Boarding radius: definition, calculation and maintenance | Vroomly, turning radius: everything you need to know |
Turning radius: everything you need to know
Such tires would considerably reduce adhesion and driving would be impossible because of unbearable brutality for vehicle passengers. In summary, it would not only be uncomfortable, but also very dangerous.
We must therefore find the best compromise between the drift angle and the characteristics of the tires.
Ray of turning: definition, calculation and maintenance
Find the best garage to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
Also called robbery diameter, the turning radius is a measure of the maneuverability of your car, especially in terms of wheels. Accompanied by the power steering, The turning radius will thus define the ease of handling the car and pointing its wheels in one direction or another. This turning radius is all the more important depending on the size of your automobile in order to allow you to maneuver without difficulty.
- �� What is the definition of the robbery ?
- �� How to calculate a turning radius ?
- �� Interior or exterior turning radius: what difference ?
- �� What a car has the best turning department ?
- �� What is the price of maintenance of the turning radius ?
Find the best garage to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
�� What is the definition of the robbery ?

When you want to direct your vehicle to the right or left, the wheels of it will pinch thanks to the moving column in motion. So, The diameter of the circle described by the wheels corresponds to the robbery of the car. It is a good indicator of the handling of a vehicle, He is always coupled with the power steering To allow you to have a good vehicle direction.
Depending on the situations, The diameter of the turning radius will vary in particular depending on the speed of movement of the car but also of the angle given to the wheels WHAT THE DRUT. In addition, the presence of 2 or 4 guidelines will vary the turning department. On average, the turning radius is 11 meters on most vehicles.
The lower the turning radius, the more the vehicle will be handy. This will allow you in particular to Easily make slots or half-tours. Some vehicles have 4 steps In order to offer greater turning capacity, they are found in particular on powerful or competition vehicles. For example, The 4 guidelines can be sprayed in the same direction or in the opposite direction. Parking maneuvers are easier to make.
�� How to calculate a turning radius ?

If you want to calculate the turning radius of your wheels, you will have to take into account several elements:
- The wheelbaseof the vehicle, that is to say the angle of rotation oftires;
- The sinus of the angle which must be calculated according to the opposite side and the hypotenuse.
Thus, the turning radius is calculated by multiplying by 2 the wheelbase then by dividing it by the sinus. The maximum robbery of a car will vary from one model to another. For example, in Germany, legislation requires that it Do not exceed 12.5 meters Whatever the vehicle model.
Find the best garage to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
�� Interior or exterior turning radius: what difference ?

Motorists can rob their wheels outside but also inside the vehicle. When we talk about turning radius, we often refer to the outside radius. Indeed, Le interior turning radius is always lower than the external radius. For example, if the outdoor robbery is 12 meters, it will be 6 meters inside. The interior turning radius is always calculated by dividing the external turning radius by 2.
To find out the robbery of your car, you can consult the technical review of it because it contains all the information given by the vehicle manufacturer.
�� What a car has the best turning department ?

The turning radius varies a lot from one car to another, so it is essential to choose a model with a good turning department. According to the latest tests carried out, the cars with the best turning radius are as follows:
- The Fortwo de Smart with a turning radius of 7.10 foot ;
- The Smart Forfour with a turning radius of 8.9 meters;
- Renault’s Twingo with a turning radius of 9.1 meters;
- The Fiat 500 with a turning radius of 9.8 meters;
- The Fiat Panda with a turning radius of 9.8 meters;
- The Mitsubishi Space Star with a turning radius of 9.9 meters;
- BMW i3 with a turning radius of 9.9 meters;
- Hyundai’s i10 with a 10.2 -meter turning radius;
- The Adam model from Opel with a turning radius of 10.2 meters;
- Suzuki’s Celerio with a 10.2 -meter turning radius.
Vehicles that turn the best are particularly acclaimed by motorists circulating in town where it is difficult to park and where the robbery is quite common.
�� What is the price of maintenance of the turning radius ?

The turning radius does not require an assiduous maintenance, it is very rarely undermined during your trip. Indeed, It will be checked every 2 years during the technical control of your car. However, if one of the parts of the direction or the transmission, is damaged, the turning radius can be less efficient. It is the same for a deflated tire, you will have less good results in the robbery of the wheels.
The turning radius is one of the important characteristics of a car. Indeed, if you drive in narrow driving areas and where it is difficult to park, you will have to take into account the turning radius of the car you want to acquire !
Find the best garage to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
- Direction & transmission
- Mechanical guide
- Tips & Tips
Turning radius: everything you need to know
The turning radius corresponds to the shortest arc radius described by your car at the time of turning your wheels. He will thus be able to assess maneuverability with the help of the power management. Its action also makes it possible to define the side towards which to rob the tires.
- �� What is a turning radius ?
- ⁉️ What a difference between interior and exterior robbery rays ?
- ��️ How to know which car has the best turning department ?
- �� How to calculate a turning radius ?
- �� How much does the maintenance of a turning department costs ?
Compare the best garages to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
�� What is a turning radius ?

To guide the trajectory of your car, several elements will intervene such as the steering column. The robbery of the wheels on one side or the other will therefore be done when it is started. Know that when you turn the tires of your car, they describe at the same time the Diameter of a circle. It is this diameter that is called turning radius.
Indeed this indicator makes it possible to measure precisely the Handling your car. He never works alone. On the contrary for an optimal direction of your car, it will always be in collaboration with the power steering.
The diameter of the turning radius is not always the same. Indeed it is on average 11 meters. But different criteria can vary it like the movement speed, L’angle that you give to tires, THE number of steering wheels (2 or 4)). Only some powerful or competition vehicles have 4 guidelines. This allows to have a better robbery capacity: the robbery of the wheels will thus be able to be done either in the same direction or in opposite direction.
Important : with a low turning radius, you have better handling of your vehicle. This will therefore facilitate maneuvers linked to half-tours Or slots.
⁉️ What a difference between interior and exterior robbery rays ?

The wheels turned to the inside as outside your car. But be aware that the external turning radius is ever higher that the internal. Besides he corresponds to his double. For example when the interior turning radius is 6 meters, The outside will correspond to 12 meters.
Good to know : to find the turning department, do not hesitate to refer to the Automobile technical review of your vehicle. You will be able to find all the information relating to your car as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Compare the best garages to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
��️ How to know which car has the best turning department ?

As you can see, there are variations in robbery between vehicles. You can take care to choose a model that gives you an excellent turning department.
Several studies have been carried out to determine the cars with the best turning department. This is a question of:
- Suzuki’s Celerio with a 10.2 -meter turning radius;
- The Adam model from Opel with a turning radius of 10.2 meters;
- The I10 of Hyundai which has a turning radius of 10.2 meters;
- BMW i3 has a turning radius of 9.9 meters;
- The Mitsubishi Space Star guarantees you a turning radius of 9.9 meters;
- The Fiat Panda with a turning radius of 9.8 meters;
- The Fiat 500 with a turning radius of 9.8 meters;
- Renault’s Twingo offers you a turning radius of 9.1 meters;
- The Smart Forfour which has a turning radius of 8.9 meters;
- The Smart Fortwo which has a turning radius of 7.10 foot.
For traffic in town, know that cars that offer greater ease of robbery are much more successful.
�� How to calculate a turning radius ?

You can choose to do the calculation of the turning radius of your wheels yourself. For this you will need to be interested in different elements:
- THE Angle sinus : the calculation of it must be done according to the hypotenuse and on the opposite side.
- L’Car wheelbase : It is therefore the angle of rotation of the tires.
To obtain the measurement of the turning radius, you must multiply by 2 the wheelbase And Divide the value obtained by the sinus. However, know that as a function of the vehicle model you have but also the country, the Maximum turning radius will vary. In Germany for example, he cannot in any case exceed 12.5 meters.
�� How much is the maintenance of a turning department ?

The maintenance of the turning radius consists in carrying out periodic checks. Indeed these are every 2 years When you do it technical control of your vehicle. But it may happen that the performance of the turning radius are altered: this is the case when one of the parts of the transmission or even the steering is damaged. The wheels will not be done optimally either if you have a deflated tire. So remember to repair these parts when you notice a breakdown before your turning radius is affected.
The turning radius is a device that guarantees better driving comfort especially when you want to circulate on roads where to park is extremely difficult. So remember to take into account the turning department you want before you choose your car.
Compare the best garages to correct the turning radius of your vehicle:
Specialist in the distribution belt
Turning angle
The corner of turning a vehicle is of paramount importance. Car manufacturers have understood this and confront each other to constantly improve the performance of their vehicles. To understand the turning angle is also one of the fundamentals of driving. No driving school instructor abuses this subject that is important to understand to approach turns in the best way.
Here is a summary concerning the turning angle that will help you understand its importance, both for your safety and for your driving comfort.

