means that they can convert mechanical energy into electricity during the deceleration phases. This principle is that of recovery braking, which stems from the alternator.
Components of electric motors
Now let’s take a look at some of the components present in the engine of an electric vehicle, such as the magnets of the electric motor, the synchronous independent excitation motors, or more generally, the Motopropulseur Group.
Permanent magnets

Some synchronous engines include a permanent magnet engine at the rotor level. These permanent magnets are integrated into the steel rotor, thus creating a constant magnetic field. A permanent magnet electric motor has the advantage of working without power supply. However, it requires the use of metals or alloys such as neodymium or dysprosium. These “rare lands” are ferromagnetic, which means that they can become magnetic and thus transform into permanent magnets. They are used for varied industrial purposes: in wind turbines, wireless tools and helmets, bicycle dynamos or traction motors equipping certain electric vehicles !
Problem: the cost of these “rare earths” is very fluctuating. Contrary to what their name suggests, they are not really so rare, but they are found almost exclusively in China. The country therefore has a quasi-monopoly on their production, sale and distribution. This is the reason why manufacturers are making a lot of effort to find alternative solutions for electric vehicle engines.
Synchronous independent excitation engines
One of these solutions, retained by Renault for Zoe and for Twingo, Kangoo and Mégane E-Tech Electric, is to make an electric motor magnet from a copper coil. This solution requires a more complex industrial process, but makes it possible to avoid supply problems, while preserving the excellent ratio between the weight of the engine and the torque generated.
Guillaume Faurie, head of the engineering service at the Renault factory in Cléon, evokes the complexity and ingenuity of the electric motor with a coil rotor: “The manufacture of an independent excitation synchronous engine requires specific winding and impregnation processes. Constraints linked to expectations in terms of product performance, the objective of reducing the weight/power ratio and the high production rate of production involve effectively using the most advanced technologies to implement these processes. »»
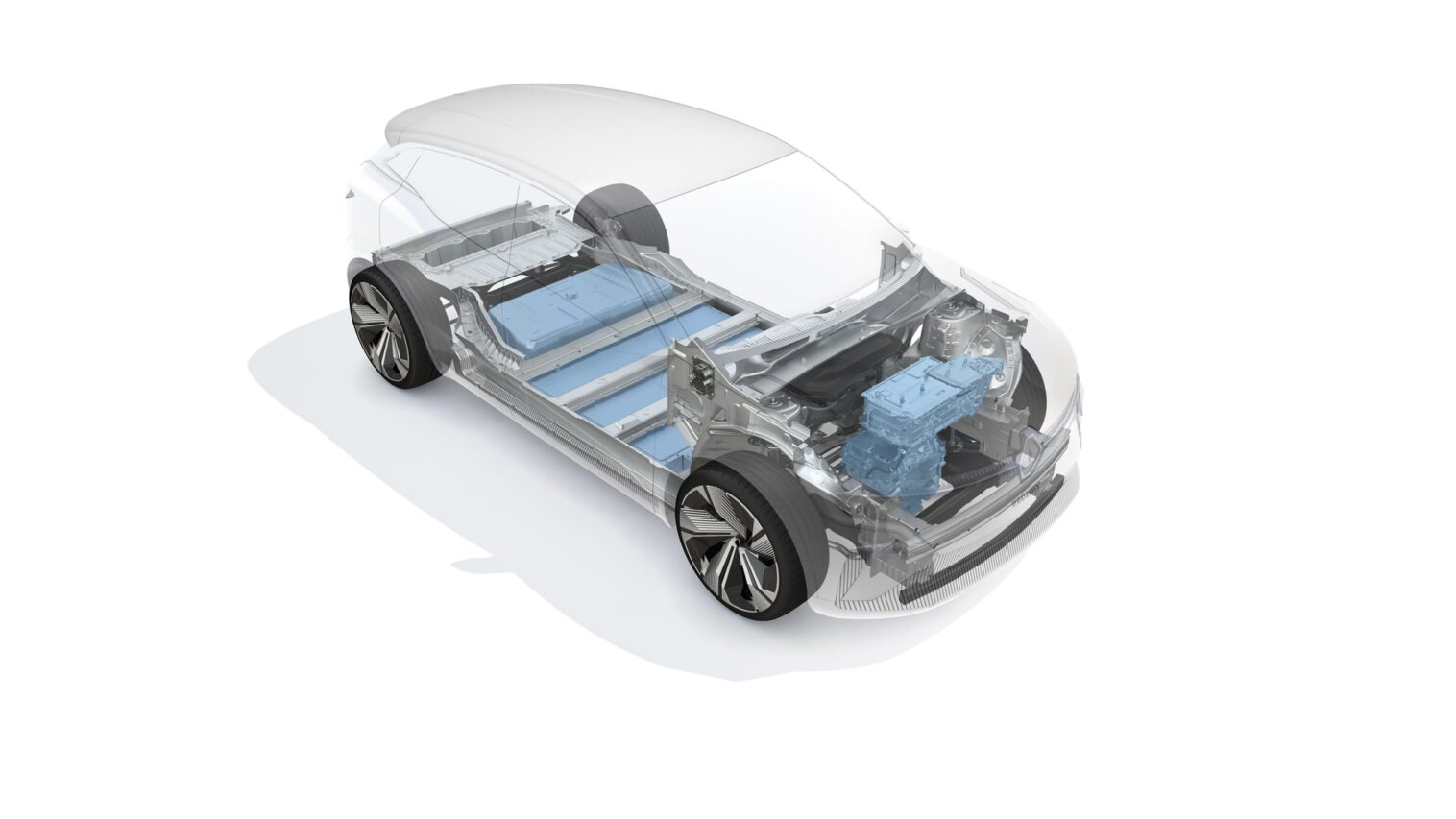
The electric motorcycle group
In an electric vehicle, the electric motor comprising the rotor and the stator constitutes a part of a larger set: the electric powertrain, an assembly which allows the operation of the electric motor.
In the latter, we also find power controllers:
- The inverter that regulates the electrical energy of the engine to control the torque and the speed of it.
- The DCDC converter, which transforms the continuously 14V battery voltage for the vehicle on -board network
- The on -board AC charger and the C Box to recharge the traction battery
Finally, the unit includes the reducer that adapts the rotation speed transmitted by the electric motor to the wheels.
The combination of these elements ensures flexible and effective operation of the electric motor. The result ? Your electric car is silent, reliable, cheaper and pleasant to drive !



