5G flow: what sail of navigation with 5G?, 5G: technology, deployment, speed
5G: technology, deployment, speed
We must also add to this that 5G is comparable to optical fiber in terms of its power, since the flows reached by these two technologies are very close and exceed 1 Gbit/s. However, a fiber connection is more stable and easily reached by Best speeds than in 5g, whose signal power varies greatly depending on the place in which we are.
5G flow: what sail of navigation with 5G ?
You are interested in 5G and more specifically in the flows that are reaching with this new mobile network ? What are the speeds reached by 5G ? Is 5G faster than fiber optics ? And what are the possible uses with speeds of this power ? Here is a little guide in which you will find the answers to your questions.
You are looking for the best 5G package ? Discover the available offers and let yourself be guided in order to take advantage of the partner offer most suited to your needs. (Free selectra service)
- The essential :
- 5G, fifth generation of mobile network, has a Extremely high navigation speed.
- 5G is up to 10 times faster than 4G, with flows going from 150 Mbit/s to 1 Gbit/s.
- Thanks to 5G, we can Download a film in very high definition in A few tens of seconds.
- THE Real 5G speeds measured via studies range from 128 to 321 Mbit/s, far from the maximum theoretical.
- THE latency (Deadline for information transmission) of 5G has been considerably reduced compared to 4G (it is Milliseconde)).
5G 5G speeds and their 5G packages
The operators announce different theoretical descendants 5G speeds on their 5G network, up to 2.1 GB/s:
- Orange : until 2.1 Gb/s (3.5 GHz antennas)
- SFR : until 2 Gb/s (3.5 GHz antennas)
- Bouygues : until 1.5 Gb/s (3.5 GHz antennas)
- Free : theoretical flow not communicated but which would be up to 3x higher than that of 4G on the bands 700 GHz (on which it develops more)
You are looking for a high -performance 5G package ? Here is our selection of Best 5G packages Among the 4 main operators Orange, Bouygues, SFR and Free:
5G speed: what can we expect with this network ?
What does the term “flow” mean ?
The flow is what characterizes the connection speed. Generally, this flow is expressed in Mbit/s, (megabits per second). Since an byte is an 8 -bit group, 8 Mbits match 1 MB.
- THE downspout (which is also called “download”) corresponds to Internet data flows that you receive on your line. It is this descending speed that conditions, with other factors, the speed thanks to which you surf on the internet, watch hd streaming movies and download heavy files.
- THE upright (which is also called “upload”) is the data flow you send On the Internet from your line. You use it for example to send emails, or to share photos on social networks.
The more the flow rates (descendant and amount) are students, The more your Internet connection is fast.
Zoom on 5G speed

5G is a network that offers a very high speed connection. This means that its connection speed is greater than that of the ADSL or 4G, with 5G flows going From 30 Mbit/s to 1 Gbit/s. These 5G flows represented theoretical estimates before the arrival of the network in the territory.
A priori, it is indicated that 5G flows are 10 times higher that those of 4G: the commercial flows announced today vary mainly from 100 Mbit/s to 1 Gbit/s in reception And From 50 Mbit/s to 250 Mbit/s in broadcast.
For the moment, according to the NPERF barometer relating to mobile connections in 2021, real speeds 5G in use have been noted, and they vary between 128 and 321 Mbit/s, which is far from the maximum theoretical flows hoped.
Future 5G networks will therefore be in theory (these are speeds that have been reached during tests but which are nevertheless estimated at the moment) capable of transferring 20 data gigabits per second from a base station to a device connected to the network, and 10 gigabits per second in the opposite direction. It is about 100 times more that what is allowed by 4G networks. Future 5G users will be able to download a high definition film in two or three seconds.
Namely 5G a priori has the capacity to process data that is different Has Different rhythms and therefore to operate a “sorting” in the flows. Operators are working on technologies called “Network Slicing», Which would make it possible to cut their network into several slices, in hierarchy transmission of information. For example, the information that will be issued by an autonomous moving vehicle will be processed in absolute priority compared to other.
What is the latency of 5G ?