The turning angle: definition and interest
The turning angle with many consequences on the maneuverability of the vehicle as well as on its handling. Let us see together what are its characteristics and what to take into account when buying a car.
What is the angle of turning a vehicle
The robbery of a vehicle is carried out by turning its steering wheel, which triggers a chain of mechanisms that are put into action to modify the orientation of the wheels and therefore of the trajectory. The turning angle is defined by the diameter of the circle drawn by the vehicle, when its steering wheel is turned to the maximum.
The turning angle determines the degree of maneuverability of a vehicle. It allows you to adjust your trajectory in the curves and make your maneuvers more easily.
It is expressed in meters and is estimated around 11 meters for an average vehicle.
When you travel, the curve that your vehicle describes depends on the turning angle and the speed at which you roll.
The robbery angle improves according to the technical characteristics which do not only concern the global direction system. For example, a vehicle fitted with four -wheel drive perfects its turning angle compared to the classic version, with two motor wheels.
If the advertisements intended to boast the merits of a car do not tell you directly about the turning angle, it is however this asset that they wish to enhance by evoking the maneuverability of their vehicle and the ease with which You can make your maneuvers.
What is the mechanism that makes it possible to run a vehicle
When you drive, just turn the steering wheel on the side where you want to go to run your car. However, there are intermediaries between your steering wheel and your wheels.
The steering wheel is connected to a steering column that affects your request on an order arm which itself is connected to your wheels.
The power steering now equipping all standard vehicles has forgotten how much the wheels of a car requires power requires power. It is generally assisted hydraulically, which requires adding to the robbery a block with central piston which assists the steering organs, thanks to a distributor, an oil tank and a pump.
Motor wheels and turning angle
The drive wheels are the wheels of your vehicle which receive the power of the engine to allow it to move. Most passenger vehicles are equipped with two -wheel drive at the front, like the engine. This is the reason why we are talking about a traction vehicle before.
There are a few cases of propulsion vehicles of which only the two rear wheels are motor. This kind of transmission is more complex and generally meets on German cars.
Finally, vehicles equipped with four -wheel drive – full -tulled traction – are the 4×4 and sometimes SUVs. The fact of being equipped with four -wheel drive improves handling and, for the subject that interests us, the trajectory and the maneuvers, because the turning angle is reduced.
Directors and turning angles
Touring cars are increasingly widespread, even if they are not yet the standard. This device makes it possible to make the rear wheels mobile, in addition to the only front wheels, as was the case until there is little.
The turning radius is considerably reduced on four -wheel steering vehicles. The advantage is obvious for all maneuvers, but the device also provides more stability to a vehicle on the road. Beyond 50 to 80 km/hour, the rear wheels adopt the same position as the front wheels and secure the handling.
Why the turning angle is one of the fundamentals of driving
Driving school monitors very often approach the subject of the turning angle. They must make their students understand the importance of adjusting it, depending on the turn of the turn and speed, in order to follow the ideal trajectory and do not risk the underside or the surveillance.
When you are already engaged in your curve, it is no longer time to brake, which is why you have to measure speed and turning angle upstream. Good management of the turning angle also has the benefit of saving the gum of your tires which will last longer, thanks to less wear and tear.
On the other hand, control of the turning angle is even more important when you make a maneuver with a trailer harnessed to your car, especially in reverse. Depending on the template of the trailer you want to tow, you can settle for your B license or have to pass a specific permit that corresponds to the letter E. If necessary, you will have the opportunity to study the turning angle in its smallest detail !

The turning angle in technical control
Several elements of the management of the vehicle switched to fine during the compulsory technical control: angle and front shift, steering steering wheel, steering anti -theft, steering column and couplings, rack, steering case, connecting rod, steering wheel. ball joint, steering articulation, management relay and management assistance system.
If your vehicle does not meet the established standards, you will have the obligation to make repairs. It can even be immobilized, as long as you have not corrected the faults. The turning angle of your vehicle is inevitably impacted by management problems.
It is also important to take care of speeds without taking risks and without diverting your attention from a potential obstacle. Thus, prefer to change speed on a straight line.
All steps to pass the speeds
So concretely, how do you go on speeds ?
Let us decompose together each of the actions that will have to be started to move up a gear:
- Raise the right foot of the accelerator pedal,
- Press the clutch pedal as much as possible with your left foot,
- By keeping the clutch pedal pressed, pass the speed with your right hand,
- Lift your foot from the clutch pedal in two stages,
- Take your position on the accelerator pedal.
All steps to demote
The action of downgrades consists in passing the lower ratio on the gearbox.
So let’s see the steps necessary to demot and slow down the speed of the vehicle:
- Raise your right foot of the accelerator,
- Gently press the brake with your right foot to slow down the pace of it,
- With your left foot, drip the clutch pedal until the end,
- By keeping the clutch pedal pressed, pass the lower ratio on the gearbox,
- Remove your left foot from the clutch pedal with flexibility,
- Take your position quietly on the accelerator pedal.
Know the gearbox
For fluid driving and in order to keep all your attention on the road, it is important to know the position of each speed on the case.
So you will intuitively know which movement to pass from one relationship to another without having to look away from the road.
Whatever the vehicle equipped with a manual gearbox, the speeds are in the same location. It will therefore be easy to retain them once and for all.
Thanks to this, the gear passage movement will very quickly become an automation.
Only the location of the reverse varies from one car model to another.
Adjust your position
The first action to be taken, before even thinking about holding the steering wheel, is to properly settle in the driving station.
It is then necessary to adjust the position of the seat as well as the height of the steering wheel to be in an optimal posture for driving.
It is only once this position will be found that we can take the steering wheel of the vehicle in his hands in good conditions.
Place your hands well on the steering wheel
Sitting in front of the steering wheel, it is now time to position his hands on it in order to ensure stability and comfort.
By imagining a clock dial, your hands must be positioned at “9:15 am” or at “10:10 am”.
In these positions, you ensure a precise and controlled trajectory. You can then fluidity the curves and turns.
You will then take care to always keep your two hands on the steering wheel.
Keep your steering wheel in a straight line
In a straight line, your hands will keep the position “9:15 am” or “10:10 am”. It is strongly advised to keep your two hands on the steering wheel even in long straight lines in order to be able to react quickly in case of difficulty or obstacle. You will then be well placed to react quickly.
Hold its steering wheel in a light curve
During a slight curve, no need to move your hands from their position. Indeed, you can simply keep them in the parallel position and accompany the road curve movement while avoiding jolts.
No need to make great movements and move your hands beyond the extent.
Hold a wheel in a turn
When you approach a turn, your hands must move on the steering wheel to follow the trajectory.
Here you will use the so-called “shooting” technique.
- Place your hand on the side where you are about to turn at the top of the steering wheel (position 12 noon),
- Open the other hand,
- Pull the steering wheel to follow the turn trajectory,
- Once the turn is finished, the hand previously open comes back to land at 10 a.m. and pulls to put the steering wheel in its initial position.
Hold its wheel in a turning point
During a turning point, you will also have to move your hands on the steering wheel to allow it to make a greater rotation.
You will then use the overlapping technique that breaks down as follows:
- Place your hand on the side where you are about to turn at the top of the steering wheel (position 12 noon),
- Pull the wheel of a U-turn in the desired direction,
- The other hand then takes over to accompany the steering wheel in the right direction
- Then the first hand returns to continue the movement ..
- Continue these maneuvers until reaching the desired trajectory.
At good speed, the steering wheel will resume its initial position itself after your turning point. Then let it slide in your hands. If however you drive at a slow pace, repeat the operations in the opposite direction.
The importance of the gaze
Remember that the gaze holds a very important place in maintaining a good trajectory.
Indeed, we spontaneously move the vehicle in the direction where the gaze looks.
So put this one in the direction you want to turn to allow your hands to engage a natural and fluid movement.
By making your gaze far and in the right direction, you will also have the possibility of detecting information, obstacles and thus anticipating your actions if necessary.
What is a roundabout sense ?
The gyratory crossroads, more commonly known as “roundabout”, is a circular infrastructure which allows users to take several directions, but also to turn around.
In France, it approachs by following the direction of circulation, that is to say by bypassing it by the right, in the antihorarous sense.
It is often wrongly confused with the roundabout. So what differentiates them ?
- The roundabout is subject to the rule of priority on the right. It does not have any ground marking and any traffic sign.
- The roundabout has signaling panels indicating that it responds to the “yield” rule “
How to approach a roundabout ?
Even if there are very specific rules ensuring the safety of drivers, the roundabouts are very often ill -addressed, without compliance with the positions defined by the highway code or the warnings by the indicators.
Let us therefore recall the rules to follow to borrow in the right way any crossroads in roundabout.
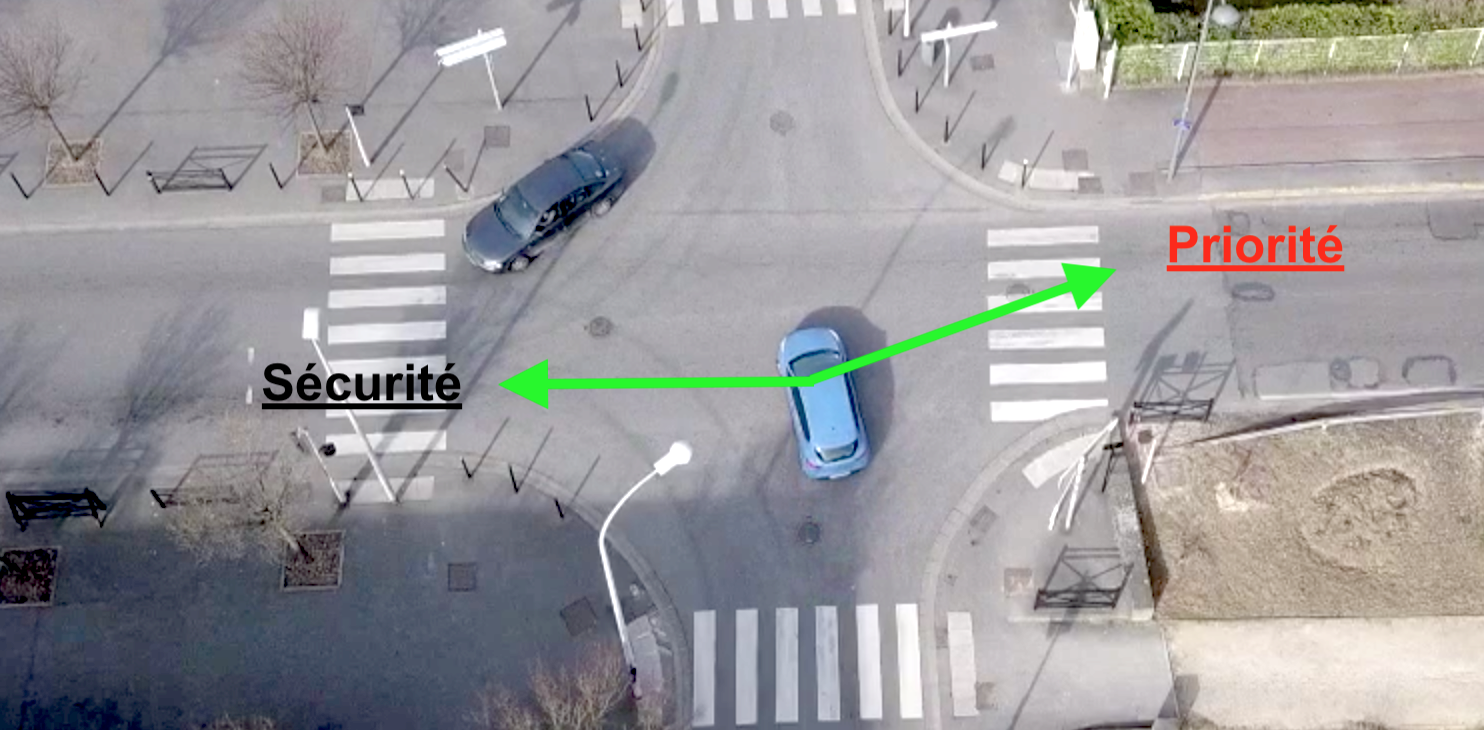
As we have seen, this type of crossroads responds to the rule of the “yield the passage” as well, you must give priority to vehicles already engaged on the roundabout.
If you know which direction you are going to take, you will have to choose the adequate path.
- If you go right or straight: you will take the most outside path.
- If you go to the left or turn around: you will have to take the most inside track to resume the outer track just before getting out of the roundabout.
If however you do not really know which outing way you will choose before entering the roundabout, you will take the outer path to be ready to go out at the right time and not to hinder other users.
The use of indicators on a roundabout
During management changes, it is necessary to use the indicators to warn other users. The maneuvers implemented to cross a roundabout sense do not escape this rule even if many users seem not to respect it.
So let’s see how to use the indicators according to the directions that you need to borrow.
- If you have to go out at the first outing, that is to say the one just right, you need to activate your right indicator before even going in the roundabout,
- If you take another exit to the right or want to go straight, you will need to activate your indicator on the right as soon as you have exceeded the previous output.
- If the exit you want to take is on the left or want to turn around, you will activate your left indicator before even approaching the intersection. By entering the roundabout you will take the most interior path. When you get out of the roundabout, you will put your turn signal to the right to warn that you change your way and get out of the crossroads.
Visual checks to be carried out
This intersection requires being particularly attentive to other users who according to the direction they wish to take may have to be on your trajectory.
- If you take the outer way, you will check your right and left mirrors as well as your left left angle before taking the outing.
- If you take the inner path, you will need to control your right rear view mirror, your central mirror and your blind spot before committing to the exit.
You must take care in all circumstances not to hinder traffic and to be reactive to maintain the fluidity of it.
Punishments
The rules for crossing these crossroads are governed by the highway code and their non-compliance implies sanctions.
Thus, two types of offenses should be noted:
- Failure to comply with the use of the indicator can cause a flat-rate fine of € 135 as well as a withdrawal of 4 points on your driving license.
- The lack of priority, on the other hand, is sanctioned with a flat -rate fine of € 35 accompanied by a withdrawal of 3 points on the license.
Rules of conduct at intersections
To start, you should never cross a continuous line.
So, if you ride on a double -directed road with a white line in the middle, it will be interspersed with dotted lines where you can turn. If it remains continuous, it means that you are not allowed to turn. You must therefore continue, until the white line is interrupted.
If the intersection you take is not regulated by a system of tricolor fires or by a particular signaling (stop, give way or marking on the ground) you must then respect the rules of priority on the right on the right. Therefore, when you turn left, you must always give priority to other vehicles arriving by your right.
Before committing, you must make sure that the road is free and that you are not likely to be immobilized. This recommendation is important because it prevents you from blocking a crossroads, especially when traffic is not fluid.

