Advantages and disadvantages of the electric car | Fortrainjobs mechanical blog, electric car: its advantages and disadvantages | eco -founder
Electric car advantage and disadvantage
There production Batteries of electric cars poses large Environmental and social problems. The battery is made up of three main elements: an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte which allows the passage of ions.
Advantages and disadvantages of the electric car

The electric car is undoubtedly the vehicle of tomorrow. The concept of this new type of automobile is constantly evolving, impacting the world of mechanics. Manufacturers seek to improve them in order to make them ever more efficient. Let’s see together the advantages and disadvantages of current electric cars.
1 – The advantages

A – A less polluting vehicle on a daily basis
- These cars do not consume fossil energy (petrol, gas, diesel). They therefore have a low impact on the greenhouse effect compared to conventional vehicles.
- They can be recharged thanks to green energy (resulting from renewable energy sources).
B – Comfort for the driver
- Its engine is silent, especially at low speed.
- The electric car does not hold. In addition, it starts quickly even in winter.
- It is very easy to recharge it: just connect it. No need to go to the petrol station.
C – Economy on a daily basis
- The electric car is economical in fuel, electricity costing less than fossil fuels.
- It requires different maintenance of conventional vehicles. Garage owners and Mechanical training will be led to adapt to this new market. There is no need for oil, so no emptying. There is no more clutch or gearbox. But when repairing an electric car, it is a work under tension. European reflection is underway in order to supervise this specific maintenance.
2 – Disadvantages

A – The impact of the battery on the environment
- Lithium is mainly used for the production of batteries. It is a rare metal, mainly from South America. Its extraction requires large quantities of water. However, this has significant consequences on local populations and the eco system already suffering from drought.
- The recycling of the batteries is not yet developed.
B – An important investment
- Electric cars are expensive to buy (€ 20,000 for an entry -level).
- An electric car battery has a lifespan of 7 to 10 years. It must then be changed – and the cost is high (around 4000 € for a small car).
C – charge difficulties
- Electric vehicles offer an average of 150 km of autonomy, which can be problematic on long journeys. In addition, the use of heating, air conditioning and driving style have a clear impact on battery charging time.
- The charging time is very variable from one vehicle to another and depending on the type of connection. Thus, a banal domestic socket requires a load of 7 to 8 hours. There are certain terminals made available in public spaces, allowing to load in 30 minutes.
- However, these recharging terminals are not all well maintained.
- In addition, they are not suitable for all existing batteries. Before traveling, the driver must find out about the places where he will be able to recharge his car.
Depending on its way of life and its values, these elements are therefore to be taken into account for the purchase of an electric car. And you what do you think ?
Electric car: its advantages and disadvantages