5G also has a Response time faster than 4G, that is to say better latency. Latency corresponds to Information transmission period. In other words, this is the time that information takes from a point A to a point B. This value is expressed in milliseconds. The lower this value, the more quality the latency.
Generally, with 4G, you should expect a latency time around 50 milliseconds (25 to 40 milliseconds for 4G+). Latency is considered to be excellent when it is below 30 milliseconds. With 5G, the latency should be lower than a millisecond.
5G 4G and 3G flow: what differences ?
Networks 3G, 4G and 5G are different generations of mobile networks that have followed one another.
THE 3G network (3rd generation) was the first mobile network to provide a broadband Internet connection, with a minimum speed of 144 kbit/s (0.14 Mbit/s) and which goes as far as 200 kbit/s. Thanks to this flow, 3G allows you to surf the internet quickly from a smartphone, watch videos, make downloads, but it quickly shows its limits, for example to broadcast a high definition video stream (HD).
There 4G provides a flow of 100 Mbit/s. It allows faster than 3G navigation, with shorter loading times and reduced reaction times. There 4G+ As for it makes it possible to obtain practically doubled flows compared to 4G (approximately 180 Mbit/s)). The real rate measured in 4G is however located between 40 and 70 Mbit/s. 4G today covers almost all of the French territory: more than 90% of its area is covered by the 4 main mobile operators (SFR, Free, Bouygues and Orange). If you have any doubts on the 4G coverage of the area where you live, you can do an eligibility test.
There 5g As for it, by being able to reach flows that go as far as 1 Gbit/s, which is, as we have developed previously, approximately 10 times faster than 4G. It allows the same uses as the latter but offers even more possibilities, with in particular a more effective care of connected objects.
Namely each generation of network has a lifespan of approximately 20 years.
5G, a mobile network with revolutionary flows
5G is what ?
5G is the brand new generation of mobile network, which succeeds and completes 4G. This network has been deployed in France for a few years, and the first 5G mobile plans were launched at the end of 2020. 5G has been developed To avoid saturation of 3G and 4G networks, was predicted for 2022. You should know that according to Arcep, in five years, the Mobile data volume consumed by the French has been multiplied by ten (especially with the development of video streaming).
The mobile network of the future

5G is considered a rupture technology (that is to say an innovation that will replace a dominant technology on the mobile networks market), because it offers Much superior flows to those of 4G. Its ability to move a very large number of data so very fast Allows a number of uses to develop in France (such as virtual reality and augmented reality), which are currently not completely possible with 4G.
It is expected that 5G also interferes with several Pans of French industry To support their modernization and digitalization (autonomous vehicles, telemedicine, connected territories, etc.).
How will 5G unclog networks ?
To fully understand how 5G works, it is important to dwell on 4G. 4G operates thanks to Mobile communication antennas which cover a given area. The problem is that the more you have connected to this network, the more saturation sets in.
5G has an operation similar to that of 4G, except that everything has been improved: 5G requires antennas which will also cover the territory, but it also goes through micro-antenns which will take over from these main antennas in order to target very precise areas. These small antennas allow communication with mobile phones, but also connected objects. Thanks to this, the saturation problem is much less than with 4G.
In addition, many 5G antennas are called Smart antennas by some operators, because they have the capacity to activate only when a 5G device looking for a network is within their department. The rest of the time, they are in standby In order to save energy.
5g vs fiber flow: can we compare the two networks ?
Why do we compare 5G with optical fiber ?
5G is very often compared to optical fiber. We even call it “Mobile phones fiber»». This comparison is used because fiber offers more powerful flows than ADSL, which are even today Best Internet flow rates Reachable for fixed lines in France. In the same way, the 5g is the mobile network that offers the best speeds.
We must also add to this that 5G is comparable to optical fiber in terms of its power, since the flows reached by these two technologies are very close and exceed 1 Gbit/s. However, a fiber connection is more stable and easily reached by Best speeds than in 5g, whose signal power varies greatly depending on the place in which we are.