The use of the turn signal
Before detailing the different situations you may face, remember that the use of the indicator is not optional, but rather an obligation that corresponds to article R412-10 of the Code of the Code.
The use of the indicator is too often forgotten although it is part of the fundamentals of driving and that it is crucial for everyone’s safety.
Blinking is your way to communicate with other road users.
Note that if you omit to put your turn signal, you expose yourself to a second class fine representing the loss of three points on your license and a flat -rate fine of € 35.
Putting your turn signal when you are about to turn left allows you to warn other road users, including pedestrians. So be sure not to put it at the last moment, but enough in advance before slowing down to start your turn and allow other users to anticipate your trip.
Turn left properly when you run on a one -way road
If you run on a one -way road, you can easily position yourself on the left side of the road and perform your visual checks before turning. Do not forget to think of activating your turn signal sufficiently upstream to warn other users.
Turn left properly when you run on a double -direction road
The double -direction road represents the most frequent configuration on the French road network. When you turn left, you necessarily cut the axis of the road, as well as the vehicle pathway that faces you. You must therefore take all possible precautions and control everything that happens around you.
First, see your mirrors then switch on your turn signal. Slow down your look to the turn.
Check if vehicles come on the opposite path.
If there is none, then you can turn.
If vehicles come opposite, set to the left without however exceeding the axis of the road and stop even if it involves stopping the vehicles that follow you.
Once the way is free, proceed to your maneuver.
Turn properly to the left when you run on a route with several lane, double -directed
If you travel on a road that has several tracks, to turn right on the left, you must position yourself on the most left -wing track available in your direction of traffic.
If the road has a ground marking made up of arrows, follow the indications of these.
To do this, switch on your turn signal to indicate your intention to change your way. Control your mirrors to make sure that no vehicle arrives behind you and get to the left to reach the right track.
Once well positioned, make sure that no vehicle is circulating on the opposite or reverse direction. If they are free, then you can turn. If one or more vehicles arrive on these tracks, stop and wait for the road to free up to turn left.
Turn left properly when you arrive at a Indonesian crossroads
The Indonesian crossroads is an intersection developed using a ground marking indicating a storage route to take to turn left.
On this type of crossroads, only one track is arranged for vehicles coming in both directions of traffic to turn left.
The difficulty of this type of crossroads is that you are facing the vehicles which also will turn left and which can thus plug your view. You must therefore make sure that he does not arrive behind them another vehicle which will continue straight, and which you risk cutting the road, while it is a priority.
When you have made sure that no vehicle arrives behind the one facing you, you can then engage and turn left.
Why do you have to know how to fall back on a path
When you change direction or double a vehicle, you must then fall back in order to find the positioning imposed by the Highway Code. This position is in the majority of cases on the right right of the roadway.
However, you must only consider the ways reserved for you, which excludes emergency stop bands, exit suspenders or acceleration routes.
Fall back on a safe path
The term “falling back on a track” means that you are going to perform an action which consists in modifying the direction taken by your vehicle at the end of an overtaking for example to join the most right way.
You must first take all the precautions to make sure you can make your downside maneuver. To this end, you must use your side mirrors and your central mirror. For more precautions, you must turn your head slightly on the right, to make sure you cover the dead angle.
Any displacement is subject to minimum safety distances and falling back on a track is no exception. To do this, you must take into account the displacement of other road users, as well as their speed.
Knowing how to fall back on a road on a double -sensitive road
On a double -direction road, you must fall back on the right track after having exceeded another vehicle. To make this maneuver, you will need to be observed. So when you see this vehicle in your interior rear view mirror, turn on your right indicator, just before you start falling back. Be careful not to slow down, otherwise the safety distance will be reduced between you and the vehicle you have just exceeded.
Once you have repositioned yourself in the right track, check in your interior rear view mirror where the vehicle you have just exceeded to make sure everything is in order.
Knowing how to fall back on a track on the highway and the fast tracks
Knowing how to fall back on a track on a highway or on the fast tracks follows the same protocol as on a normal road.
You must always respect the fundamentals of driving and drive as much on the right possible. All drivers who regularly take France’s highways can see that the most frequent highway offense is committed by people who remain on the midst of three -way highways, or on the left path on A two -lane highway. This bothers the vehicles that arrive from behind and sometimes gives rise to overruns by the right, also in violation of the law, and above all very dangerous.
Regarding the obligation to drive to the right, you should however note an exception when a track is reserved for slow vehicles in the event of a significant elevation. This slow route is signalized by a panel indicating the low speed of the speed and by marking on the ground. It is forbidden to you, unless you have a lack of power yourself and forces you to drive below the speed indicated for this track, most often 60 km/hour.