The electric car does not produce CO2 or air pollutants to use, apart from the particles from tire and brake wear. She makes little noise. It therefore offers solid advantages, especially in the heart of cities. Let’s all ride electricity one day ?
Is it the vehicle of the future ? The electric car has one or more electric motors, powered by batteries, and recharges at home or outside via a special terminal (in the street, parking lots, service stations).
There are also hybrid cars, which have an electric motor and a heat engine, as well as rechargeable hybrids (or plug-in) which can recharge like an electric car (via a domestic outlet or a terminal) and while driving.
Summary :
- Advantages of the electric car
- No air pollutants and no CO emission2 to use
- A nice future
- Silent
- Economical to use
- Little maintenance
- Disadvantages of the electric car
- Not everything is nickel in the batteries
- Recharge remains a constraint
- The recharge time and the availability of terminals
- It costs the purchase
- Electric: yes, under certain conditions
- Choose a light car
- Recharge with green electricity
- Do not compete with walking, cycling ..
- Carpool or share a car
Advantages of the electric car
1. No air pollutants and no CO emission2 to use
Electric cars do not reject pollutants in the atmosphere when they roll. There is no combustion so no noX, fine particles, flawless hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide . often incriminated for their health impacts. However, there are particles emissions from tires and, to a lesser extent, brakes (thanks to regenerative braking the brakes are less stressed than those of a thermal vehicle).
Going to the electric vehicle therefore has an immediate benefit for air quality in cities and near the roads. On the other hand, the way of producing electricity must also be taken into account: if it is produced on coal, particle and sulfur emissions are considerable.
Electric vehicles also do not emit CO2 when using. And if the electricity used is not very carbonated as in Belgium (230 g co2/kWh) or in France (60 g co2/kWh) The carbon footprint of the electric car is better than that a thermal car (petrol or diesel).
2. A nice future
To limit global warming and comply with the Paris agreement, Belgium must reduce its emissions by 80 to 95 % by 2050 (compared to 1990). To get there, you must in particular drastically reduce the use of fossil fuels (diesel and petrol) for transport.
One of the technical solutions is to drive to electricity. Provided you reduce the total number of vehicles in circulation and produce electricity from renewable energy sources (solar, wind, etc.).
To give an idea, the number of electric cars worldwide (including hybrids) should go from 10 million in 2020 to 150 million in 2030 according to the policies and measures provided for by the states (in particular the climate commitments made in the agreement from Paris). [1] It is the “Stated Policies Scenario”. A more proactive scenario, named “Sustainable Development Scenario”, imagines a share of 30% of electric vehicles among new vehicles in 2030. This would give 225 million electric vehicles (including utility vehicles) on this date.
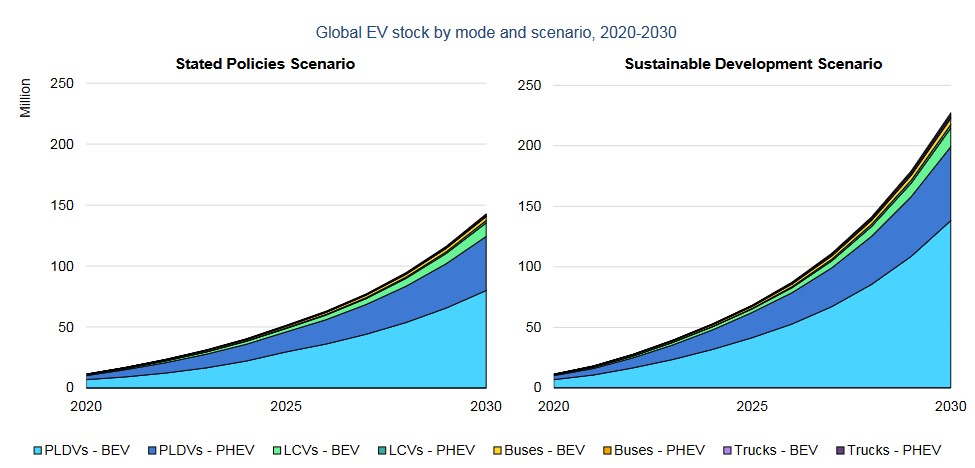
PLDVS = Light vehicles for passengers; LCVS = light utility vehicles; BEV = Battery electric vehicle; Phev = hybrid plug-in.
Source: Global EV Outlook 2021, IEA3. Silent
When it starts and when it rolls, the electric car is almost silent. A real asset for the tranquility of cities. It is not the inhabitants close to the main axes that will contradict him. The problem: this can represent a danger for pedestrians who do not hear it happen. Caution therefore !
4. Economical to use
We know that current vehicles consume theoretically between 13 and 25 kWh/100 km (standardized cycle). This comes up at a cost of € 3.25 to € 6.25 per 100 km (1 kWh costs on average € 0.25).
A petrol or diesel vehicle which theoretically consumes 5 l/100 km costs between 6 and 7 € of fuel per 100 km.
5. Little maintenance
The electric car requires little maintenance. The engine system is very simplified compared to a thermal vehicle (petrol, diesel or gas). There are a hundred times less rotation parts, there is no gearbox and no oil to change.
Thanks to regenerative braking (we recover part of the kinetic energy to make it electricity), the brakes are less stressed by and the platelets must be replaced less often than with a car.
On the other hand, it can happen that you have to change the battery of your electric car, after 1000 to 1,500 recharge cyles or 8 to 10 years. [2] The price of a new battery is very high: € 8,100 for the battery of a small Renault Zoe type car (52 kWh). [2b] In order to limit the replacement cost, some brands offer to rent the batteries rather than buying them.
Disadvantages of the electric car
1. Not everything is nickel in the batteries
There production Batteries of electric cars poses large Environmental and social problems. The battery is made up of three main elements: an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte which allows the passage of ions.
The anode is generally in graphite and electrolyte is a lithium salt. As for the cathode, it can have different chemical compositions: NMC (nickel, manganese and cobalt in different proportions), LMO (lithium, manganese and oxide), LFP (lithium iron phosphate), NCA (nickel cobalt aluminum),…
These concerns remain topical, even if the effectiveness of the batteries evolves quickly. Between 2009 and 2016, they went from 100 WH/liter to 350 WH/liter, a capacity 3.5 times higher for the same size. At the same time, their price was divided by three. Everything indicates that the performance of the batteries will still improve.
The capacity of batteries decreases over time. When it only reaches 70 to 80% of the initial capacity, they are no longer efficient enough to be used in vehicles but can still be served as a stationary storage solution (for example as a domestic battery if you have photovoltaic panels).
End -of -life batteries can pose a waste management problem. Their recycling is gradually developing, especially with Umicore in Belgium. Ultimately, a good part of the materials used in the batteries could be used to make new ones.
2. Recharge remains a constraint
Long considered a limiting factor, the autonomy of electric cars evolves dramatically. More and more models offer 300 km, or even 600 km of autonomy with a single load.
Obviously, more autonomy means greater capacity batteries (up to 100 kWh), more weight, more impact to manufacturing and more time to recharge them.
A range of 200 km is more than enough for daily use. It is only for longer journeys that the recharging time can be disabling, as long as the network of rapid chargers (high power) is not sufficiently developed.
Aggressive driving and the use of heating or air conditioning decrease the autonomy. To go far, you have to spare your mount !
3. The recharge time and the availability of terminals
The remaining autonomy, the ease of recharging is an important criterion. You can load your electric car at home via a normal socket or on a domestic, public or business terminal. The number of terminals is increasing but remains limited.
In town, where you don’t necessarily have a garage, a network of public terminals facilitates vehicle recharge. [3]