There optical fiber, is today the privileged technology for very high speed internet offers (greater than 30 Mbit/s). Today there are more homes subscribed to fiber optics than to ADSL. Fiber is a data transmission medium that uses light, and today allows individuals to take advantage of the most efficient flows. The highest theoretical flow with fiber (by free via its freebox delta, and by SFR via its 8x power box) is today to 8 Gbit/s.
What are the advantages of fiber compared to 5G and vice versa ?

The advantage of 5G is that this is a wireless network, Suitable for mobility, While the optical fiber is reserved for Closed or delimited places.
However, optical fiber has an important quality that 5G does not have: it is possible to know the Minimum speed of a fiber optic connection (which is on average 450 Mbit/s According to operators, in real debit measured). In addition, the signal weakening is almost zero with fiber optic technology, unlike an ADSL line whose maximum flow depends on the length of the copper line.
With 5G, there are still a lot of uncertainty, because the stability of the connection will depend on the signal quality and number of people connected at an instant t (even if 5G can support a large number of simultaneous connections).
And, to be able to really measure all the potential of 5G and really compare it to the performance of fiber optics, we will have to wait a few years. Indeed, the commercial launches of 5G offers are only the first stages of a wider deployment. In other words, they do not exploit all the capabilities of 5G technology, since current 5G services use Lower frequency bands of 5G. 5G will therefore not reach predicted flows before at least two years.
Ultimately, 5G will nevertheless be able to represent a good alternative to optical fiber, in the regions where the latter is not yet fully deployed, and also to cover temporary needs in some places such as companies for example. But 5G is rather intended for mobility and at The Internet of Objects.
You want to know if you are eligible for optical fiber (FTTH or FTTLA) ? Contact us so that an advisor will direct you among the most competitive partner offers, depending on your eligibility. (Free selectra service)
09 75 18 80 51
Ask for a free reminder by an orange advisor:
Service reserved for new subscriptions. Already customer ? Please contact 3900.
By clicking on “validate”, you agree to be recalled by an orange advisor. Your number will be used only for this recall request and will not be sent to third parties.
Ask for a free reminder by an orange advisor:
Service reserved for new subscriptions. Already customer ? Please contact 3900.
An orange advisor will remind you of within 48 hours
By clicking on “validate”, you agree to be recalled by an orange advisor. Your number will be used only for this recall request and will not be sent to third parties.
Updated on 09/12/2023
Magali joined Selectra in 2020 as a freelance editor. It mainly takes care of articles on subjects linked to mobile and internet themes.
5G: technology, deployment, speed

5g. Launched in November 2020, 5G is a real issue for operators, who work hard to deploy their network in an increasing number of cities.
- 5G
- 5G networks
- Flows
- Speeds
- Branches in France
- Deployments in France
- Frequency bands
What is 5g ?
5G, whose official name is IMT-2020, is the fifth generation of standards for mobile telephony. It is characterized by its flow, low latency and ability to connect a large number of objects. It was developed to “avoid saturation of the networks announced in 2022 and make it possible to follow high -speed objects, which is not capable of 4G”, recalls Nicolas Sironneau, consultant for the Concorde Foundation. But 5G is also other uses. “We focus on radio technology, but 5G is not just that, underlines Lionel Morand, network architect at Orange and Chair President at the 3GPP standardization organization. It will also be the possibility of creating specialized service interfaces for industry (NDLR Network Slicing). Omitting this detail is to remove 50% of the interest of 5G.””
What 5G networks ?
Different types of networks intervene when we mention 5G deployments:
- Public networks, operated for the general public by the four national operators.
- Private networks, deployed for a company specifically on a dedicated strip. In addition to national operators, several telecommunications operators offer the implementation of private networks, such as Hub One or Weaccess Group.
- The hybrid networks, also dedicated to companies, to enable them to switch from the public network to their private network according to their needs, such as the traceability of equipment from the site of one supplier to another warehouse.
What flows in 5G ?