Knowing how to fall back on three -way roads with simultaneous overtaking
On the three -way roads with simultaneous exceeding, the central track is used to overcome users rolling in both directions. This type of track tends to disappear, but it still sometimes finds this configuration.
You must show the greatest caution and make sure that you have the time required to double. As you dislocate, you must ensure that a vehicle from opposite, did not simultaneously have the same idea as you, in which case you must fall back without exceeding if it has been a slightly preceded.
After your overtaking, you must fall back as quickly as possible to leave the central track available.
Knowing how to fall back on roads 2 + 1
For security considerations, the three routes with simultaneous surpassing are gradually replaced by double -way three -way roads, with widening and narrowing of the tracks. These roads are more commonly called 2 + 1.
The midfielder is always reserved for surpassing, but its access is alternated between both senses. You are notified by panels, as well as by marking on the ground when this route is reserved for you.
The change of slot of the niche is indicated by downside arrows which appear on the marking on the ground, as well as by panels on a blue background which store your obligation to fall back. After the last rolling arrow, a zébra tells you that you must fold up, after making sure that there is no vehicle on the right lane.
The other cases in which you must fall back
All the other cases in which you must fall back to you are reported to you by ground markings. Arrows, as well as panels, tell you which way take, depending on the direction you are about to take. You find this type of signaling in agglomeration, but also on the roads of the national and departmental network.
Why do you have to know how to pin and go back and forth
Braquer means turning your steering wheel in one direction until the maximum position and counterbalance simply describes the fact of turning it in the opposite direction generally to return to the initial position.
When examining the driving license, you must master different maneuvers:
- The reverse in a straight line,
- Curved online reverse,
- The U-turn,
- The precision stop,
- Niche storage,
- Battle storage,
- EPO storage.
You find that five of the seven maneuvers involve knowing how to rob and counterbric. They are among the fundamentals of driving and are eliminations in the event of a defect.

Spanning and countering: hand positioning
The position of the hands on the steering wheel is fundamental to keep control of your vehicle and control your trajectory. These positions are generally symbolized by the orientation that the needles of a watch would have.
In a straight line, the balanced position corresponds to 9:15 am or 10:10 a.m. This location on the steering wheel ensures you a great amplitude of motion and perfect precision, while retaining an ideal balance between the two hands.
When you approach a light curve, if the amplitude of the action remains less than a quarter of the steering wheel, you did not need to move your hands.
During a more pronounced turn or a maneuver to park, you will have to move your hands on the steering wheel.
Take the example of a right turn. As soon as you exceed the quarter of the steering wheel, you release your right hand to go and grab the highest point of the steering wheel and run it an additional quarter turn. Meanwhile, your left hand has opened to let the steering wheel spin between your fingers, while staying on its initial position.
You of course adjust the maneuver depending on the corner of the turn and repeat the displacement of the hands, until you get the necessary turning department. Your hands must tighten on the steering wheel when they find themselves in a balanced position.
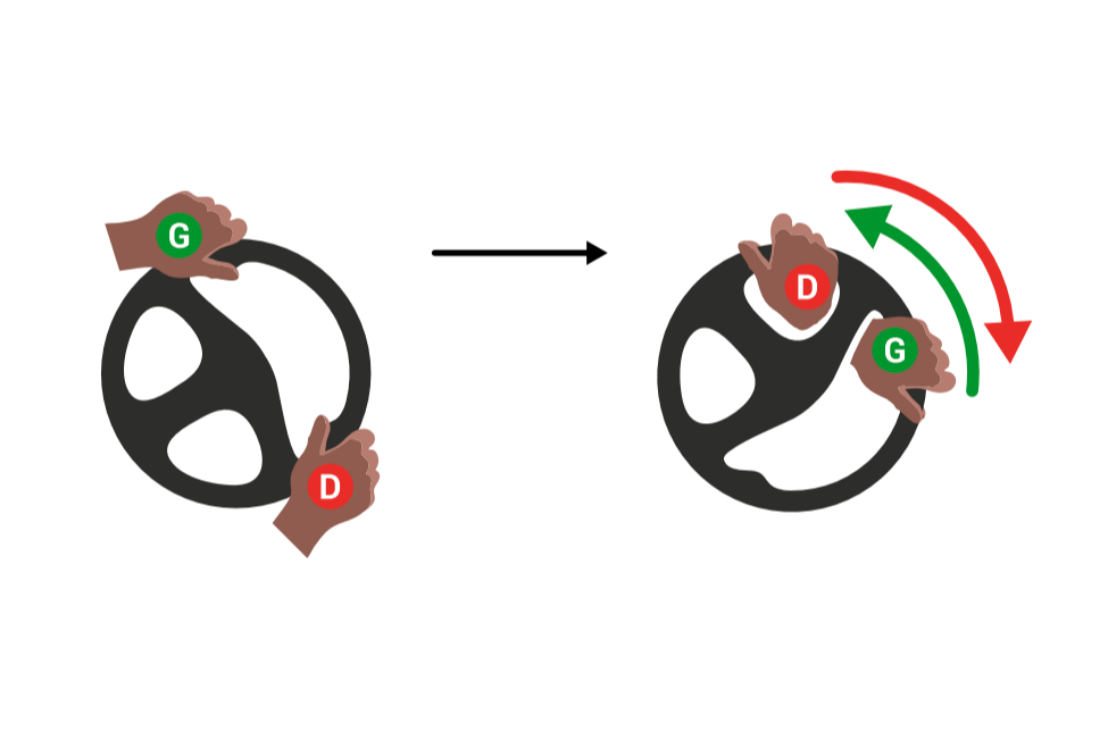
To come back in a straight line, you follow the same method in the opposite direction. It is your left hand that turns the steering wheel by catching it by its highest point, while the right hand relaxes to let it go between your fingers.
Be careful, you should never enter the steering wheel from the inside, nor hold your steering wheel when crossed hands.
Pin and counterattack to make a niche
The niche is a maneuver which consists in park between two vehicles, or between two fixed elements, close enough to prevent you from making your maneuver before.
The niche is one of the most dreaded maneuvers by driving license candidates. It requires a little training and above all to respect the steps that involve pointing and contrainding it.
Remember that when you make a maneuver, you are never a priority. This means that if a vehicle arrives by the front or from the rear, you must interrupt to let it pass. To give you every chance of succeeding in your niche, proceed slowly and above all by maintaining the regularity in the look, at the same time as you turn the steering wheel.
Take the example of a niche on the right:
- Start by backing up to see the rear light of the vehicle behind which you want to park (in half of the large back window.
- Stick to the right to the right and go back.
- When the rear light of the vehicle behind which you want to park is visible in half of the front window, missing the wheels at the bottom left and continuing to go back.
- When the front is perfectly aligned with the front car, straighten the wheels (1 lap and 1⁄2 on the right), deadline, handbrake
Braque and counterbricate on snow and ice
When the roadway you borrow is covered with snow, ice, excessive rain or is made particularly slippery due to gravel or a fatty substance, knowing to rob and counterbalance allows you to limit and thwart all the effects of vehicle shift. Thanks to these maneuvers, you can escape the head or the exit from the road.
If you feel your car escape and slide, you must act extremely quickly. Your first reflex must be to let go of the pedals. Any braking, acceleration or clutch action can only worsen your situation. Defereting will stop the engine transmission from the engine to the wheels, which will allow the vehicle to slow naturally. Conversely, braking will amplify the slippage.
If it is your front wheels that slip, you are in a situation of understeer. Let go of the pedals and, as soon as you feel that your wheels have resumed ground grip, straighten your steering wheel.
If it is the rear wheels that slip, you are in surveillance. In this case, you must miss it, which may seem to you against intuitive, but it is the only solution to prevent the head. For example, if your wheels go to the left, you have to rob all on the left. As soon as your tires hang up, straighten the steering wheel.
What is the angle of drift
The angle of drift of a vehicle influences the lateral force which applies to the wheels. It makes it possible to fight against the centrifugal force in the corners and to avoid the slippages and outings of the road. Indeed, when you turn your steering wheel to pass a curve, the vehicle must generate an equivalent force, but contrary, to the centrifugal force. When this is not the case, the vehicle simply comes out of its trajectory.
The mechanism that brings into play the drift angle is called drift and defines the variation between the direction of the wheel and the trajectory that the vehicle will follow.
The quality of the tires strengthens this ability to stay on the trajectory, thanks to the gum which deforms to stay in contact as widely as possible with the soil and which also generates a lateral effort.
What is the relationship between the drift angle and the tires
From a strictly theoretical point of view, the lower the angle of drift, the greater the stability of the vehicle. We would therefore tend to promote low drift angles, but it is necessary to count with mechanical constraints, in particular the influence of tires.
Indeed, if your drift angle was zero, you should use tires whose transverse part would be strictly rigid, which is impossible.
Such tires would considerably reduce adhesion and driving would be impossible because of unbearable brutality for vehicle passengers. In summary, it would not only be uncomfortable, but also very dangerous.
We must therefore find the best compromise between the drift angle and the characteristics of the tires.