Charge.Brussels, a universal charging network in Brussels, plans to deploy a hundred 11 kW terminals.The recharging time of an average electric vehicle is very variable. It depends on the power available at the recharge point:
- At home, on a classic 3 kW socket it takes 5 to 6 hours to recharge a 27 kWh battery at 80%;
- With a domestic terminal (7 kW), the recharge takes half the time;
- On a 24 kW terminal outside the house (parking lots, supermarkets, service stations. ), the load is carried out in an hour;
- With a 50 kW terminal (same types of places), the load is reduced to 30 minutes;
- Tesla superchargers (250 kW) allow 235 km recharging in 15 minutes;
- other fast chargers like Ionity go up to 350 kW
To install a terminal at home, you must address an installer like Enersol, Voltco, Schneider Electric, Evbox.
4. It costs the purchase
The manufacturers offer more and more models but the market is currently limited and prices are always very high compared to a conventional vehicle.
Electric cars generally cost more than € 30,000 for popular models in Belgium: Renault Zoe (€ 32,600 or € 24,400 if you choose battery rental), VW Egolf (€ 33,000), Nissan Leaf (36 € 500), BMW i3 (€ 40,700). Only the Smart Fortwo (€ 25,000), the Renault Twing (€ 23,250), the Fiat 500 (€ 27,300) and the Dacia Spring (€ 20,000) descend under the € 30,000 !
A used electric car can be an interesting alternative, provided that the battery does not have to change.
Electric: yes, under certain conditions
If the emissions in the use of an electric car are almost zero, we are however far from “zero pollution”. If we analyze the life cycle, an electric car produces 20g to 250g of Co2/km according to the energy mix used to produce electricity. [4]
How to reduce the impact of displacements by electric vehicle ?
Choose a light car
We prefer lighter vehicles: a 2600 kg car, even electric, will always be synonymous with waste. The Tesla Model X, for example, uses twice as many batteries as a Renault Zoe, for autonomy only 50% higher. Normal: it weighs 1100 kg more ! A Belgian company wanted to offer a barely. 630 kg (including 80 kg of batteries) but the project has not succeeded. [5]

Recharge with green electricity
Depending on the electric mix used, the electric vehicle will most often be supplied by fossil fuels (as in China), nuclear (in Belgium and France) and more rarely by renewable energies.
We obviously do not master the supply of public limits. But at home, you can choose to eat thanks to photovoltaic solar panels or to take out a contract with a green electricity supplier.
The time of the load is all its importance: we prefer the moments when electricity production is maximum (in the middle of the day, when the photovoltaic panels produce well) and we avoid advanced consumption moments (between 18 and 9 p.m., especially in winter )). The electric vehicle can thus contribute to the balance of the electrical network or, on the contrary, increase consumption during critical periods. The driver warned will carefully program his recharge moments.
Do not compete with walking, cycling ..
Under the pretext that it pollutes less, the electric car can quickly become a fully found alternative to the means of gentle displacement. Even for small journeys, cycling or walking remain the most economical and ecological options.
Carpool or share a car
With the cost of using the electric car, carpooling may seem less tempting. However, sharing a vehicle or a journey remains more economical for the portfolio and the environment. Not to mention that it reduces parking problems and queues !
Interested in electricity but slowed down by the too high purchase price compared to the planned use ? Shared car systems are booming. And some platforms offer electric cars.
Tomorrow, all in electric car ?
We will not all be able to have an electric car and drive in the same way as today, we would only move the impacts: the electric car is little polluting for use but its production remains problematic for the environment, essentially Because of the batteries.
However, this type of car is part of the solutions. We must decrease the consumption of fossil energy, doomed to run out and which are the main cause of global warming. The electric car therefore has its place with a view to sustainable mobility, but only in combination with other solutions such as bicycle, public transport, carpooling ..
> See other ideas in our climate checklist. Stop making tons of them !
More informations
- What car to use to pollute ?
- What is the most ecological car ?
- Less drive by car to preserve the climate
[1] According to the International Energy Agency in its Global EV Outlook 2021.
[5] The E-Car 333 was proposed by the company Ecar Belgian Green Vehicle