Debit is one of the major assets of 5G. It should be up to 3 to 4 times faster than 4G (see our internet debit test). Nevertheless, “he is not the same from one operator to another, or even from one city to another. It all depends on the equipment of each antenna and the frequencies used, “said Ariase. In 4G sites using a 5G protocol, the theoretical maximum flow rate is equal to 240 Mbit/s. In the 3.5 GHz band, Orange evokes a flow of up to 2.1 GB/s.
What speeds to expect ?
Another key advantage of 5G, its data transmission speed. 5G is characterized by:
- The volume of data transmitted multiplied by 100. Future 5G networks will be theoretically capable of transferring 20 gigabits of data per second, from a base station to a device connected to the network, and 10 gigabits per second in the opposite direction
- Latence time should be less than a millisecond, compared to 25 to 40 milliseconds for 4G.
Future 5G users in the general public will be able to download a high definition film in two or three seconds.
How many 5G antennas in France ?
The antennas are essential to relay and transmit the 5G signal. As of March 1, 2023, ARCEP counted 39,350 5G sites, including 24,635 in 3.5 GHz band, the 5G heart band.
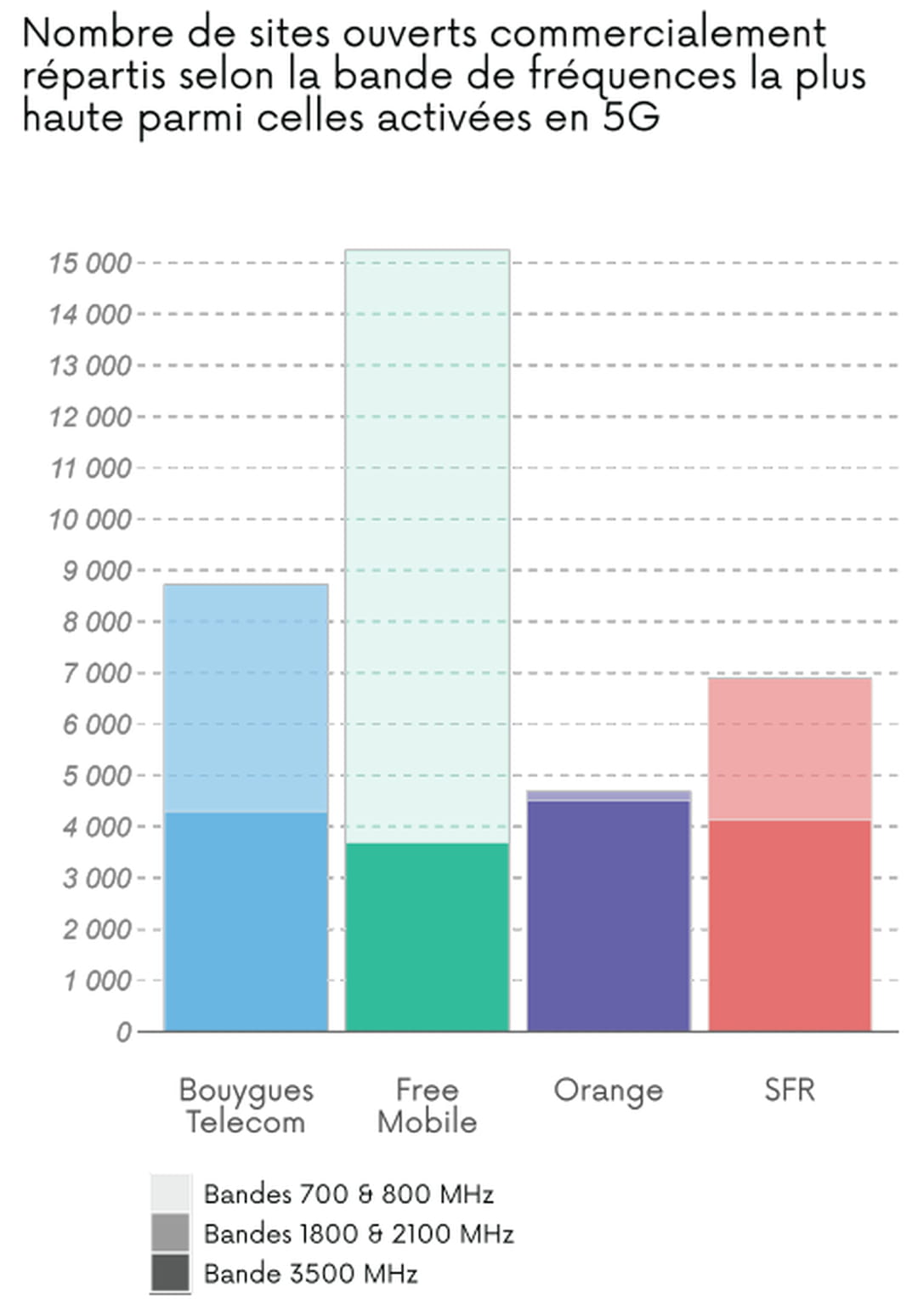
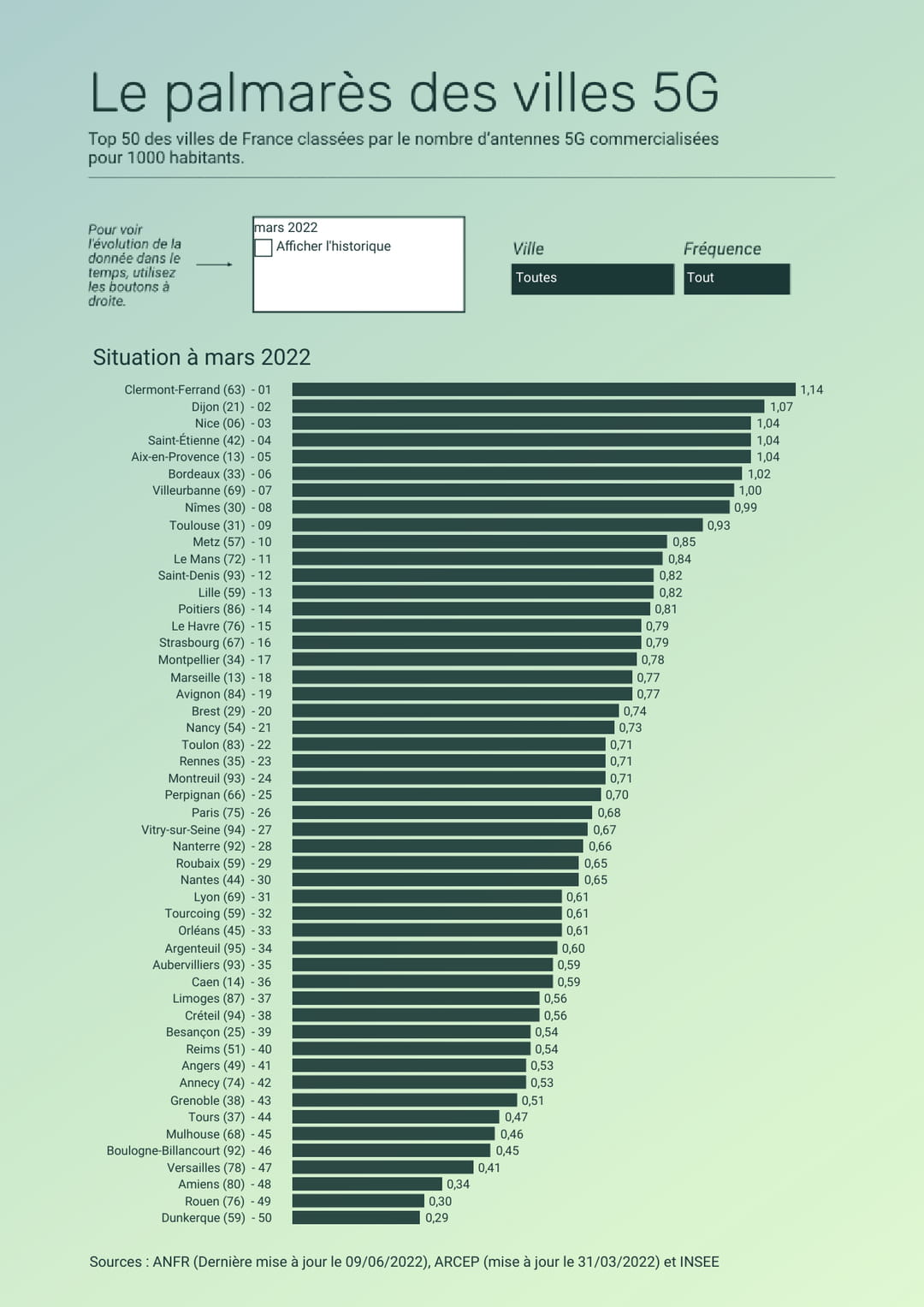
The deployment of 5G in France
To take full advantage of 5G, it is in Clermont-Ferrand that you have to be. According to the ranking of large 5G cities established by Lemon.FR and the agency specializing in data flashes (Last update in November 2022, editor’s note), The city of the center of France occupies first place with a ratio of 1.14 antenna for 1,000 inhabitants. Dijon and Nice complete the podium, with 1.07 antenna and 