How the drift angle applies in practice
Take the most common example, with a two -wheeled carrier car before.
When you arrive in a curve, you turn your steering wheel in the direction in which you want to go. The steering wheel controls the steering column which, itself, prints the angle on the control arm connected to your two front wheels. At that time, the tires run and drift. The lateral force generated at the axle then rotates your car gradually.
By the laws of physics, the phenomenon spreads to the back of the vehicle, until inducing the drift of the rear axle. The car then follows a continuous trajectory which revolves around its center of gravity, without risking ending in a tail.
If you are using a four-wheeled car, beyond 50 km/hour, the rear wheels run in the same direction as the front wheels. This peculiarity prevents the trend that the car to derive from the rear might have. Therefore, you benefit from a more direct direction, you need less turning the steering wheel and the stability of your car is improved.
The other advantage of four -wheeled vehicles is to react better in emergency situations. If you avoid an obstacle by brutally stirring your steering wheel, mass transfers are attenuated and you risk less uncontrolled slippage.
Tire pressure and drift angle
Tire pressure is the first criterion you can play on. It is in any case crucial for your safety and you must always ensure that it complies with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The ideal tire pressure appears on the label stuck in the opening of the driver’s side door and is sometimes mentioned inside the fuel hatch. It can be differentiated between the front tires and the rear tires.
If you have traveled more than 10 kilometers before checking the pressure of your tires, you must increase the recommended pressure by 0.3 bar.
Do not forget to check your spare wheel from time to time so as not to be caught up in the day you need it.
If your tires are under-inflated, the behavior of your car is changed and your risk of drift increases. You therefore explode more at the risk of slippage. On the other hand, your fuel consumption also increases.
Do not take the risk of overfalling your tires either, because you lose comfort and especially in grip, especially on a wet road. You must therefore strictly hold on to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Also note that the drift is greater with classic structures than with radials.
How to optimize your drift angle
The drift angle of your vehicle is determined by the manufacturer. However, some tips allow you to optimize it. These are external factors on which you can intervene and which will impact the variation in the degree of the drift angle.
Too heavy vehicle load impacts the angle of drift and increases the risk of slippage. If you need to transport a large cargo, try at least to balance it between the front and back of the vehicle, as well as on each side.
Adjust your speed in turns, because, if your drift angle no longer has the capacity to fight against the push exerted by the centrifugal force, it is the insured road exit. In addition, an overly intense thrust automatically reduces adhesion.
Finally, the larger your rims, the more they increase the contact surface, therefore transverse rigidity, which reduces your drift.
What is overlapping ?
The overlap of a line means that you deport your vehicle laterally until your wheels encroach on the line.
What is crossing ?
We consider that there is crossing the line when your wheels exceed the line.
Know how to apply the difference between overlap and crossing according to horizontal signaling
The lines drawn on the ground are considered as horizontal signaling (in opposition to the vertical signaling of the panels). You must learn to recognize them to know if you have the right to overlap them and/or cross them.
There are four horizontal signaling colors:
- THE white for permanent markings;
- THE YELLOW For temporary markings, prohibitions to park and reserved locations (bus, delivery, taxis, etc.);
- THE blue For places reserved for the disabled, and parking spaces in the blue zone which are governed by the disc placed on the dashboard;
- THE Green For cycle bands.
You must then understand the meaning of the different lines, in order to know whether or not you have the right to overlap them and/or cross them.
- The White Line continues that it is forbidden to ride and therefore to cross.
Note all the same that you are allowed to ride a continuous white line on the double -direction roads limited at 50 kilometers/hour, in order to double a bike. This maneuver is only tolerated if you have enough visibility.
There is a tolerance threshold to overlap, even crossing, of the white line that many police officers and gendarmes admit. This applies in three cases which are not, however, registered in the law.
- An irremovable or long motionless obstacle: falling from rock, stopping bus, delivery truck, etc.
- A work of work in progress.
- Overcoming horsemen or animals. For the latter case, do not hesitate to cross the line, as many animals fear vehicles and can have untimely reactions.
- The discontinuous line can be ride or crossed to exceed or change track. However, you should only do it briefly, before falling back in your way so as not to risk colliding with a vehicle from opposite, or to hinder those who follow you.
- The deterrent line is implemented in dangerous areas and can only be ride or crossed to exceed slow vehicles, such as tractors, or low template, such as bikes.
- The mixed midline is continuous on one side and discontinuous on the other. You can only cross it when it is discontinuous on your side.
- The shore line delimits the road on the side of its shoulder. It does not exist on narrow roads, for example on departmental roads. You should not cross it, except in the event of a breakdown to extract you from traffic.
If the left bank line is continuous, this tells you that the road you take is one -way.
- The emergency stop band, Although it has the width of a traffic lane is not one, even in the event of a traffic jam. You are authorized to cross it to park in the event of a breakdown or discomfort of an occupant.
- The route reserved for slow vehicles is the right track, delimited by a very wide discontinuous line. You must cross it on the right if you run below 60 kilometers/hour, but you are also allowed to cross it on the left to exceed a vehicle that would drive even slower than you.
-
- You are forbidden to ride or cross the line that separates your path from the route reserved for buses or bikes, Unless it is not directly against the shoulder and you have to cross it to turn or access a parking space.
What are the sanctions in the event of illegal overlapping or crossing
There is no difference between crossing and overlapping with regard to the sanction when it is a continuous line. In one case as in the other, you are liable for a fourth class fine. The flat -rate price is € 135, reduced by € 90, increased by € 375 and maximum of € 750. Add the withdrawal of a driver’s license to this.
What are the panels that signalize dangerous climbs and descents ?
The panels signaling the dangerous climbs and descents, like all the panels announcing a danger, are triangular in shape, the tip directed upwards and their framing is red.
To announce the dangerous descents, it is the A16 panel which schematically represents a car descending along a sloping road. On the black diagram is inlaid in white the figure which announces the percentage of the tilt of the road.
The dangerous descent panel must be placed before roads whose slope has a drop greater than 10 % and 4 % on highways.For dangerous climbs, it is the same triangle, but the scheme represents only the road which rises, without the symbol of the car. The figure of the percentage of the tilt of the road is always registered in white smashes in the black diagram.
The panels must be installed at a distance of 150 meters in the open countryside and 50 meters in agglomeration, before the start of the drop.
How to approach dangerous descents
The notion of dangerous descent means that there is a significant elevation. You must control the speed of your vehicle and, for this, revise your driving style. You must take into account the fact that inertia created by physical laws extends your braking distance.
When you approach a dangerous descent, you will use your engine brake, a technique being part of the driving fundamentals and the driving school instructor will teach you, once you master the first bases of driving.
The engine brake is a mechanical phenomenon automatically caused by the engine itself. It allows it to automatically regulate its speed by demoting. This prevents you from using the brake pedal too much and therefore the braking mechanism which would quickly reach overheating, before no longer operating. You understand there, the concept of danger.
Using your engine brake is all the more important if you tow a trailer. This pushes you and naturally increases your speed, while your braking distance is still lengthening.In a dangerous descent, you should in no case be pressed on the clutch pedal or go to a standstill. This action unlins of your gearbox, while your engine must be taken, with a speed triggered, so that the engine brake process works.
If you must still brake, you must proceed by successive thrusts on the brake pedal and not brake continuously so as not to overheat.
How to approach dangerous climbs
Dangerous climbs can also cause problems. In the event of a very important elevation and/or if the climb is very long, you must have a vehicle powerful enough to reach the top, without heating your engine too much. When you lose too much speed, you are forced to demote to find power and then accelerate.
If the configuration lends itself to it, you can speed up a little before approaching the climb, in order to give you a little momentum. This must of course be done while respecting speed limitations, which restricts your action. You must then accompany your vehicle by demoting so as not to find yourself in sub -regime, or by on diet. Both are bad for your engine and affects your fuel consumption.
The routes reserved for slow vehicles in dangerous climbs
On some dangerous climbs, you have access to a line on the right for slow vehicles. It is separated by a fairly wide discontinuous white line with fairly close dotted. It is also announced by a blue round panel, with white text.
You must take this route reserved for slow vehicles if you drive below 60 kilometers/hour. However, if you find yourself behind a vehicle that runs slower than you, you are entitled to double it, after of course verified that no one arrives behind you and after putting your turn sign.
Distress routes in dangerous descents
There are specific paths called “distress roads” which are used for emergency situations, especially when defaulting brakes, when you take dangerous descents.
The distress route – also called emergency stop bed – is signalized by a panel, on a blue background. He schematizes the normal road in white and the bifurcation towards the distress lane by a red and white checkerboard. This bifurcation makes it possible to take a path further right of the road, in order to be able to stop if you encounter a problem of engine or brakes.
The distress route consists of gravel at the entrance. They are reinforced by natural means, such as the slightly climbing road allowing to slow down thanks to inertia, or by artificial means with bits. The means to stop the vehicle can sometimes undergo damage to it, but they are always minimal compared to the danger incurred by a vehicle which can no longer stop its race and which risks in addition to causing a collision.
The distress route is reserved for all vehicles in difficulty. This layout is more frequently used by large vehicles, heavy goods vehicles and bus, but cars can also need it. It should be noted that the considerable progress made by car manufacturers have drastically reduced accidents due to the failure of braking systems.
The importance of vehicle adhesion on the road
The friction between two surfaces defines the concept of adhesion. In this case, for the subject that interests us, it is the contact between the tires and the road.
It is not constant and depends on the pressure of the tires, the room temperature, the covering of each surface and the climatic conditions in the event of snow, rain or ice.The rubber is a polymer while the structure of the asphalt is crystalline.
When the tire comes into contact with the road, it deforms. Some connections are formed, while others break, which makes it possible to absorb the energy of accession.
During driving, the surface of the tires which is in contact with the road supports the acceleration, braking forces, as well as the centrifugal forces in the turns. Tire structures influence its deformation, as well as its ability to evacuate water.The impact of tire coverings on driving
To date, there is a universal tire that would be efficient everywhere and all the time. Your car tires must adhere to the roadway, but it also depends on the roads you take.
Conditions are not the same depending on the temperature and climatic conditions such as humidity, snow and ice. You will not choose the same tires if you live in Brittany, in the south of France, or in the Alps.
In addition to coating of the tire, you must take care of its wear, because, once the structures have been used, it loses its adhesion and its ability to evacuate water. Finally, the pressure is also crucial for your safety.
If there are no ideal tires, manufacturers have developed different types tires.
The different tires
You can roll with the same tires throughout the year or change them depending on the season. This alternative is more expensive. It also requires labor and a storage place for tires that you do not use. If you live in a temperate region, it is not particularly recommended.
The “summer” tires gum has the ability not to soften too much when the temperature is high. You can drive normally, without using them excessively. Standard tires, known as “four seasons”, represent an excellent compromise if you live in a temperate region.
If on the other hand you use them when it is very hot, they will wear out much faster than summer tires, in addition to making you consume more fuel, because of their gum.Winter tires use gums that are resistant to very low temperatures and are recommended, as soon as the mercury falls below 7 ° C. The gums of conventional tires become under these conditions too hard to ensure good adhesion.
Snow tires have deeper structures whose large grooves make it possible to evacuate rain and snow. Their fine side structures compress and thus heat the snow that melts and is easily evacuated.If you choose winter tires, you will have to equip your four wheels. You can roll all year round with your snow tires and enjoy their grip in the rain. However, in hot weather, their high grip will significantly increase your fuel consumption.

The impact of driving road coverings
Road coating is the other factor that determines the grip of your vehicle.
Road coverings are varied and do not offer the same qualities, which considerably influences your driving. During your lessons, your instructor will make you experience these different coatings, because the way of approaching them is one of the fundamentals of driving.- The coating you will meet most is asphalt, otherwise called bituminous concrete. It is made up of sand, gravel and Brai, an oil derivative.
- The bbe (waterproof bituminous concrete) that is most often found on the roads of France presents very few interstices where rain could nestle, which considerably reduces the risk of aquaplaning.
- The hollows of the BBDR (draining bituminous concrete) are interconnected to also avoid this phenomenon of aquaplaning.
- The compromise between the BBE and the BBDR is the SMA (Stone Mastic Asfalt).
- Cement concrete is also one of the coatings that you will often meet. It contains more sand than bituminous concrete, hence its smoother aspect. It is placed by plates connected by dilation joints, or goes through an reinforcement to avoid these joints.

The drawback of cement concrete in rainy weather lies in the fact that water is not evacuated and the tire loses its adhesion more easily, which harms your safety. It is also noisier, therefore less pleasant for drivers and their passengers.
- Finally, the cobblestones can be in natural stone – often in granite – or be made of concrete or terracotta. Their forms are varied, but always designed to overlap in each other, in order to strengthen the stability of the coating. The pavers are reserved for agglomerations and their grip is of very poor quality.
Industrialists are working on the development of new coatings that could improve vehicle adhesion, deteriorate less quickly, but also do without any derivative of oil. Experiments are regularly carried out, without the miracle solution having yet been found.
Why is it so important to rest regularly for a long journey
The need to take breaks primarily concerns your safety, as well as that of your passengers and other road users.
Your well-being comes immediately after.
Even if you are comfortably seated, long car trips are tiring, whatever the nature of the roads you take.On the small roads, you are constantly on the alert because of the turns and elevations which force you to change direction and to adapt your speed. You must also take into account other vehicles that drive in the same direction as you, as well as those you meet. This standby state is exhausting, both physically and nervously.
On the highway, fatigue is not the same, but it is however very real. You are less subject to changes in pace and steering and, moreover, since the multiplication of speed regulators, you run a little in automatic pilot, especially if the circulation is perfectly fluid. Your fatigue is more due to weariness generated by monotony. You are totally static, your gaze moves little and lethargy wins you insidiously.
In any case, your attention decreases and your reflexes weaken, which makes you less effective to react to any obstacle or danger that could arise on your way. The most dangerous is obviously drunkenness which can have fatal consequences. A single second of sleep can lead you to make an involuntary steering wheel gesture that takes you out of the road or find yourself in the way of vehicles coming opposite. This moment of inattention can on the contrary prevent you from reacting and braking or changing direction to avoid another vehicle in front of you or leaving you to miss a turn.
You understand why it is so important to rest regularly for a long trip. The general instruction is to stop at least every two hours, and even more often in the event of night driving. At night, the daytime creature that you are difficult to see and has to concentrate even more, which leads to faster fatigue.
The only configuration that can exempt you from these breaks is to alternate driving with one or more other drivers. In this case, you can stop the time to change your place.
Learn to spot signs of fatigue
Of course, the two -hour rule between each pose is only theoretical. You must learn to recognize the signs that require you to stop to rest regularly during a long trip.
When you start yawning and your eyelids become heavy, the alarm signal is obvious. However, you have probably felt a few previous symptoms that should have alerted you.
Any difficulty in concentrating, pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulders or the inability to find a comfortable position are signs of tiredness of fatigue.You should never wait before you stop, as these symptoms can only get worse. Putting the music to its maximum or opening your window as large, even if it is very cold, will not prevent you from falling asleep.
You are more exposed to the risk of drowsiness if you lack sleep or if you lead to a schedule to which you usually sleep, generally very late or very late.On the other hand, even if you are not customary in the nap, your metabolism tends to mark the step in the early afternoon and this schedule is conducive to driving.
There is no rule specified in the fundamentals of driving as to the duration of the break to be carried out, but the average stop time runs around the quarter of an hour.Should you organize your breaks to rest regularly for a long trip ?
The answer is yes and no !
Yes, you can plan your breaks before your departure. When you prepare your itinerary, cut your journey into several parts, taking into account predictable obstacles, such as plugs during rush hour when you arrive around a large agglomeration. Then plan a break. You can spot more sympathetic arrest areas than others, and even make a detour and take advantage of it to visit a local curiosity or feast on a restaurant that tempts you.
No, you are not required to organize all your breaks, because if you feel fatigue win you and you have not planned a break at that time, then you will still have to stop. This judgment will be added to the breaks already planned.
Try as much as possible not to set yourself an hour of arrival.There is another slogan that you can read on the motorway panels and which very much ensures that it is better to arrive late than not to arrive at all !
If you set a schedule, you are tempted to cut on your break times and commit some reckless. In addition, imposing a strict delay increases your stress and the fatigue that accompanies it.
If you have an appointment, you always have the possibility of sending a message to warn your delay, rather than taking the slightest risk.Sports driving
Adopting sporting driving is to drive in a little fluid way and to intervene by accelerating, braking and often changing speed. This does not mean breaking the highway code, you can of course drive in a sporty way, while respecting speed limitations, lights or priorities and all signage.
It is a fairly brutal style for which you often expect the last moment to brake, instead of gradually demo. On the contrary, you exaggerately press the accelerator to regain speed.
Sports driving is more suitable on a circuit than on the road ! She is quite unpleasant for passengers who are tossed. Indeed, they do not have the steering wheel which ensures the stability of the driver who crashes there.
It also appears aggressive to other road users, because sports drivers often tend to neglect the safety distances. Finally, it increases noise pollution.Sports driving is also disastrous for your wallet. It significantly increases your fuel consumption, with a supplement of up to 50 % compared to a normal driving style.
At the same time, it increases gas emissions harmful to the environment.
Tires and brakes are the first victims of sporting driving, rather aggressive, and their wear could cost you dearly.More generally, it is the whole mechanics of the car which is exaggeratedly requested and which will wear out prematurely.
Flexible driving
Among the different driving styles, flexible driving is that taught during driving lessons by the driving instructor.
As its name suggests, it does not have the brutality of sporting driving. Everything is more progressive, acceleration such as braking, as well as how to press the pedals and pass the speeds.For passengers, as for other road users, it is a much more respectful driving that invites better road sharing. You anticipate your speed changes and direction changes, and you respect the safety distances.
Flexible driving is beneficial to the mechanics of your car and your consumption. You do not rush the engine and all the rolling organs, which increases the lifespan of the parts. Your tires are also spared.Eco -driving
Eco driving is more and more taught during driving lessons.
Some companies even offer their employees often on the go – salespeople, maintenance technicians, truckers, deliverers, etc. – Driving courses that teach them eco driving.Eco driving is even more gentle than flexible driving. It spares mechanics and saves fuel. She also advises, as far as possible, certain comfort equipment, such as air conditioning which is a big energy consumer.
The consequence of course benefits the environment, with reduced gas emissions.
Eco driving is also called eco -citizen driving. This implies that it is more ecological, but also more respectful of other road users.Eco driving goes through a vehicle in good condition and regularly controlled. Elements such as the air filter which should not be dirty or the tires whose pressure must correspond to the recommendations of the manufacturer have an impact on your consumption and your rejection of gas in the atmosphere.
An engine that runs at low speed is less greedy in fuel. To optimize your driving, you need to drive at low speed, but with the highest box ratio. So you will pass the speeds faster, on average before 2,500 rpm for a petrol car and 2,000 rpm for a diesel vehicle.
Holding a stable speed is one of the fundamentals of eco driving. It is an essential factor for consuming less fuel. You must drive by anticipating your changes of direction and appearance as much as possible, as well as taking into account traffic conditions. If possible, you can avoid accelerating in the descents and leaving your car decelerate with a high ratio. By respecting safety distances, or even accentuating them, you can more easily anticipate the changes in pace and have less to brake.
The loading of your car is also important. You must properly distribute your luggage in your car and prefer the chest to the roof gallery which affects your aerodynamics and makes you consume more fuel.
What is surveillance