1.04 antenna sold for 1,000 inhabitants. Marseille, 18th city in the ranking, welcomes the experiments of Sony and Orange regarding future 5G services for the media at the Vélodrome. The capital ranks 26th place. At the bottom of the ranking, Dunkirk, Rouen and Amiens always close the 50 largest cities for the deployment of 5G.
What frequency bands for 5G ?
5G needs frequencies in three frequency bands to offer wide coverage, namely:
- Frequency bands of 700 and 800 MHz. These are those used to offer wide coverage of urban areas and to provide the IoT services in LTE-M and NB-IOT
- The frequency band between 3.4 and 3.8 GHz, necessary for the capacity of 5G and the first industrial uses
- Millimeter waves at 26 GHz in France, essential to reach the high speeds promised.
For manufacturers wishing to test the contribution of 5G in band 3.8 – 4.0 GHz, the arcep offers an experimentation window, open until December 31, 2023. Since its implementation in March 2022, the ARCEP issued 25 frequency use authorizations, for health uses with the Strasbourg Hospital-University Institute, in the industry with EDF in Palaiseau or for the autonomous vehicle With Orange in Balma.

A counter for open 5G experimentation platforms in 26 GHz band, called “millimeter” band, was launched in January 2019. Eleven project leaders have frequency bands of 26 GHz since January 1, 2021 at a price of 200 euros per year and per 200 MHz block, for three years. Among the projects selected are that of the Metropolis of Bordeaux, which aims to set up intelligent lighting along the quays, that of the port of Le Havre which aims to increase its performance and to achieve predictive maintenance, or that of the City of Saint-Priest, to allow the emergence