Surviving occurs when your rear tires reach the adhesion limit in a turn. This leads to the uncontrolled slippage of the rear of the vehicle which can lead to the head-on and therefore, at the exit from the road. It can occur because of different factors such as the state of the road, an inoportune acceleration or a bad maneuver.
Surface: what are the factors involved ?
Surfaceing results from a number of factors.
Some are linked to the characteristics of the car, and others to the way it is led.- The vehicle -related factors are:
– weight distribution,
– engine arrangement and its type of drive,
– Suspension adjustment,
– the type of tire, taking into account their pressure and their wear.The state of the road is of course not unrelated to the risk of surveillance. A slippery road due to rain, ice, too smooth coating or presence of gravel is obviously an aggravating factor.
You must regularly check the wear of your tires due to the essential impact on adhesion. Also observe how they wear out. If wear is asymmetrical, it is a problem. The causes are diverse: deficient parallelism, poorly adjusted bodywork, poorly distributed load, poor tire pressure, deformed rims, tired shock absorber, unbalanced braking system, etc. In this case, it is imperative that you make your vehicle check by a professional, because your safety is at stake.
What are the causes of surveillance ?
Surface occurs for various reasons:
- You approach your turn too quickly: accelerating once in the turn or, on the contrary, to release the accelerator pedal is another common cause.
- Braking in a turn is a common error of the beginner who has misused his speed before approaching the turn. If you brake as you turn your wheels, the rear axle is relieved and may go on a slide. The exterior front wheel is the most loaded following the movement of the mass of the vehicle and it becomes the pivot around which the vehicle rotates. This is valid, regardless of the transmission of your car, traction, propulsion or integral. The phenomenon increases according to the mass and the wheelbase of the car.
- When you drive a propulsion car, accelerate too much at the output of the turn makes you take the risk of skating the rear wheels, causing the rear sliding and causing the survey.
How to react in case of surveillance ?
Never forget that your gaze is one of the fundamentals of driving: you have to look where you want to go. Even if you are not aware of it the importance of the gaze is crucial, because it helps you adjust your gestures as you restore your trajectory. You must always focus on your destination.
To correct the loss of grip in the event of surveillance, you must react instantly. In all cases of surveillance, you will have. However, the amplitude of your counterporage depends on the motor wheels of your car.
Another point in common with all situations, when you manage to restore the grip of the rear wheels, your front wheels must be in the axis of the vehicle.
Your reaction must be adapted to your vehicle.- If you drive a traction, start by accelerating smoothly, to put the vehicle back in the axis. If you have slowed down too much and you have therefore gone too much weight on the front, you will redress the mass backwards by accelerating. You must counterbalance the wheels to straighten them, but it is not recommended to go beyond the median axis and to rob the wheels in the other direction. You should only counterbag only when the drift angle is really too large and your acceleration power is not enough to straighten your trajectory.
If your surveillance is due to too strong acceleration and you drive a propulsion or integral car, you must temper to find a normal rotation speed of your four wheels. At the same time, you adjust the trajectory with the steering wheel.
The different braking systems
There are three elements to brake to slow down the vehicle and stop it that it is important to know and distinguish:
- the handbrake that is used for vehicle parking as well as for hill starts;
- the brake pedal that allows you to slow down and stop the vehicle;
- the engine brake that only slows down the vehicle.
When you have to brake ?
The situations requiring to brake are numerous and varied and are not always linked to an imminent danger. The vehicle brake is used very often during a car trip and is one of the most demanded organs. You use it for example when you slow down, you stop at the lights, you give way to other users, you follow other vehicles in a traffic jam … and to many other occasions.
For an optimal and safe braking action, it is obviously advisable to anticipate your action by positioning your right foot above the brake pedal and starting to brake well upstream of the place of stopping or final slowdown when that is possible.How to brake ?
To start, the best time to start braking is when the vehicle wheels are stable. We will therefore avoid braking during a sudden maneuver on the steering wheel.
You will also have to be vigilant about the condition of the vehicle, that of the roadway, the traffic density as well as the weather of the day. All these factors play an important role in your way of braking and your driving lessons will allow you to understand both of these various situations. Because if the theory is important, only practice and experience allow you to best judge different situations.In order to warn the vehicles that follow you that you are about to brake, you can exert light pressure on the brake. This will result in lighting your “stop” fires at the back of the vehicle without however triggering the braking process which would require more frank pressure from the pedal. After warning them, you can start your braking by pressing the pedal more intense.
To do so, release the accelerator and press your brake fluidly and smoothly, without crushing the brake pedal to dose the necessary power.The best way to brake is being decreased, that is to say by performing more intense braking at the start than at the end of the action.
Thanks to this method:- You avoid being surprised by the lack of time to brake,
- You avoid misunderstanding on the part of the vehicles that follow you by increasing braking as you advance without they can make a difference when your stop lights are lit,
- You avoid a brutal stop that would be unpleasant.
It can be wise when buying a new vehicle or when you take one to test the brakes beforehand in a secure place. Each car is different and this will allow you to read the braking sensations on this vehicle that you are not used to using. You will be less surprised in the event of a different attitude from what you know when you have joined traffic.
Emergency braking
If the situation requires you to achieve emergency braking, two cases arise:
- Your car is equipped with the A.B.S. In this case, simply press the brake pedal as much as possible. The device will manage the dosage itself to avoid blocking the wheels.
- Your car does not have the A.B.S. You will have to find the “racing point” by activating the brake in a frank manner without however breaking it completely to avoid blocking the wheels.
In any case, you will have to think about making your visual checks to listen to other users and your environment.
Brakes in good condition
To ensure your safety, that of your passengers and other road users, it is important to regularly check the condition of your braking system.
To do this, you will have to get into the habit of regularly checking the brake fluid level and respecting the revisions imposed by the manufacturer. In case of doubt or anomaly, it is imperative to consult a professional for verification and if necessary repair, a change of brake pads or discs.Pass the speeds and downgrade
Pass the speeds and downgrade is one of the first lessons instilled in the driving school instructor. From his first driving lesson, the candidate will indeed learn to use his gear box at the same time as the clutch pedal. This first learning can be perceived as difficult for some, and the concentration is. But rest assured because Caller arrives at everyone, so we must not be discouraged, because persistence will pay !
Hold up
As soon as you learn to control the speed of your vehicle, well hold up is fundamental ! Thus, succeeding in driving in a straight line, or curve, perfectly managing the trajectory of your vehicle, ensures the safety of all on the roadway, avoiding the crossing of lines and the risks of collision. The two -handed socket, in position 10:10 am is the ideal position to ensure good support for your vehicle.
Adjust your look
Control the speed of your car is to know adjust your look Depending on the situations we face on the road. Thus, depending on the traffic conditions, but of course in compliance with the speed limitations of the highway code, the speed of the vehicle must be controlled by its driver. This allows you to always keep control of your car in the event of an unexpected on the road.
Cross a roundabout
The roads are dotted with intersections, and Cross a roundabout consists in respecting a set of very specific rules. By slowing down to his approach and adapting his conduct, the apprentice must learn to position himself properly on the road, and respect the priorities of access to the roundabout.
When and under what conditions brake ?
Learning to brake at adequate moments is just as important as knowing how to increase the appearance of your vehicle. Thus, the driving school instructor teaches his student When and under what conditions brake with practical exercises. Thus, as an example, braking makes it possible to slow down the look of your car, but also to respect a stop or a tricolor fire, even to give in to another vehicle.
Turn left
The Highway Code imposes traffic on the right on the French road network, and in most European countries. However, changing direction during your journey is recurrent, and involves knowing turn left . Indeed, by turning to the left, this generally involves crossing the path coming in the other direction. This therefore claims to position yourself well on the road to signify its intention with caution, and not to embarrass other users. But also to control on the left and right, for safety and/or priority according to the highway code.
Knowing how to fall back on a track
On the roads with several lane, like the highway, it is not always easy to Knowing how to fall back on a track at the right time. However, depending on the situations, to facilitate the passage of other users or even change direction, it is essential to learn to place yourself in the right place on the roadway. This involves controlling your mirrors and dead angles well, and estimating a distance and a speed.
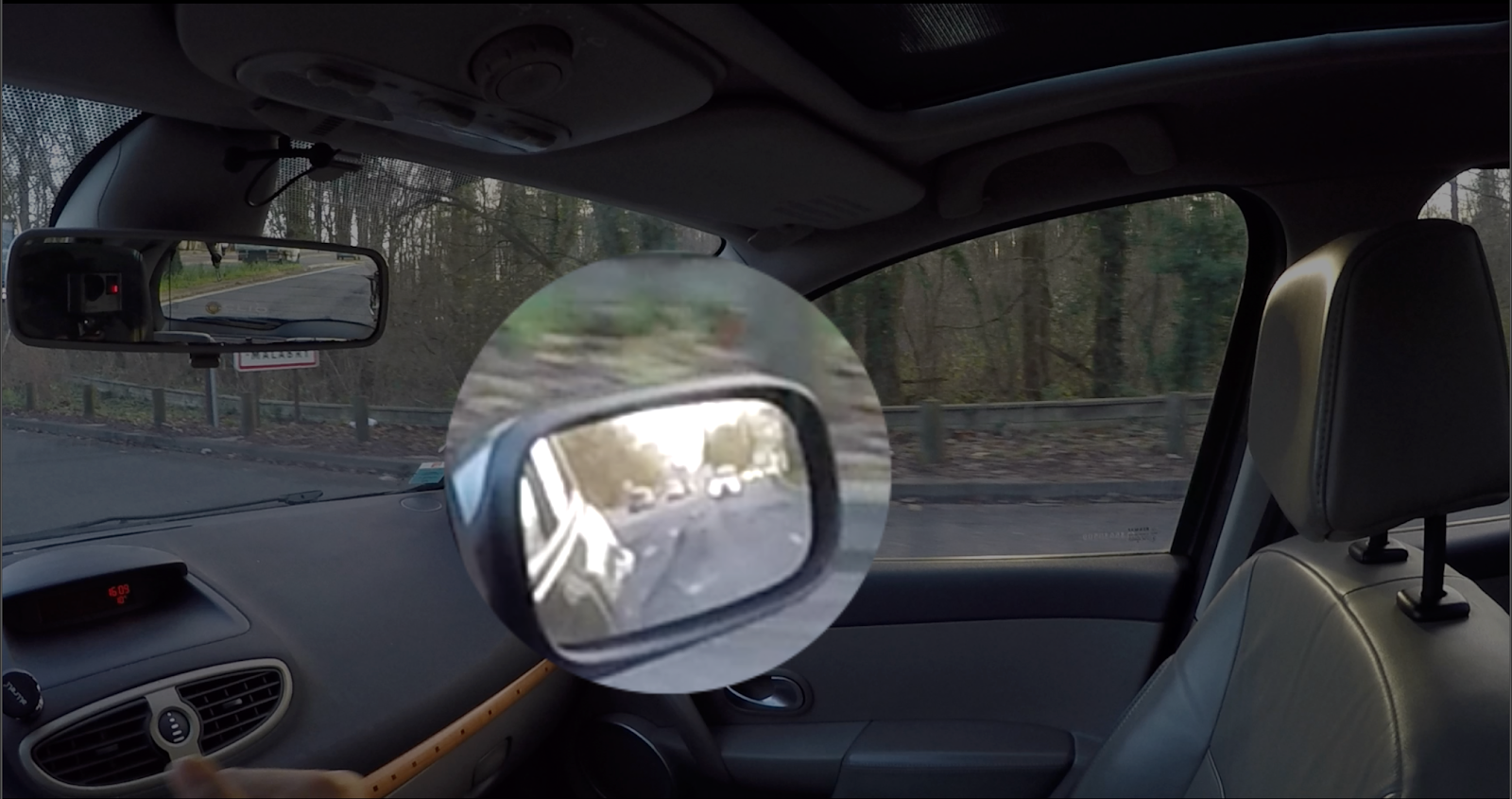

Pin and contravene
By changing direction, a driver must master the fundamentals of driving that are the maneuvers of pin and contravene . Thus, whether it is turning right or left, or even parking, an apprentice driver must learn to modify the direction of his vehicle by turning or counteracting his steering wheel until reaching his maximum tilt.

Turning angle
During the robbery and counter-handling movement, at the time of a niche, the apprentice driver learns to master the turning angle . Indeed, pointing your vehicle meets the requirement of a precise angle, which makes it possible to fully govern its trajectory, by adjusting its speed at the same time.
Drift angle
Less known, the drift angle However, go hand in hand with the turning angle. It is in fact a reactive lateral force at the time of robbery, and which will fight against centrifugal force. Concretely it is an opposite force that keeps the vehicle in its trajectory, and is located at the wheels. In short, the drift angle defines the difference observed between the direction taken by the wheels, and the trajectory of the vehicle ultimately noticed.
Difference between overlapping and crossing
During his trajectory, a young driver must make the difference between overlap and crossing , which represent offenses in the case of a continuous white line. These two actions do not imply the same sanctions with regard to the Highway Code. Indeed, there is a crossing when the vehicle is fully deported to the left, and this strictly prohibited behavior represents an offense of 4th class and the withdrawal of 3 points from the permit. The overlap is when part of the vehicle only is deported, and the driver then faces a fine of 4th class with a withdrawal of 1 point only on his license. Of course any of these two actions on the day of the exam, you will adjourn immediately, then prudence.
Dangerous climbs and descents
THE Dangerous climbs and descents involve particularly cautious driving. Indeed, uphill, you have to know how to master your acceleration pedal perfectly, while downhill, it is the brake pedal that will manage the look of your car according to the elevation. It is essential to adapt your behavior to traffic conditions, and to always remain vigilant to vehicles behind and before you.

Impact of tire and road coverings on driving
The motor skills force of a vehicle is dependent on its good grip at the roadway. So, the Impact of tire and road coverings on driving is indisputable. Depending on their respective states, and the quality of their contact, driving will be improved or altered. It should be noted that bad weather is an external element that will degrade the quality of adhesion, and require the greatest caution on the part of users.
Rest regularly during a long journey
Fatigue is the number 1 responsible for road accidents. Therefore, rest regularly during a long journey is essential to keep its increased vigilance, and have the right reflexes in the event of an unexpected on the road. In addition, it is proven that stretching your legs every 2 hours would make it possible to fight against the natural falling asleep of the human body. In case of big fatigue, do not hesitate to take a nap, before hitting the road more serenely.

Different driving styles
Even if the teaching given to future drivers is generally the same, each one adopts over time bad and good habits, revealing of Different driving styles On Pavement. Between the sporting driving of some, the more cautious driving of others, even the ecological driving of the most responsible, all styles are in nature !
Survey
The phenomenon of survey Generally appears in the event of rain or frost, and implies the shift of the car in full shift, which can cause a road trip. This technique, nicknamed “Drift”, is highly sought after on automobile circuits for the thrills it provides. But in practice, this wheels skating must be perfectly controlled, to avoid the road accident and succeed in making your car effectively in the axis.
Discover the fundamentals with Roule Raoule
It is essential to understand the importance of the turning angle to adopt good conduct. If you want to learn more about driving fundamentals, do not hesitate to go to our other pages on the subject.
-