of high speed IoT in an industrial area. “We still have little visibility on the use cases that 5G will really allow, which is why we want to associate the start-ups of French Tech with our experimentation platform,” said Christophe Trouillet, manager of the ‘Digital regional planning in the Bordeaux Metropolis.
5G should also be able to process data of different natures at different rhythms. Operators work on technologies to cut their network into several tranches, to circulate more or less priority information. This is called Network Slicing. The information issued by an autonomous moving vehicle will be processed in absolute priority, while data sent by an intelligent gas counter may be sent with a certain period. However, this technology is debated, because it is synonymous with partial end of net neutrality. Under this principle, operators have so far been obliged to process all the data that passed on on their networks, without analyzing their content. But to prioritize the processing of certain data in relation to others, they will have to know what type of information their customers make pass via their antennas.
IoT Dictionary
- Automation
- Firmware over the air
- Edge Computing
- Beacons
- Objenious
- Apple VR
- Smart GRID: Definition and operation of these intelligent networks
- 5g millimeter: definition and operation of these waves
- GTB: how the technical management of buildings works
- Poe Definition
- The drawbacks of telematics
- IoT platform
- Boots
- UA OPC
- Augmented reality: operation and uses of this technology
- Ikea Home Smart: What is the brand’s home supply ?
- LWM2M Protocol
- Fuchsia bone
- IoT Industrial
- Drone price
- IoT Crypto
- Mes: IoT in the service of production lines



